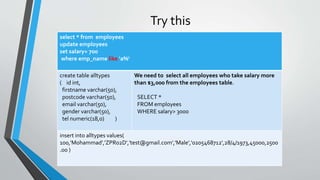
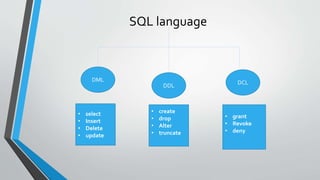
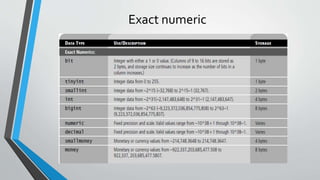
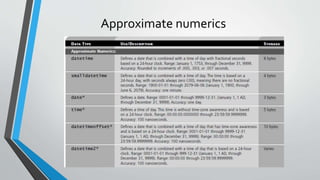
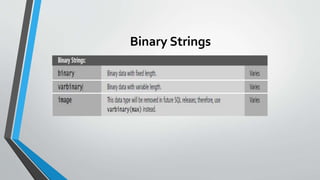
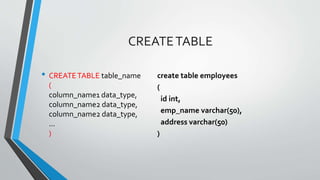
The document discusses SQL concepts including data manipulation language (DML), data definition language (DDL), data control language (DCL), and data types. DML statements like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE are used to query and manipulate data. DDL statements create, modify and delete database objects. DCL controls user access and privileges. Data types specify the type of data stored and supported types include numeric, character, date/time etc. Examples of SQL queries, operators and DML statements like INSERT, UPDATE, ALTER, DROP are also provided.











![Recap of SQL Queries
• A query in SQL can consist of up to six clauses, but only the first two, SELECT and
FROM, are mandatory.The clauses are specified in the following order:
• Allows users to retrieve specific information from the database.
SELECT <attribute list>
FROM <table list>
[WHERE <condition>]
[GROUP BY <grouping attribute(s)>]
[HAVING <group condition>]
[ORDER BY <attribute list>]
• There are three SQL commands to modify the database: INSERT, DELETE, and
UPDATE
Select statement syntax :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation2-150211130507-conversion-gate01/85/intro-for-sql-17-320.jpg)