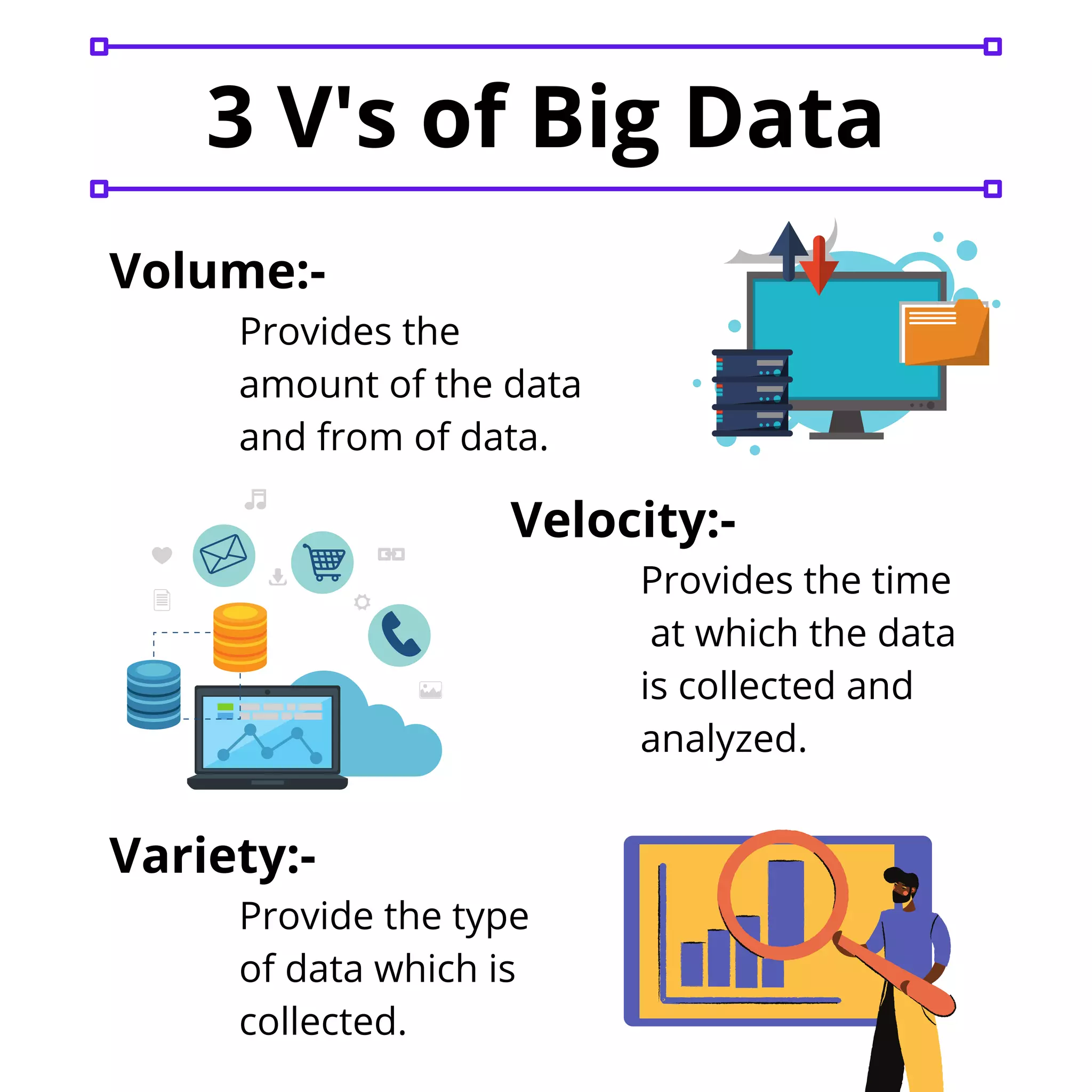
Big data refers to vast amounts of structured and unstructured data that exceed one terabyte and pose challenges for IT and computational technologies. It is characterized by three main aspects: volume, velocity, and variety, which influence business decision-making. Organizations must effectively analyze and manage this data using appropriate storage solutions and techniques to enhance strategic choices.