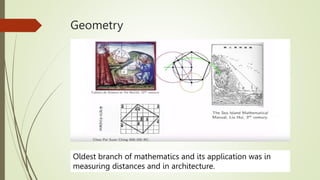
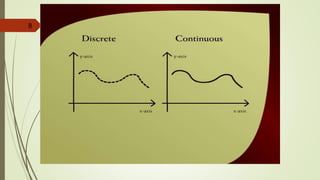
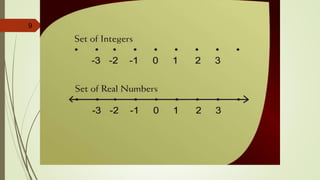
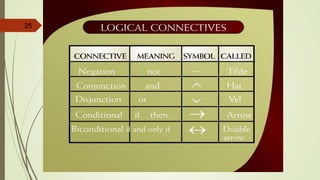
This document provides an overview of a lecture on discrete mathematics. It introduces the topic by listing relevant textbooks and reference books. It then defines four main areas of mathematics: geometry, calculus, number theory, and discrete mathematics. Discrete mathematics is described as the study of mathematical structures that are discrete rather than continuous, such as graphs, integers, and logical statements. The lecture continues by explaining concepts in logic, including statements, truth values, logical connectives, and compound statements.