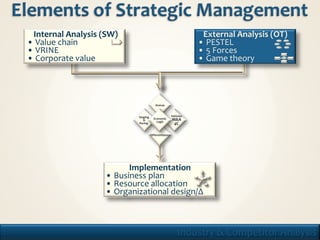
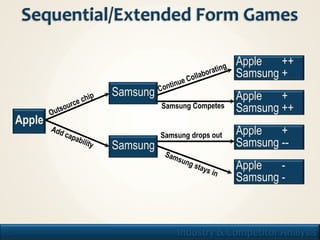
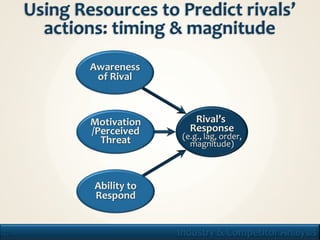
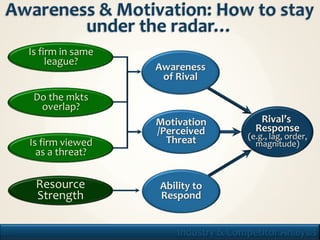
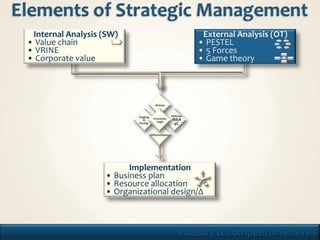
1. The document discusses frameworks for analyzing industries and competitors, including PESTEL, Porter's Five Forces, and game theory.
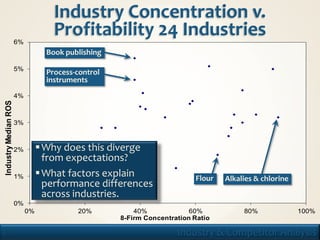
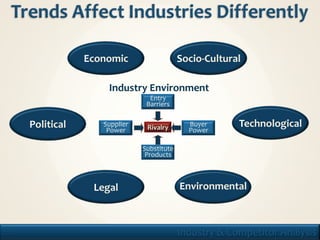
2. It covers topics like industry profitability, concentration, entry barriers, supplier/buyer power, rivalry, and substitution.
3. The purpose is to understand what determines industry profitability, how industries evolve, and how firms can formulate strategy based on this analysis.