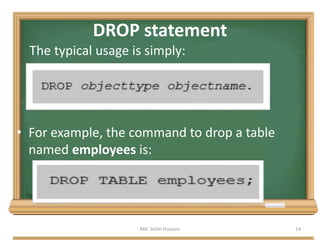
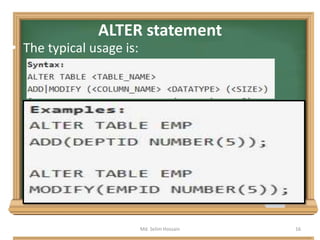
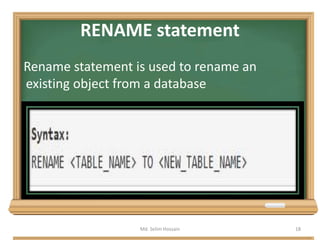
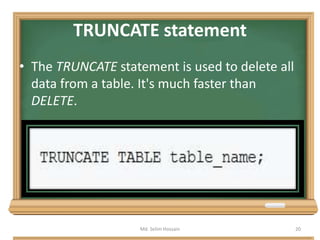
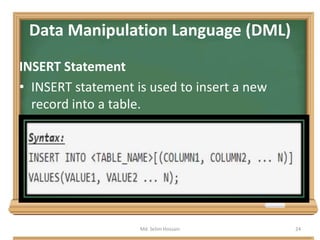
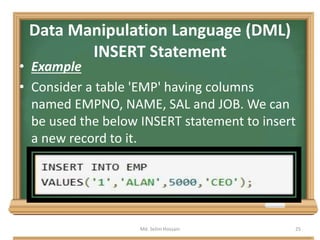
The document is a lecture outline by Md. Selim Hossain on Database Management Systems (DBMS), focusing on Data Definition Language (DDL) and Data Manipulation Language (DML) as sub-languages of SQL. It details various SQL statements, including CREATE, ALTER, DROP, TRUNCATE for DDL, and INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE for DML, explaining their functions and example usages. Additionally, it distinguishes between commands that modify database structures and those that manipulate the data within those structures.






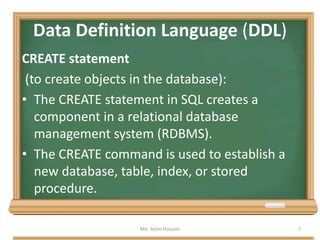
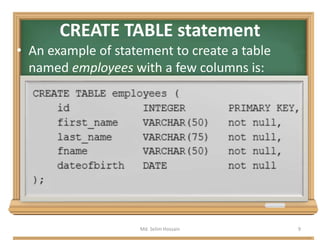
![CREATE TABLE statement
• A commonly used CREATE command is the
CREATE TABLE command. The typical usage is:
CREATE TABLE [table name] ( [column
definitions] ) [table parameters]
Md. Selim Hossain 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finaldatabaseworking-170320202709/85/Data-Definition-and-Data-Manipulation-Language-DDL-DML-8-320.jpg)