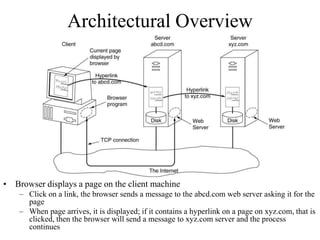
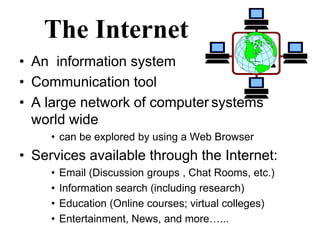
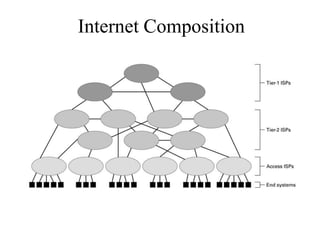
The Internet originated as a way to connect computer networks globally in a resilient manner. It has since grown to be a worldwide system of interconnected computer networks that use standard communication protocols like TCP/IP to share data. The Internet provides many services like email, information search, online education, and entertainment. It connects billions of devices worldwide through internet service providers and uses protocols like HTTP, FTP, and SMTP to transfer different types of files and messages.








![Dotted Decimal Notation
• IP addresses are written in a so-called dotted
decimal notation
• Each byte is identified by a decimal number in the
range [0..255]
• Example:
10000000 10001111 10001001 10010000
1st Byte
= 128
2nd Byte
= 143
3rd Byte
= 137
4th Byte
= 144
128.143.137.144](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internetnew-141030140208-conversion-gate01/85/Internet-new-13-320.jpg)