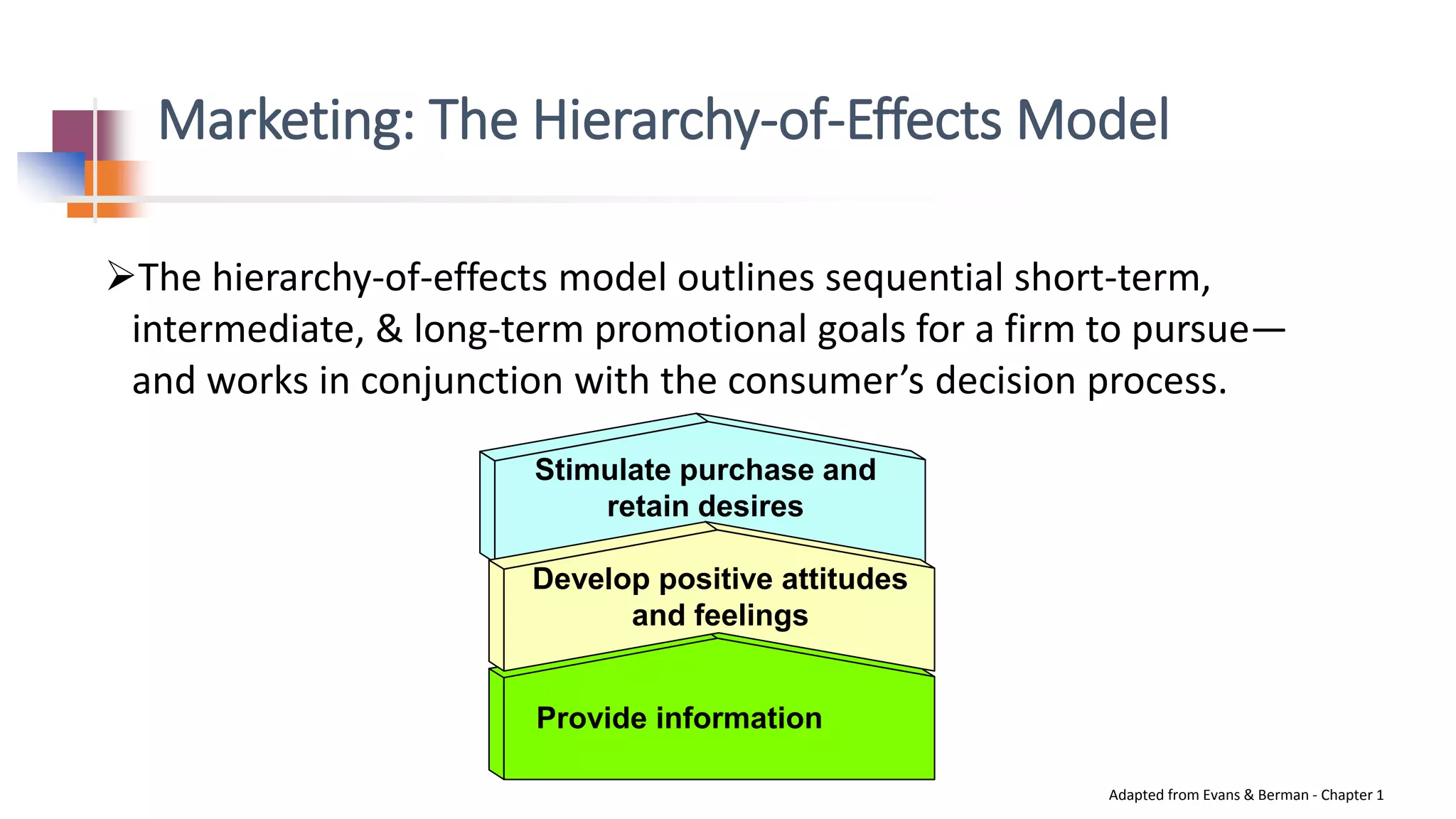
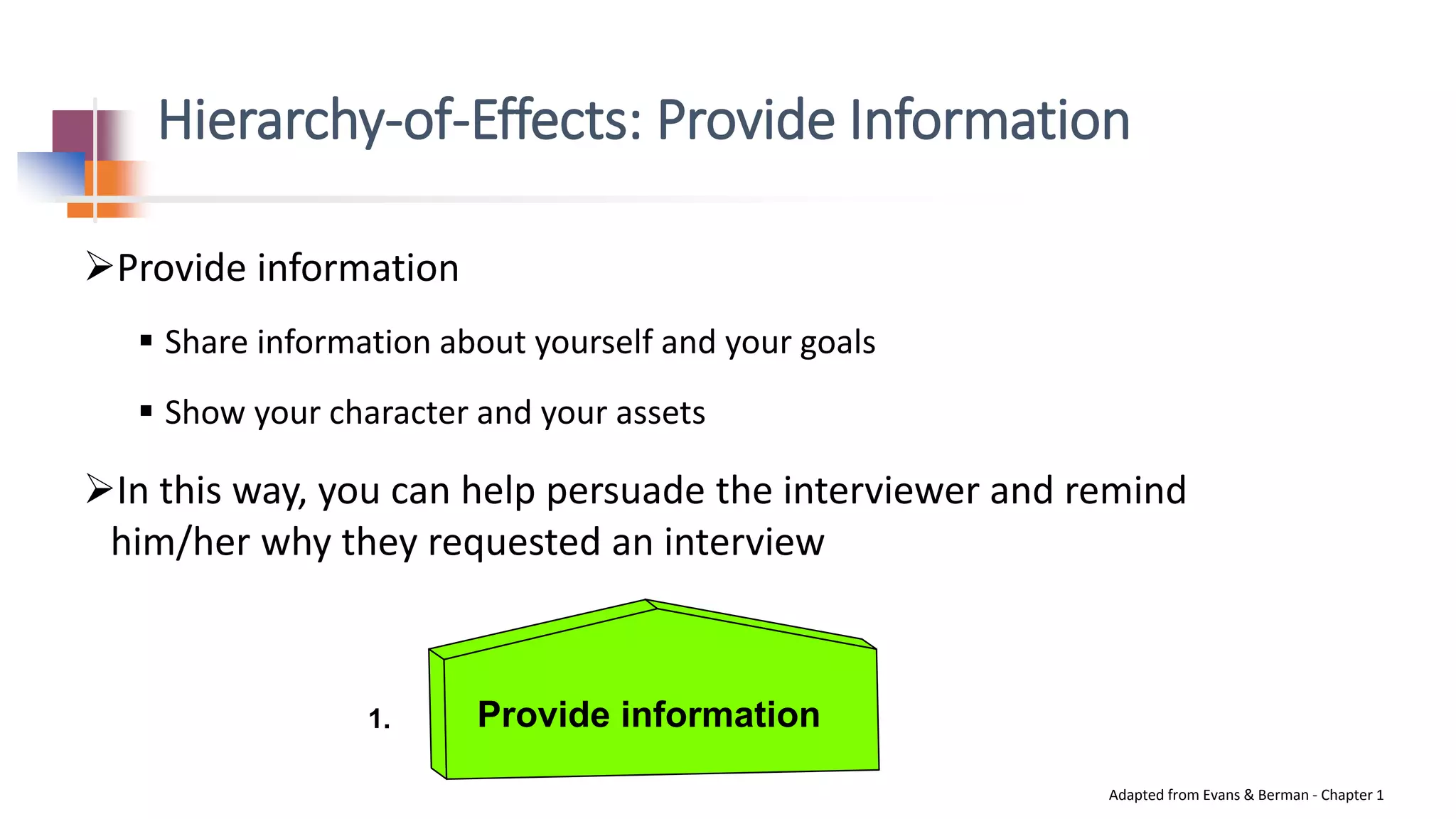
This document provides tips for improving interview skills. It discusses preparing for interviews by researching the organization and anticipating common questions. Common questions may include telling about yourself, strengths/weaknesses, and fit for the role. It's important to relax and be yourself during interviews. Answers should emphasize how you present yourself, not just what you say. Practicing interviews and learning language skills can improve performance. Marketing yourself during interviews by providing information, developing positive impressions, and stimulating interest in selecting you is also discussed.















![Language is Important: An Example
Underline
Sottolineare, evidenziare
Emphasize
Dare importanza
to ~ the importance of sth. sottolineare l’importanza di qcs.
(stress vocally) pronunciare con enfasi, enfatizzare
(highlight) mettere in evidenza [eyes etc.].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interviewskillsalternativeclass-200121184438/75/Interview-skills-16-2048.jpg)