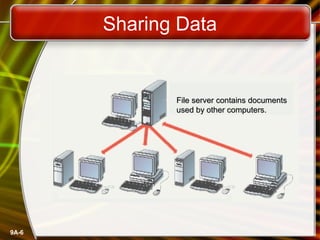
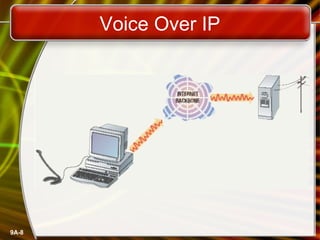
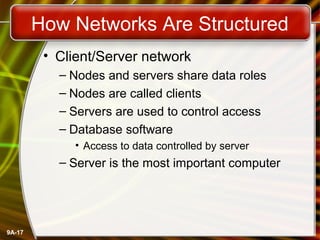
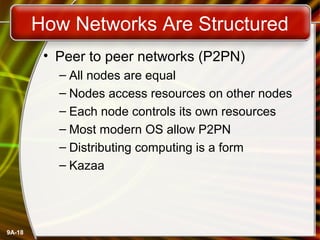
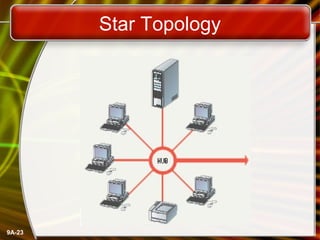
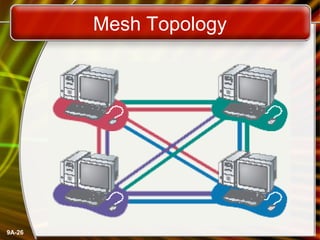
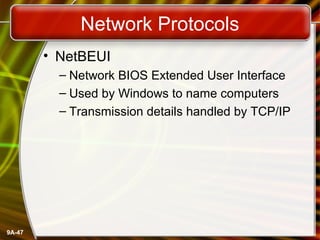
This document provides an overview of computer networks and networking concepts. It defines what a network is and discusses common network types like LANs, WANs, and wireless networks. It describes how networks are structured using client-server and peer-to-peer models. The document outlines different network topologies including bus, star, ring and mesh. It also discusses network hardware, cabling, protocols and other technical aspects of computer networking. There is an assigned networking project involving the card game FreeCell.