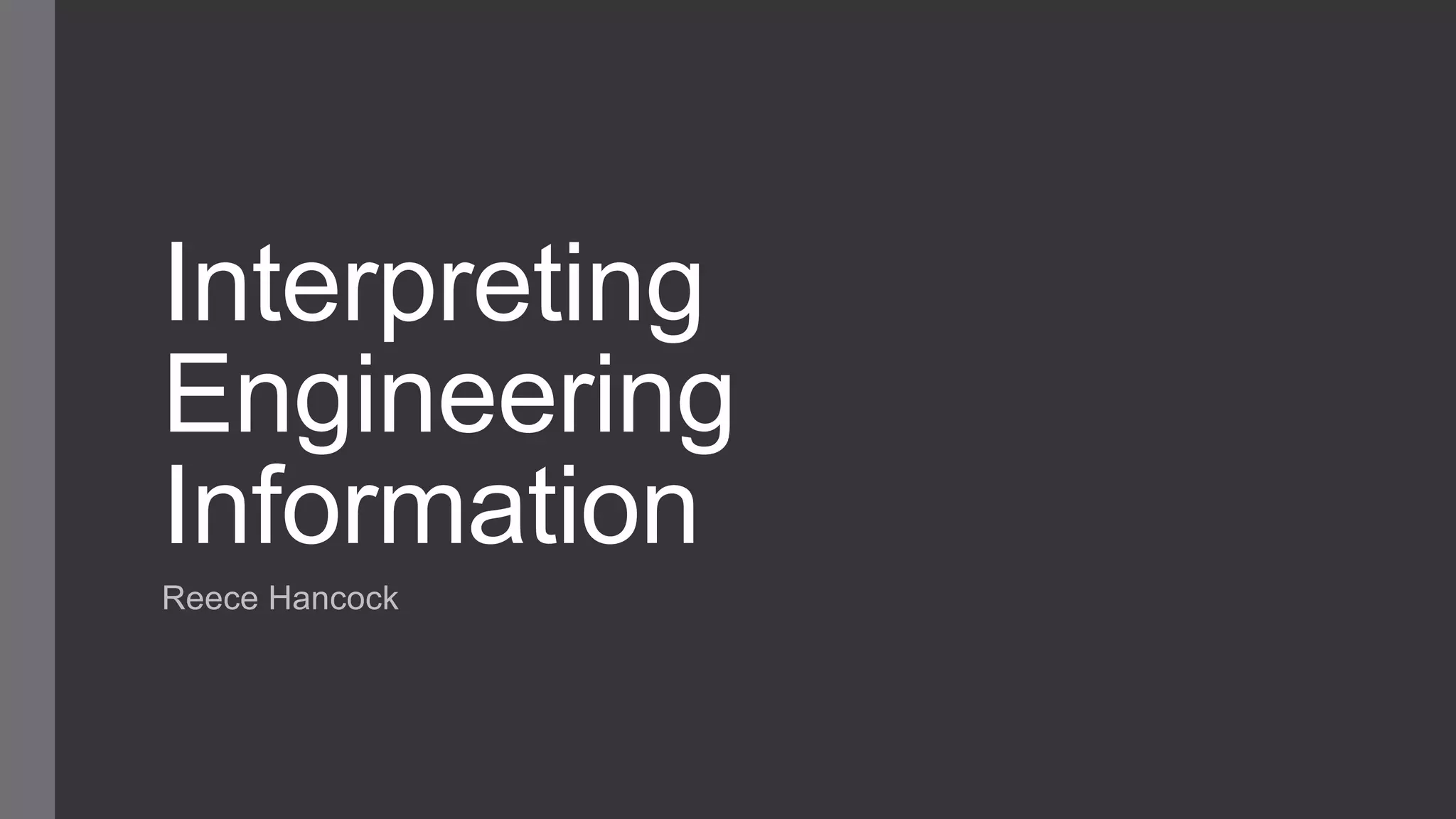
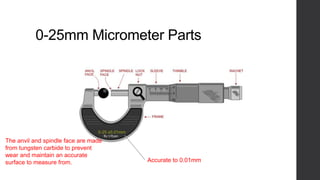
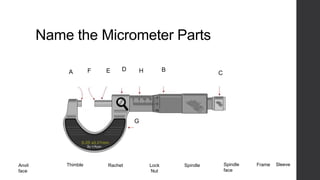
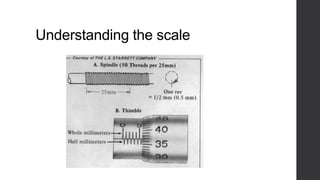
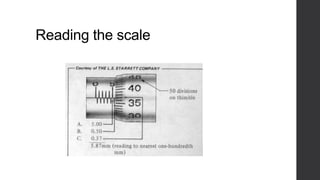
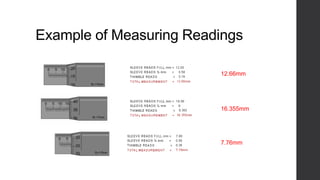
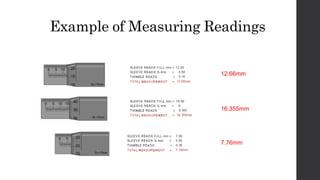
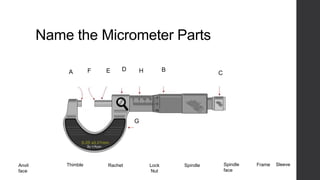
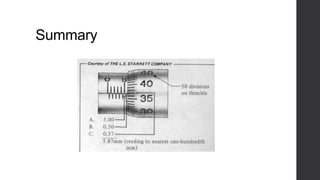
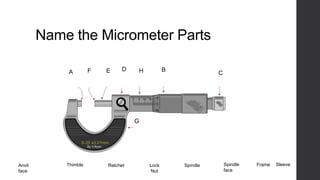
This document outlines a lesson plan for teaching students how to use a micrometer. The objectives are for students to understand the purpose of a micrometer, identify its parts, operate it correctly, and make accurate readings. The lesson covers an introduction, demonstrations of reading and using a micrometer, tests of the parts and reading skills, and a summary. It concludes by noting the next lesson will cover imperial micrometers.