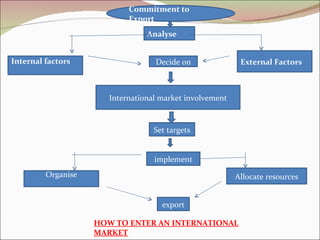
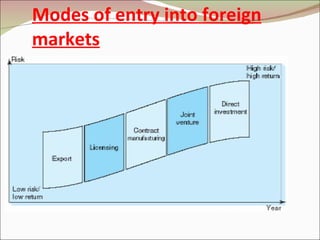
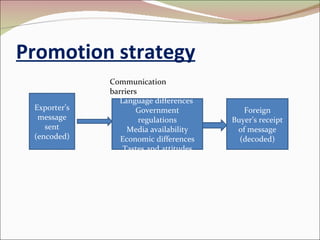
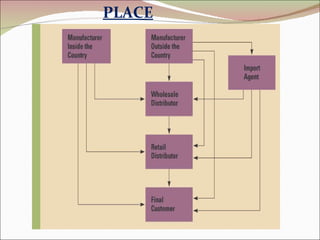
The document discusses various strategies for international marketing and market entry. It describes different modes of entering foreign markets, including exporting indirectly through intermediaries or directly, licensing, joint ventures, and direct investment through wholly owned subsidiaries. It also discusses factors that can both drive and restrain global integration. When developing marketing strategies, companies need to avoid ethnocentrism and the self-reference criterion in order to understand foreign customer needs and provide appropriately adapted products, pricing, and promotion in each market.