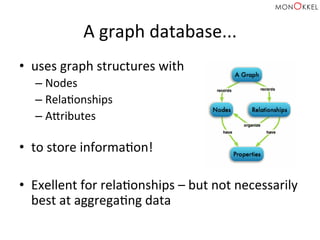
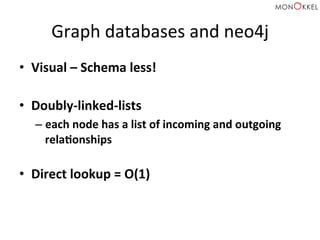
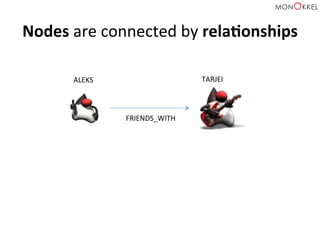
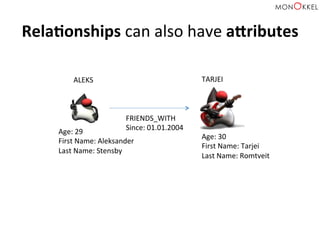
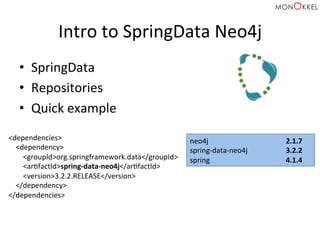
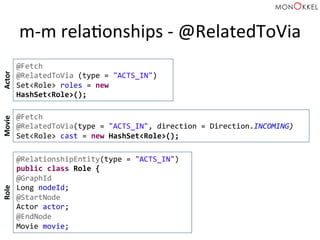
The document provides an introduction to graph databases, focusing on Neo4j and Spring Data, highlighting their advantages over relational databases for handling complex relationships. It discusses key concepts such as graph structure, Cypher query language, and various applications including social media and recommendation systems. Additionally, it offers configuration examples for setting up Spring Data with Neo4j and emphasizes lessons learned from utilizing these technologies.











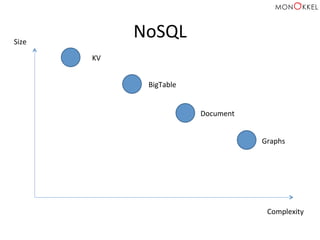
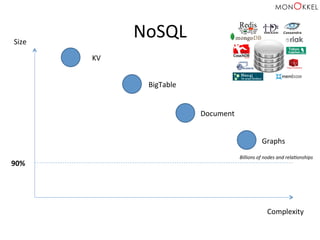


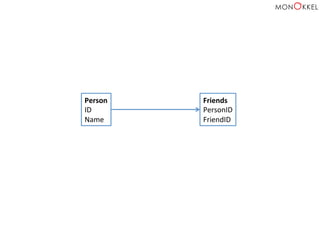
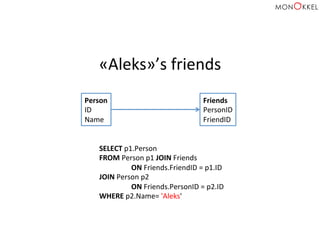
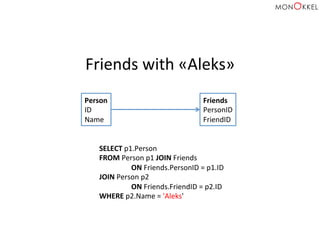
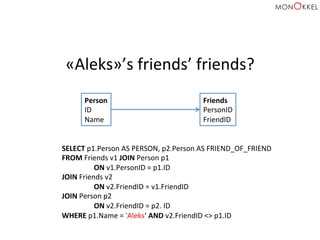
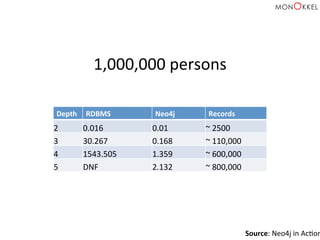



![Neo4j
–
[IS_A]
-‐>
Property
Graph](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4jandspringdatafeb2015-150220025146-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-graph-databases-Neo4j-and-Spring-Data-English-2015-Edition-37-320.jpg)


![(node)
–
[relaHonship]
-‐>
(node)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4jandspringdatafeb2015-150220025146-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-graph-databases-Neo4j-and-Spring-Data-English-2015-Edition-40-320.jpg)
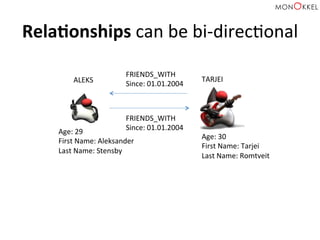
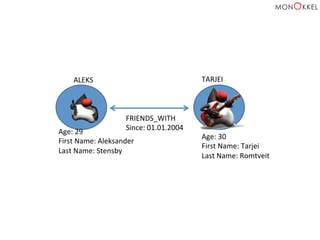
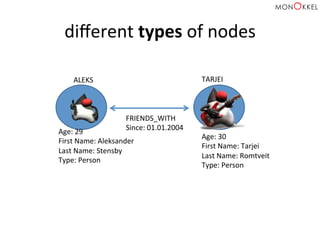
![(Aleks)
–
[FRIENDS_WITH]
-‐>
(Tarjei)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4jandspringdatafeb2015-150220025146-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-graph-databases-Neo4j-and-Spring-Data-English-2015-Edition-41-320.jpg)



![Describe
what
you
want
to
retrieve
with
PATTERNS
(a)-‐[r]-‐>(b)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4jandspringdatafeb2015-150220025146-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-graph-databases-Neo4j-and-Spring-Data-English-2015-Edition-45-320.jpg)
![(Aleks)
–
[FRIENDS_WITH]
-‐>
(Tarjei)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4jandspringdatafeb2015-150220025146-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-graph-databases-Neo4j-and-Spring-Data-English-2015-Edition-46-320.jpg)
![Path
depth
(a)-‐[*]-‐>(b)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4jandspringdatafeb2015-150220025146-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-graph-databases-Neo4j-and-Spring-Data-English-2015-Edition-47-320.jpg)






![Friend
of
friend...
MATCH
(aleks)-‐[r:KNOWS]-‐()-‐[r2:KNOWS]
-‐>(friend_of_friend)
WHERE
aleks.firstName=
'Aleks'
RETURN
friend_of_friend.firstName](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4jandspringdatafeb2015-150220025146-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-graph-databases-Neo4j-and-Spring-Data-English-2015-Edition-54-320.jpg)
![Friend
of
friend...
MATCH
(aleks)-‐[:KNOWS*2..2]-‐>(friend_of_friend)
WHERE
aleks.firstName=
'Aleks'
AND
NOT
(aleks)-‐[:KNOWS]-‐>(friend_of_friend)
RETURN
friend_of_friend.firstName](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4jandspringdatafeb2015-150220025146-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-graph-databases-Neo4j-and-Spring-Data-English-2015-Edition-55-320.jpg)

















![SpringData
Neo4j
-‐
Repositories
public
interface
PersonRepository
extends
GraphRepository<Person>{
List<Person>
findByFirstName(String
firstName);
@Query("MATCH
(p:Person{firstName:{0}})
RETURN
p")
List<Person>
getPersonWithFirstName
(String
firstName);
@Query(
"MATCH
(p:Person{firstName:{0}})-‐[:knows]-‐>friends
"
+
"
RETURN
friends")
Iterable<Person>
findFriendsOfPerson(String
firstName);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4jandspringdatafeb2015-150220025146-conversion-gate02/85/Introduction-to-graph-databases-Neo4j-and-Spring-Data-English-2015-Edition-75-320.jpg)


