This document discusses intrauterine fetal death, including its definition, causes, diagnosis, investigations, complications, prevention, and management. Some key points:
- Intrauterine fetal death refers to fetal deaths occurring during pregnancy or labor after 28 weeks of gestation. Common causes include pregnancy complications like preeclampsia and abruption, medical conditions in the mother, fetal abnormalities, and infections.
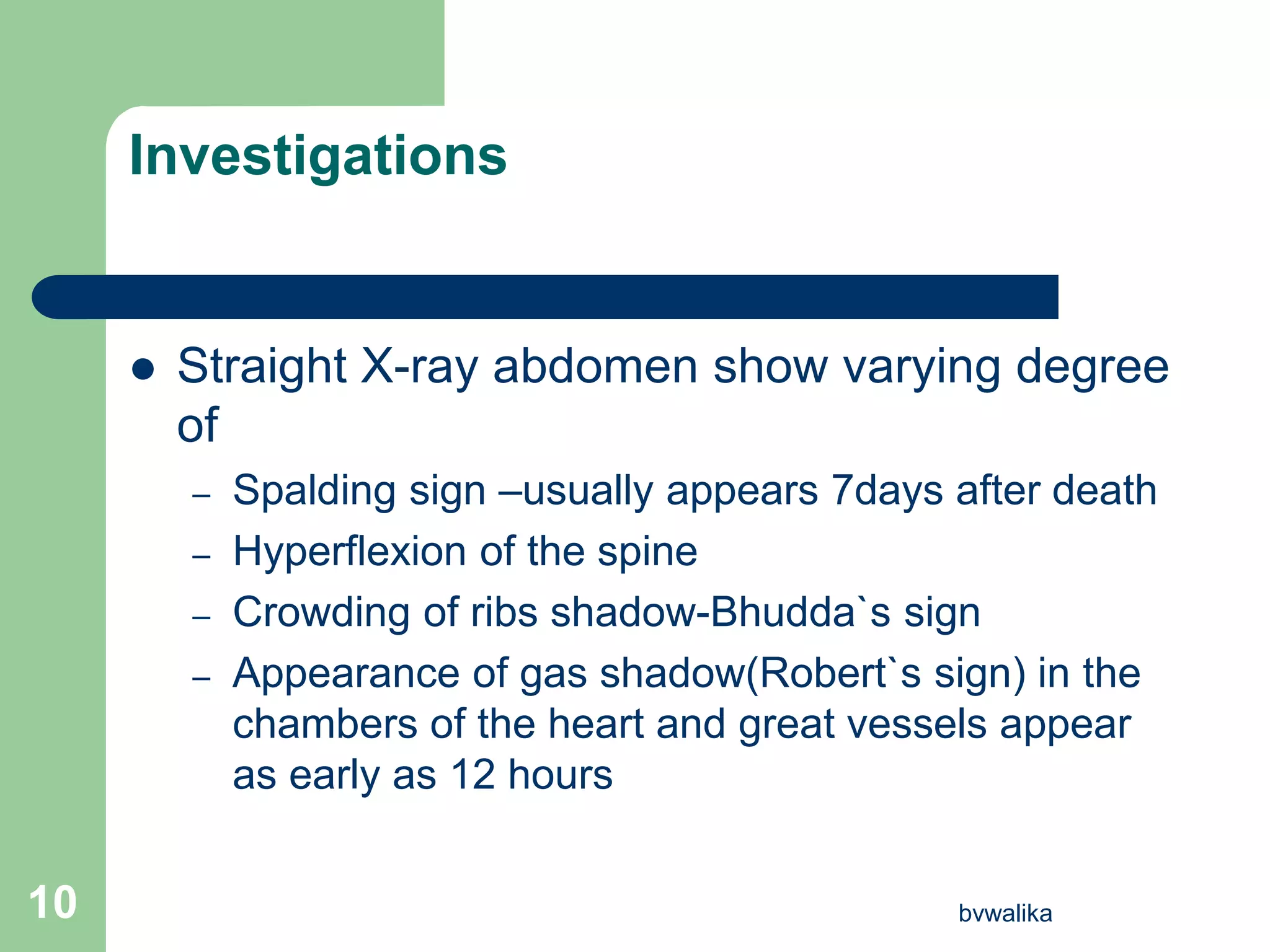
- Diagnosis involves absence of fetal movement, uterine changes, and ultrasound or X-ray findings. Investigations aim to confirm diagnosis and determine the cause of death.
- Complications can include psychological issues, infection if membranes rupture, and blood coagulation disorders if the fetus is retained for over two weeks.