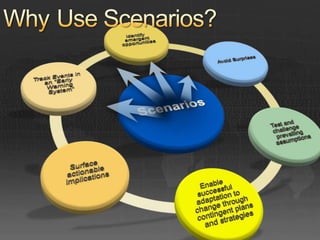
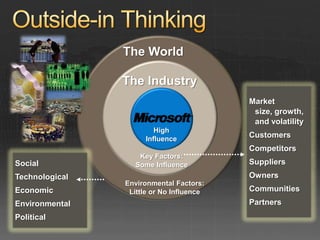
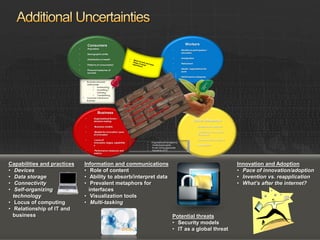
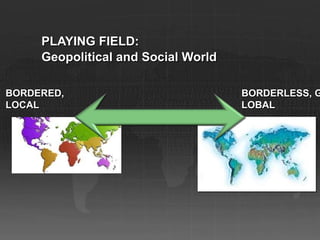
This document presents a scenario-driven approach to exploring possible futures and their implications. It summarizes a "Proud Tower" scenario where:
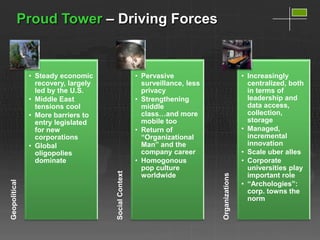
1. Borders become more fluid and global corporations are the primary organizers of commerce at every level.
2. Security needs outweigh privacy concerns, and close relationships form between corporations, the U.S. military, and other global entities.
3. Corporations pay more attention to governance and sustainability issues but new global and social tensions are rising in this increasingly centralized world with pervasive surveillance and less privacy.