The document provides a comprehensive overview of Neo4j, a graph database, focusing on its query language, Cypher. It explains how to work with graph structures, including creating, matching, and deleting nodes and relationships, as well as utilizing pattern matching and aggregation functionalities. Additionally, it highlights use cases and examples of graph data modeling and querying in various applications.
![(Neo4j)-[: ]->Cypher
Michael Hunger - Neo Technology
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/75/Intro-to-Cypher-1-2048.jpg)
![(Michael) -[:WORKS_ON]-> (Neo4j)
console
Cypher community
graph
Community
ME
Server
Spring Cloud
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-2-320.jpg)


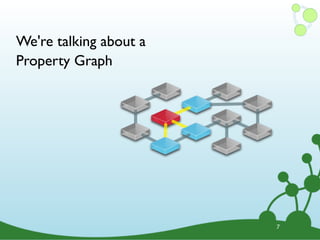
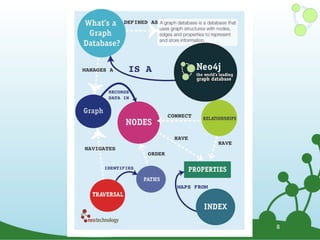
![(Neo4j) -[:IS_A]-> (Graph Database)
Lucene
Sharding 1 M/s
Master/
Index
LS
Slave
TRAVERSA
HIG
TES
H_A
VA RA
G
IL. TE
IN
PROVIDES ACID
Server RUN
S_A LI TX
S CE
NS
ED
_L
ES_T
Ruby IK
RU
JS E
MySQL
S
_A
NS
SC AL
O
Clojure
_O
NS
.net
RU
N Mongo
34bn
embedded Heroku
Nodes 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-14-320.jpg)



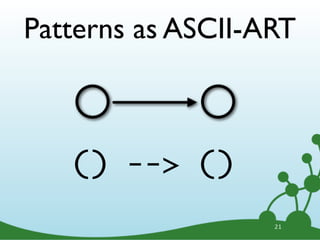
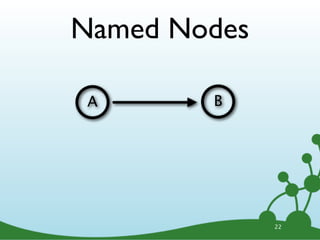
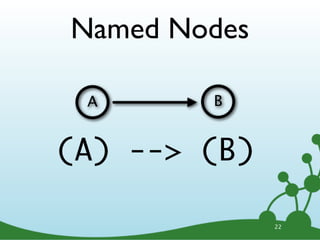
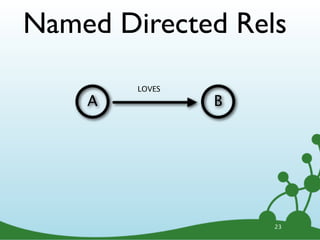
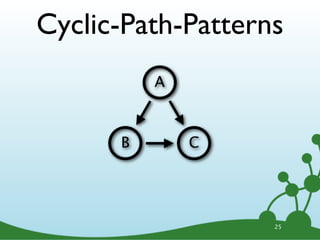
![Named Directed Rels
LOVES
A B
A -[:LOVES]-> B
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-31-320.jpg)
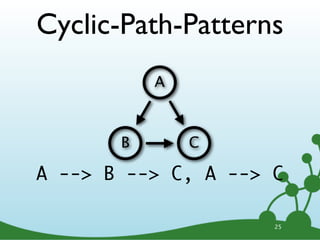
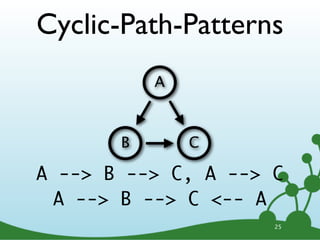
![Variable Length Paths
A B
A B
A B
...
A -[*]-> B 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-37-320.jpg)
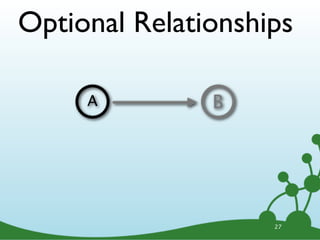
![Optional Relationships
A B
A -[?]-> B
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-39-320.jpg)

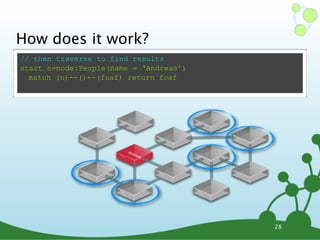






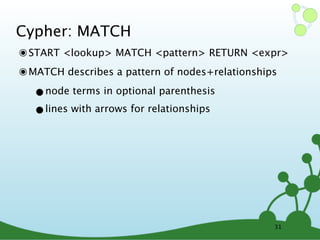
![Cypher: MATCH
๏ START <lookup> MATCH <pattern> RETURN <expr>
๏ MATCH describes a pattern of nodes+relationships
•node terms in optional parenthesis
•lines with arrows for relationships
// lookup 'n', traverse any relationship to some 'm'
start n=node(0) match (n)--(m) return n,m
// any outgoing relationship from 'n' to 'm'
start n=node(0) match n-->m return n,m
// only 'KNOWS' relationships from 'n' to 'm'
start n=node(0) match n-[:KNOWS]->m return n,m
// from 'n' to 'm' and capture the relationship as 'r'
start n=node(0) match n-[r]->m return n,r,m
// from 'n' outgoing to 'm', then incoming from 'o'
start n=node(0) match n-->m<--o return n,m,o
31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-52-320.jpg)




![Cypher: WHERE
๏ START <lookup> [MATCH <pattern>]
WHERE <condition> RETURN <expr>
๏ WHERE filters nodes or relationships
•uses expressions to constrain elements
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-57-320.jpg)
![Cypher: WHERE
๏ START <lookup> [MATCH <pattern>]
WHERE <condition> RETURN <expr>
๏ WHERE filters nodes or relationships
•uses expressions to constrain elements
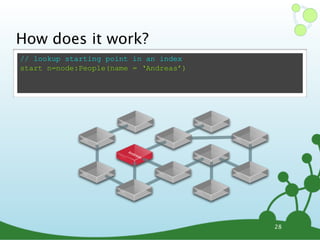
// lookup all nodes as 'n', constrained to name 'Andreas'
start n=node(*) where n.name='Andreas' return n
// filter nodes where age is less than 30
start n=node(*) where n.age<30 return n
// filter using a regular expression
start n=node(*) where n.name =~ /Tob.*/ return n
// filter for a property exists
start n=node(*) where has(n.name) return n
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-58-320.jpg)

![Cypher: CREATE
๏ CREATE <node>[,node or relationship] RETURN <expr>
•create nodes with optional properties
•create relationship (must have a type)
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-60-320.jpg)
![Cypher: CREATE
๏ CREATE <node>[,node or relationship] RETURN <expr>
•create nodes with optional properties
•create relationship (must have a type)
// create an anonymous node
create n
// create node with a property, returning it
create n={name:'Andreas'} return n
// lookup 2 nodes, then create a relationship and return it
start n=node(0),m=node(1) create n-[r:KNOWS]-m return r
// lookup nodes, then create a relationship with properties
start n=node(1),m=node(2) create n-[r:KNOWS {since:2008}]->m
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-61-320.jpg)

![Cypher: CREATE UNIQUE
๏ CREATE UNIQUE node-[rel]->(node {prop : value})
•„fixes“ the graph
•starts at bound nodes, properties rels and nodes by
comparing types and
tries to find
•if not found creates them
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-63-320.jpg)
![Cypher: CREATE UNIQUE
๏ CREATE UNIQUE node-[rel]->(node {prop : value})
•„fixes“ the graph
•starts at bound nodes, properties rels and nodes by
comparing types and
tries to find
•if not found creates them
// create a new relationship
start n=.., m=.. create unique n-[:KNOWS]->m
// create a new node AND relationship
start n=... create unique n-[:TAGGED]->(tag {name:“neo“})
// matches the tag node by name only creates new relationship
start n=... create unique n-[:TAGGED]->(tag {name:“neo“})
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-64-320.jpg)

![Cypher: SET
๏ SET [<node property>] [<relationship property>]
•update a property on a node or relationship
•must follow a START
36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-66-320.jpg)
![Cypher: SET
๏ SET [<node property>] [<relationship property>]
•update a property on a node or relationship
•must follow a START
// update the name property
start n=node(0) set n.name='Peter'
// update many nodes, using a calculation
start n=node(*) set n.size=n.size+1
// match & capture a relationship, update a property
start n=node(1) match n-[r]-m set r.times=10
36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-67-320.jpg)

![Cypher: DELETE
๏ DELETE [<node>|<relationship>|<property>]
•delete a node, relationship or property
•toall relationships must be deleted first
delete a node,
37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-69-320.jpg)
![Cypher: DELETE
๏ DELETE [<node>|<relationship>|<property>]
•delete a node, relationship or property
•toall relationships must be deleted first
delete a node,
// delete a node
start n=node(5) delete n
// remove a node and all relationships
start n=node(3) match n-[r]-() delete n, r
// remove a property
start n=node(3) delete n.age
37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-70-320.jpg)

![START user = node(1)
MATCH user -[user_skill]-> skill
RETURN skill, user_skill
SELECT skills.*, user_skill.*
FROM users
JOIN user_skill ON users.id = user_skill.user_id
JOIN skills ON user_skill.skill_id = skill.id WHERE users.id = 1
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-72-320.jpg)
![Example:
Old, Influential Friends
START me = node(...)
MATCH (me) - [f:FRIEND] - (old_friend)
- [:FRIEND ] - (fof)
WHERE ({today}-f.begin) > 365*10
WITH old_friend, collect(fof.name) as names
WHERE length(names) > 100
RETURN old_friend, names
ORDER BY old_friend.name ASC
f:FRIEND :FRIEND
me friend fof](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-73-320.jpg)
![Example:
Simple Recommendation
START me = node(...)
MATCH (me) -[r1:RATED ]->(thing)
<-[r2:RATED ]- (someone)
-[r3:RATED ]->(cool_thing)
WHERE ABS(r1.stars-r2.stars) <= 2
AND r3.stars > 3
RETURN cool_thing, count(*) AS cnt
ORDER BY cnt DESC LIMIT 10
r1:RATED thing r2:RATED
me so
TED
r 3: RA
cool
thing 41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-74-320.jpg)

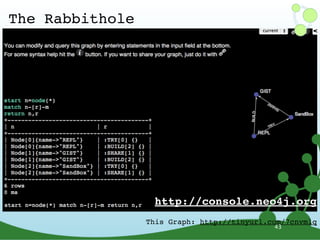

![Neo4j API
ExecutionEngine engine = new ExecutionEngine(graphDB);
String query = „start n=node:Person(name={name})
match n-[:ACTS_IN]->movie<-[:ACTS_IN]-friend
return friend“;
ExecutionResult result = engine.query(query, map(„name“, „Keanu“);
for (Map<String,Object> row : result) {
Node friend = row.get(„friend“);
}
Iterator<Node> friends = result.columnAs(„friend“);
http://bit.ly/cypher-queries
45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-78-320.jpg)














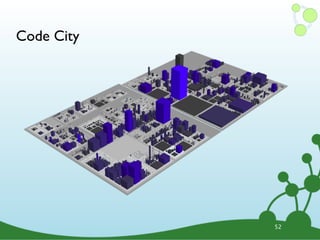
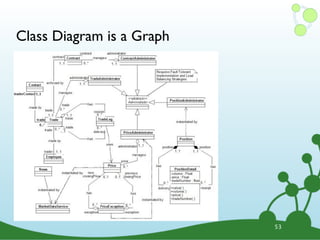


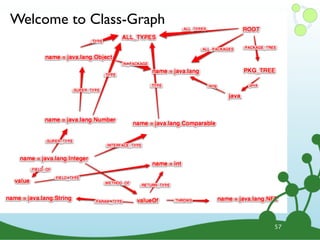




![Task: Subclasses of Number?
START n=node:types(name="java.lang.Number")
MATCH n<-[:SUPER_TYPE]-s
RETURN s.name
ORDER BY s.name;
•Return just the name
•Order them alphabetically
60](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-104-320.jpg)

![Task: Which Methods does it have / how many
START n=node:types(name="java.lang.Number")
MATCH n-[:METHOD_OF|FIELD_OF]->m
RETURN m;
•Find the top 5 classes with the most members
61](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-106-320.jpg)

![Task: Calculate the fan-out of
java.lang.StringBuilder
START o=node:types(name="j.l.StringBuilder")
MATCH o-[:FIELD_OF]->f-[:FIELD_TYPE]->tf,
o-[:METHOD_OF]->m-[:PARAM_TYPE]->tp,
m-[:RETURN_TYPE]->tr
RETURN o,count(distinct tf)
+ count(distinct tp)
+ count(distinct tr) as fan_out;
•Calculate fan-in
•Which class has the highest fan-out
•What about package-level? 62](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-108-320.jpg)

![Task: Find longest Inheritance Path
start c=node:types(name="java.lang.Object")
match path=p<-[:SUPER_TYPE*]-c
return extract(n in nodes(path) : n.name),
length(path) as len
order by len desc
limit 5;
63](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-110-320.jpg)

![Task: Find the class that used IOException
most often
START ex=node:types(name="java.io.IOException"
MATCH ex<-[:THROWS]-m<-[:METHOD_OF]-c
RETURN c, count(*)
ORDER BY count(*)
LIMIT 5;
64](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-112-320.jpg)

![Task: Which other classes did classes that
threw IOException use most often?
START ex=node:types(name="java.io.IOException")
MATCH ex<-[:THROWS]-m<-[:METHOD_OF]-c,
mbr<-[:METHOD_OF|FIELD_OF]-c,
mbr-[:FIELD_TYPE|PARAM_TYPE|
RETURN_TYPE|THROWS]->other_type
WHERE other_type.name =~ /.+[.].+/
RETURN other_type.name, count(*)
ORDER BY count(*) desc
LIMIT 10;
•What could be a source of IOExceptions
65](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-114-320.jpg)

![Task: Find a class you like and add a field with
your name and some type
START c=node:types(name="void"),
t=node:types(name="java.lang.reflect.Proxy")
CREATE c-[:FIELD_OF]->(field {name:“Michael“})
-[:FIELD_TYPE]->t;
66](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-116-320.jpg)

![Task: Delete the most annoying class and all its
methods, fields and their relationships
START c=node:types(name="java.awt.List"),
MATCH c-[r1:FIELD_OF|METHOD_OF]->mbr-[r2]-()
c-[r]-()
DELETE c,mbr,r1,r2,r;
67](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cypherwebinar-120831165136-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Cypher-118-320.jpg)