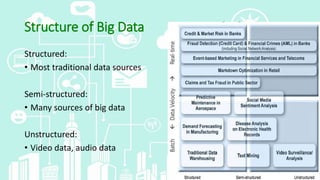
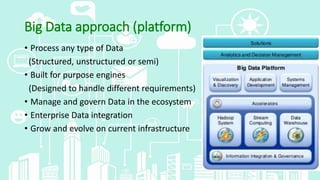
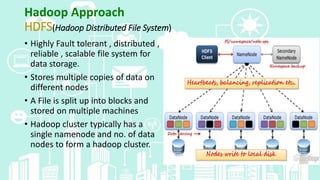
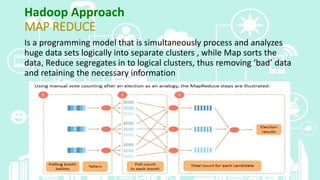
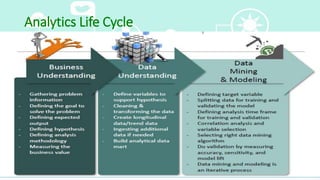
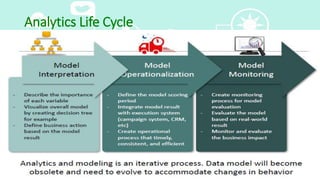
This document provides an overview of big data analytics. It defines big data as large, complex datasets that require new techniques and tools to analyze. The key characteristics of big data are described as the 5 V's: volume, velocity, variety, veracity, and value. Hadoop is introduced as an open-source framework for distributed processing of large datasets across clusters of computers using MapReduce. The document also outlines different types of big data analytics including descriptive, predictive, supervised, and unsupervised analytics. It concludes with an overview of the analytics life cycle and some common analytics tools.