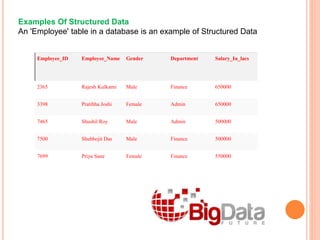
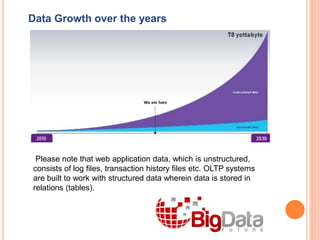
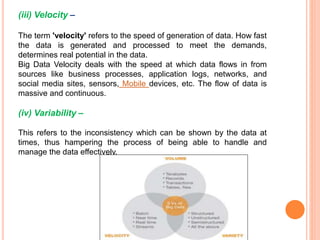
Big data refers to extremely large data sets that are too large to be processed using traditional data processing applications. It is characterized by high volume, variety, and velocity. Examples of big data sources include social media, jet engines, stock exchanges, and more. Big data can be structured, unstructured, or semi-structured. Key characteristics include volume, variety, velocity, and variability. Analyzing big data can provide benefits like improved customer service, better operational efficiency, and more informed decision making for organizations in various industries.