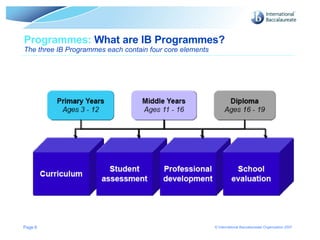
1. The document provides an overview of the Primary Years Programme (PYP), which is one of the International Baccalaureate (IB) programmes for students aged 3 to 12.
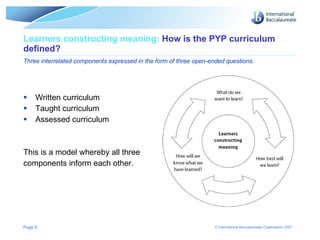
2. The PYP focuses on developing inquiring, knowledgeable and caring young people through its transdisciplinary themes and essential elements of knowledge, concepts, skills, attitudes and action.
3. The document outlines the key components of the PYP including its definition and curriculum, transdisciplinary themes and concepts, learner profile, and authorization process for schools.