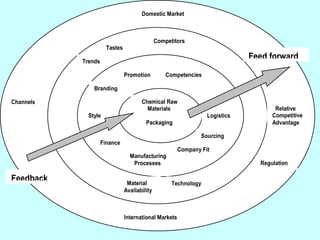
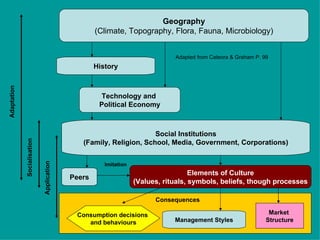
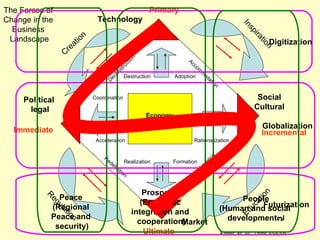
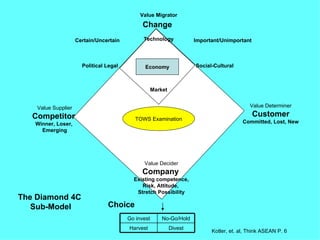
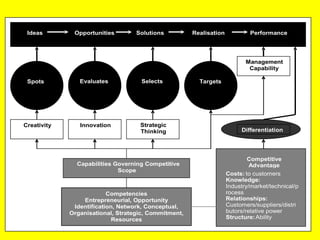
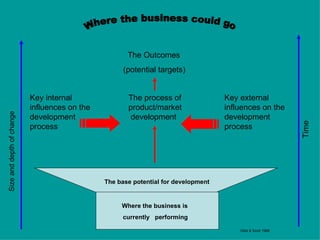
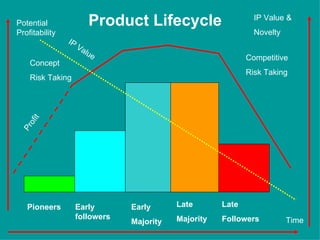
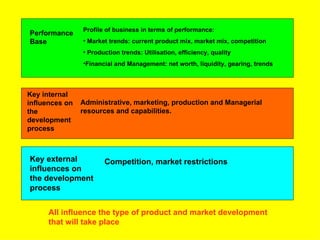
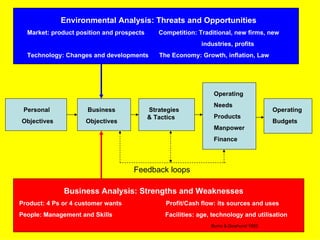
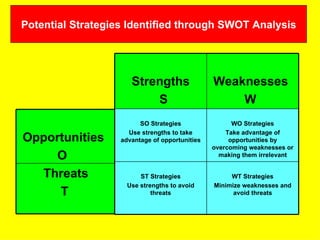
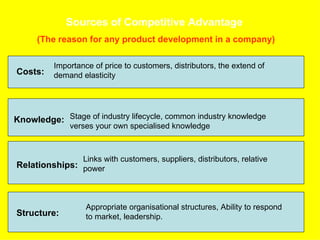
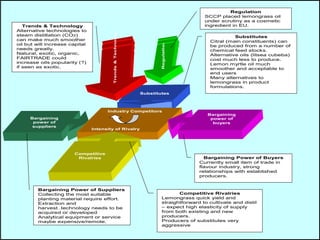
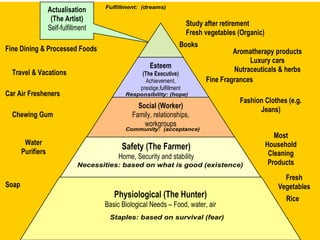
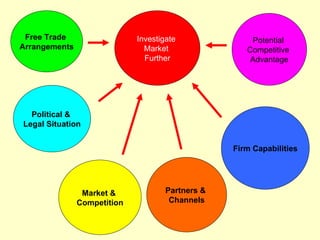
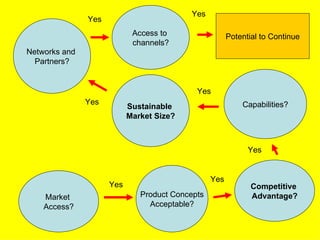
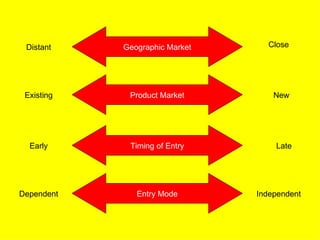
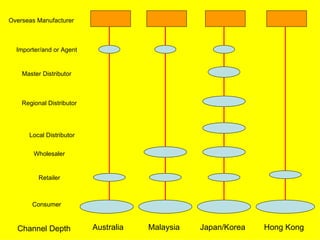
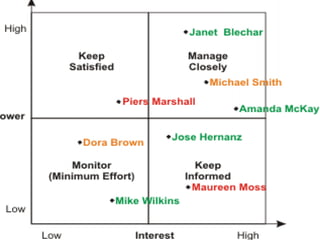
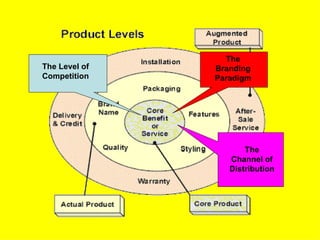
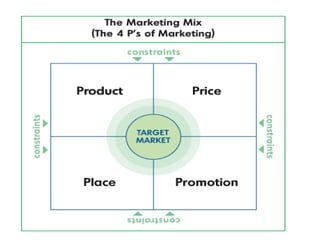
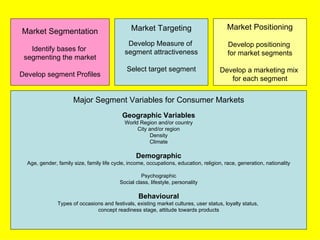
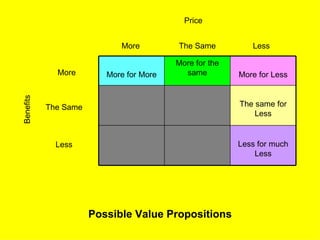
The document is a lecture on international marketing tools and strategies, focusing on the marketing mix, consumer behavior, channels, and various analytical tools in an international context. It emphasizes the importance of PEST analysis (political, economic, social, and technological factors) for understanding market dynamics, especially in Asia, and explores the implications of cultural, technological, and economic changes on marketing practices. Additionally, it discusses strategies for competitive advantage and product development in varying market conditions.