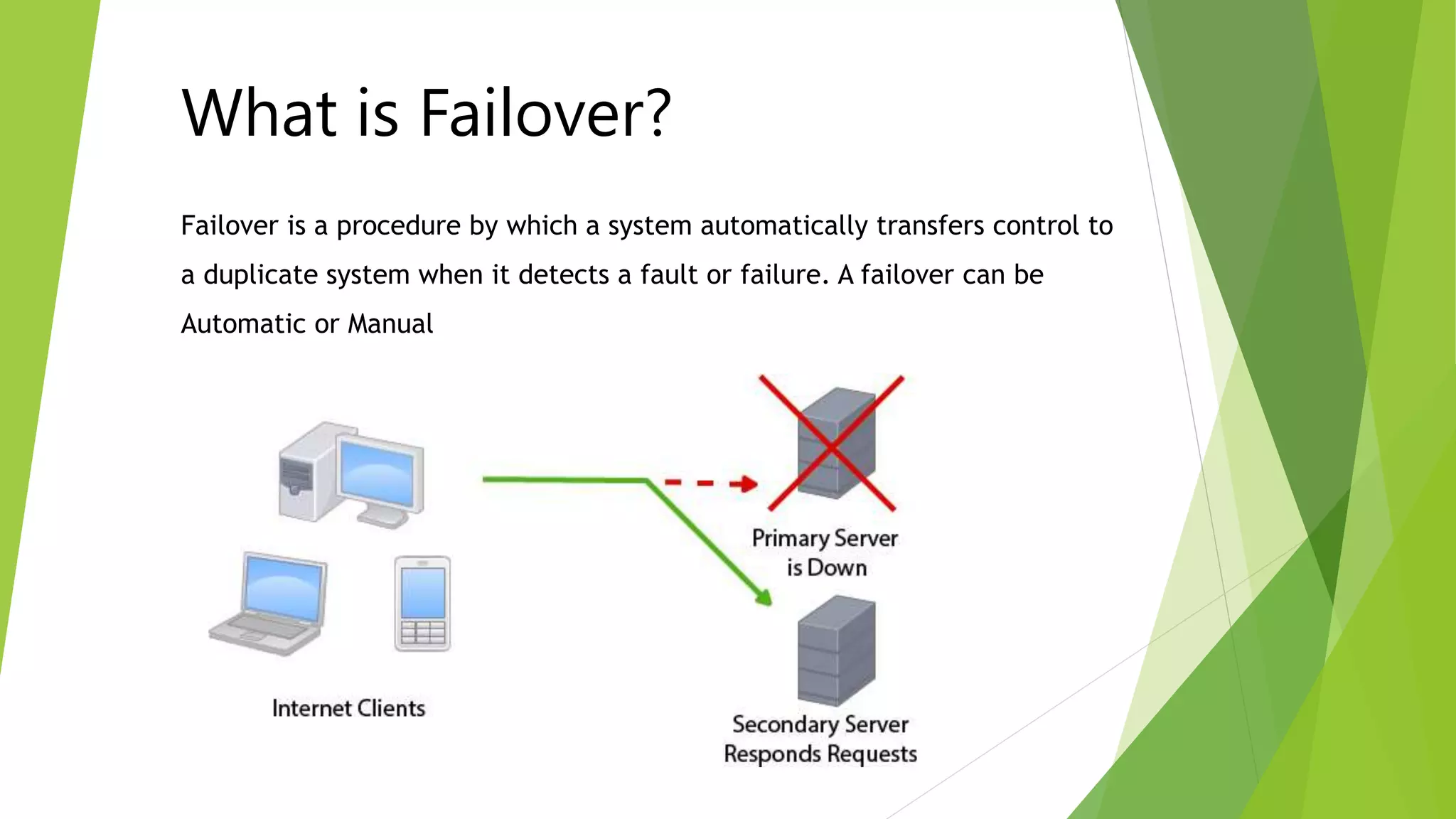
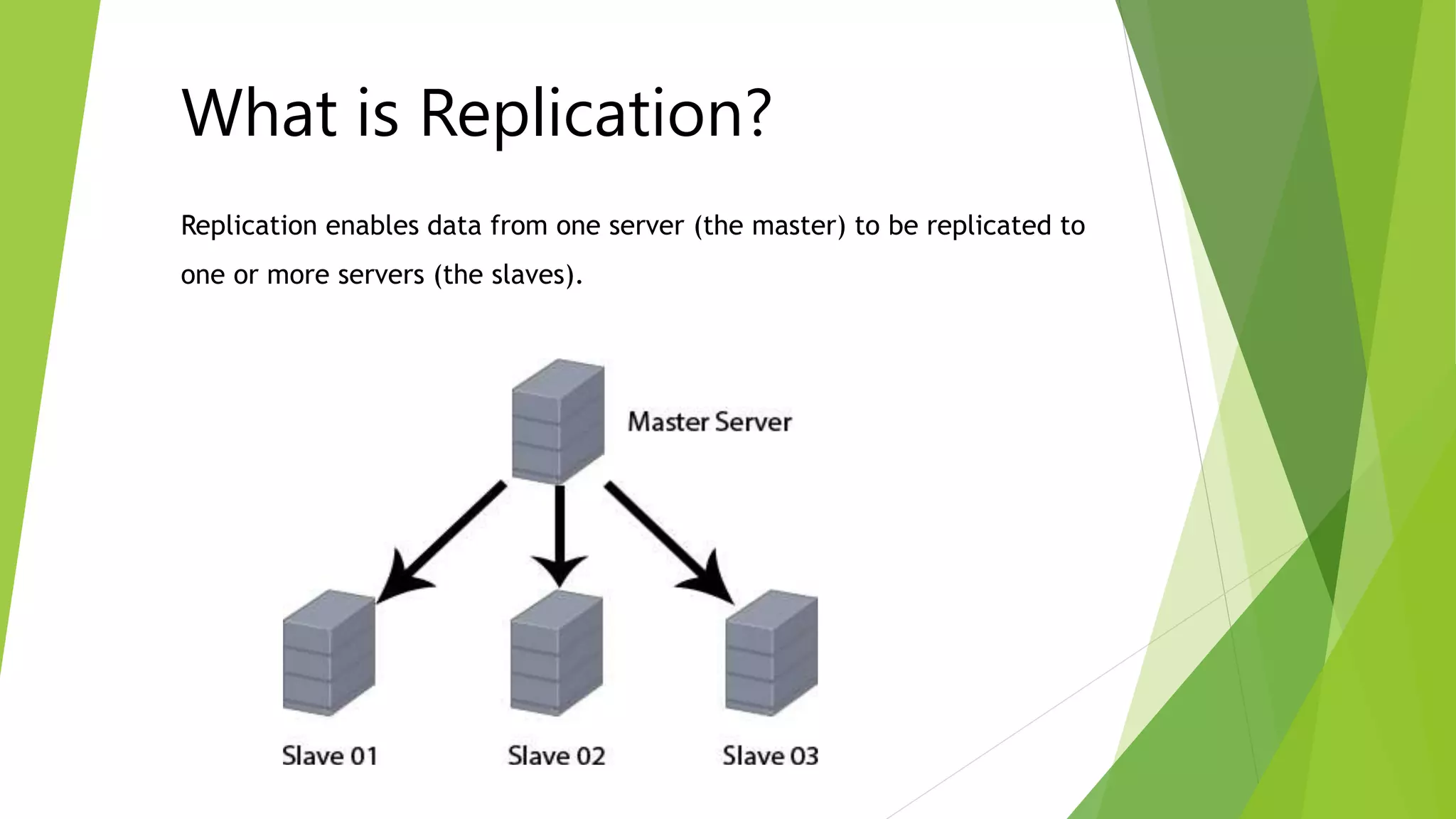
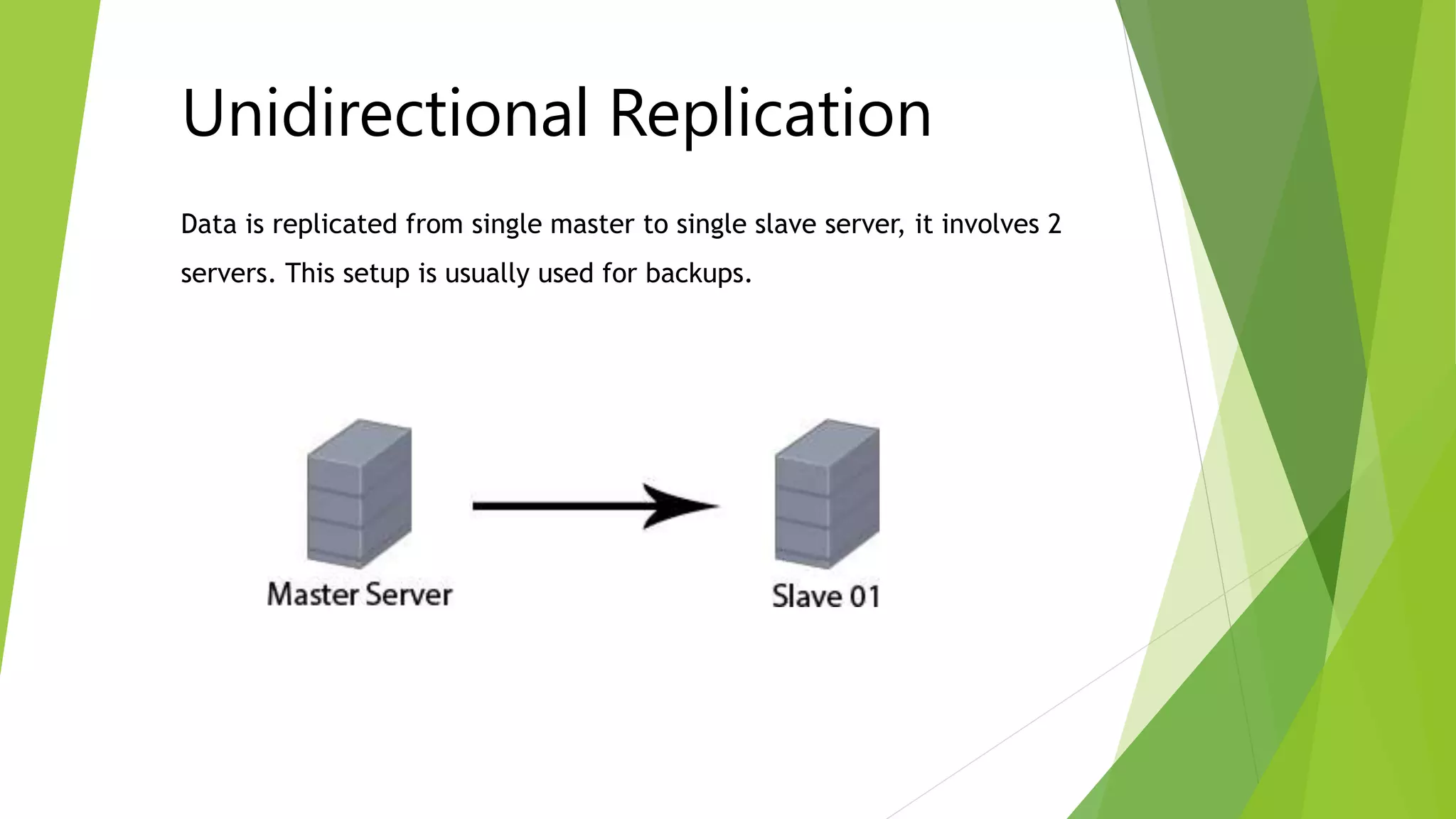
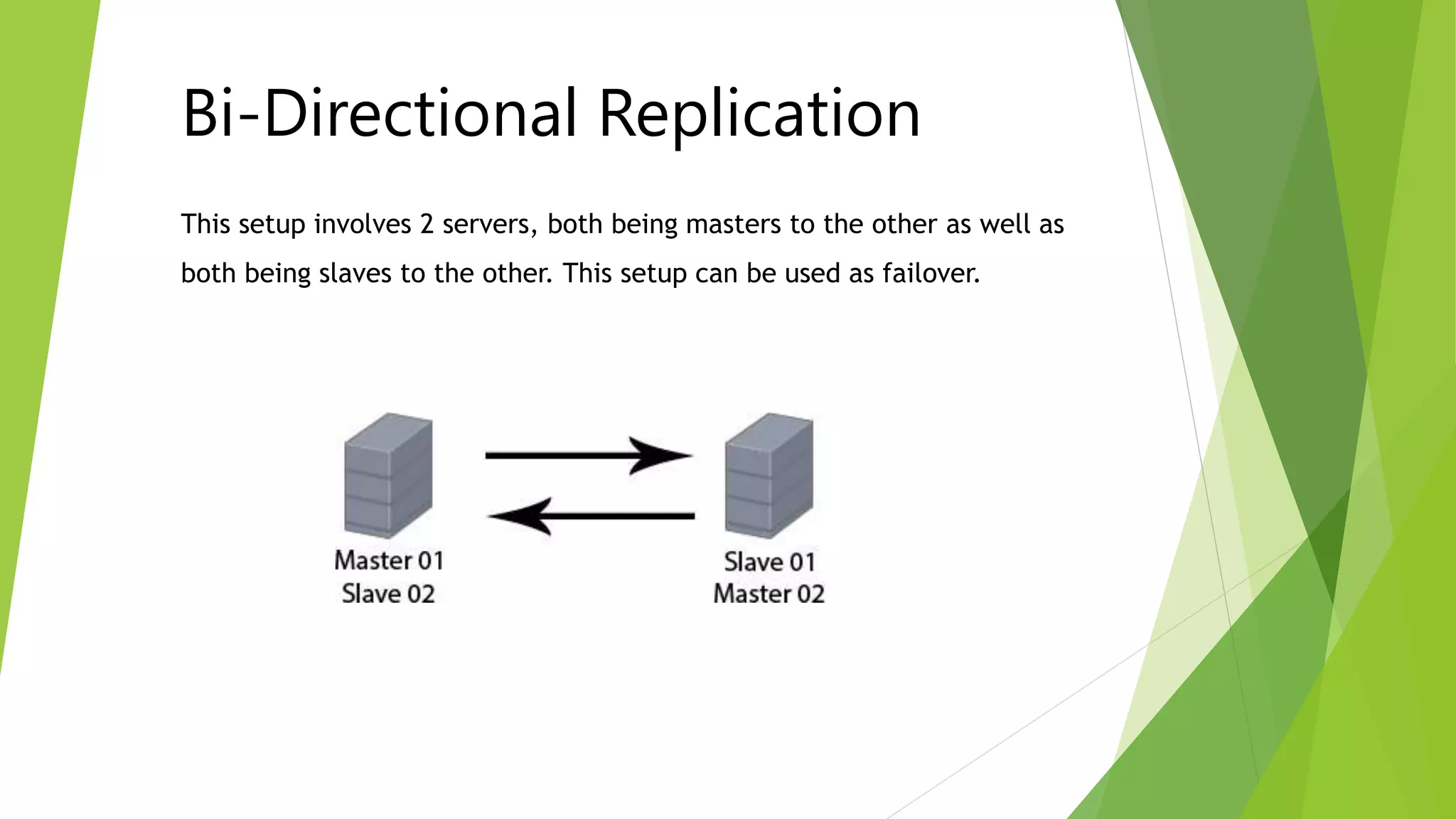
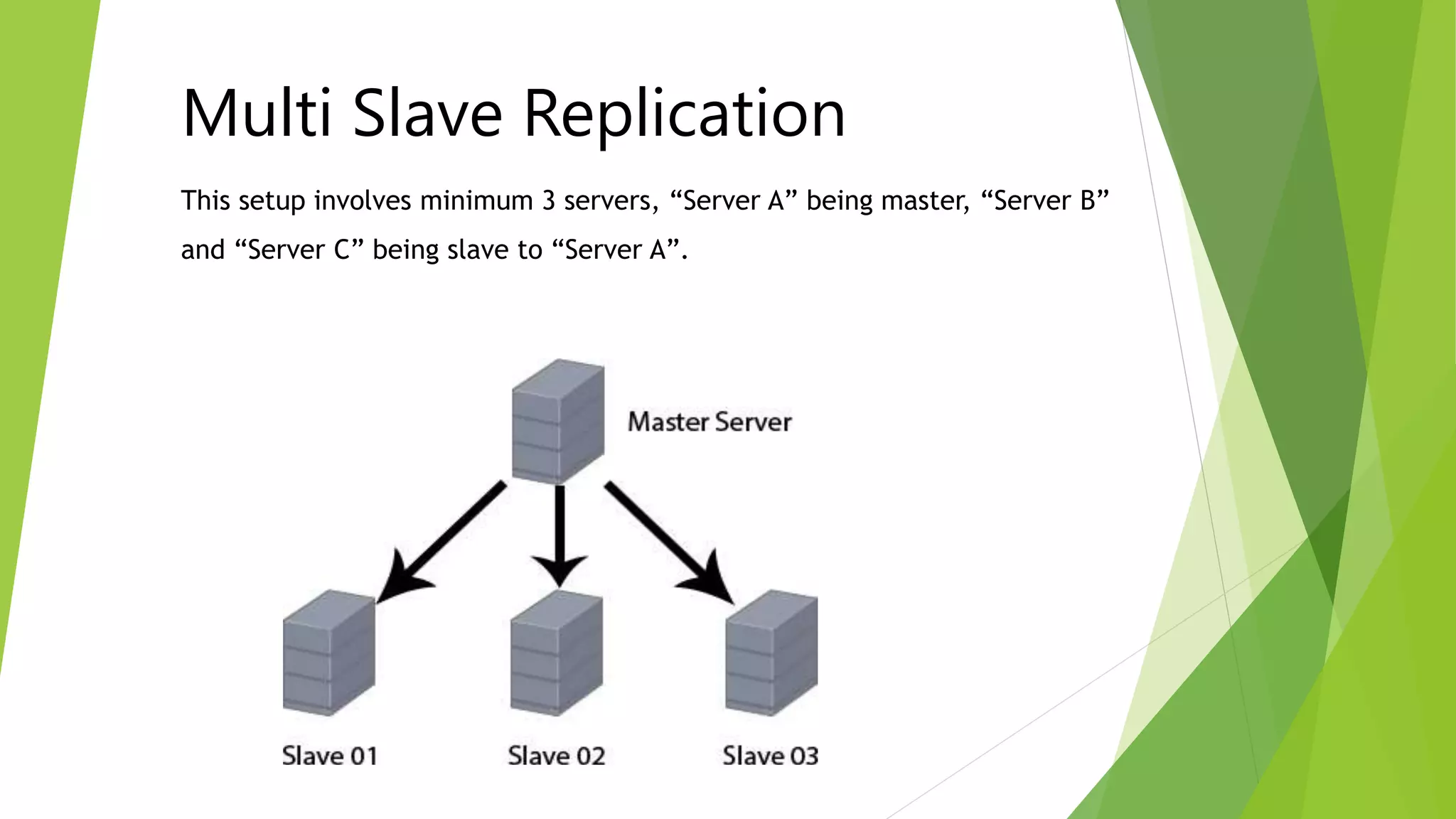
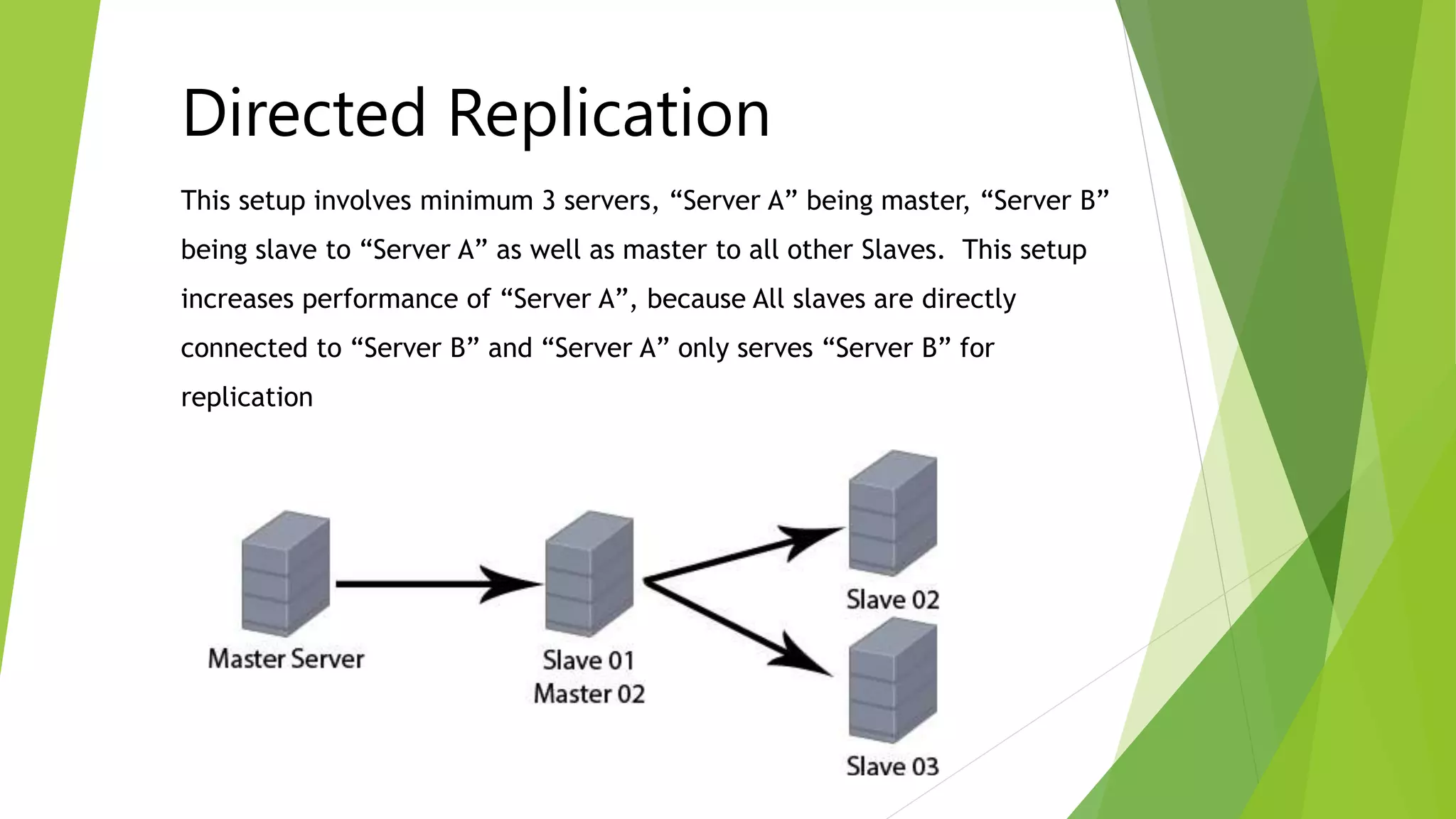
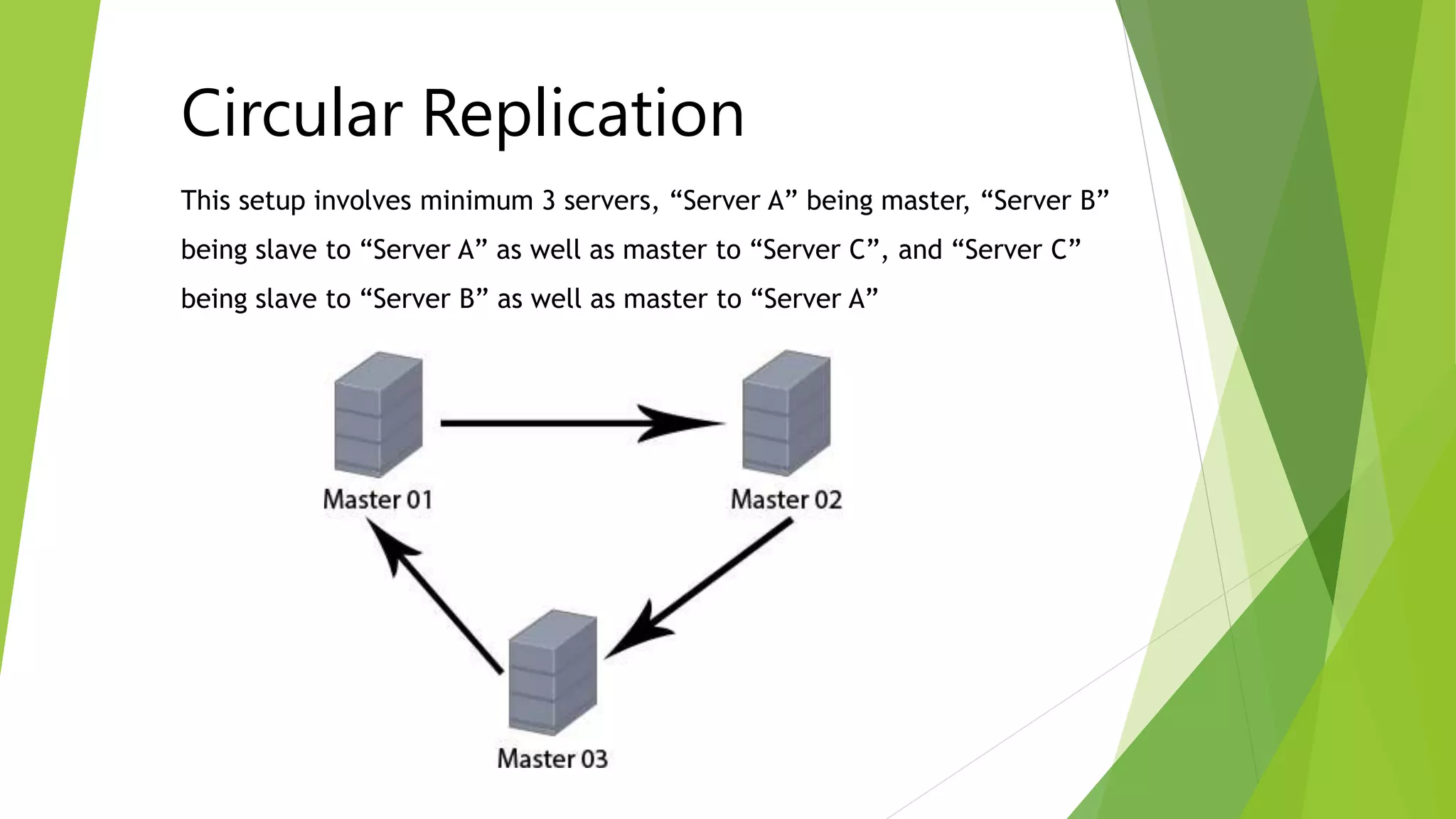
The document provides an overview of MySQL failover and replication, including definitions, advantages, types, setup instructions, and monitoring techniques. It describes failover as a process of transferring control to a duplicate system in case of a fault, while replication allows data from a master server to be copied to one or more slave servers. It outlines various replication types and detailed steps for setup, monitoring, and failover procedures.