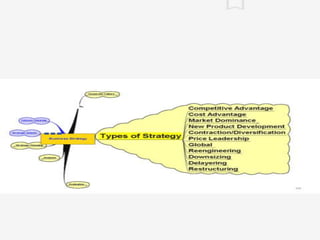
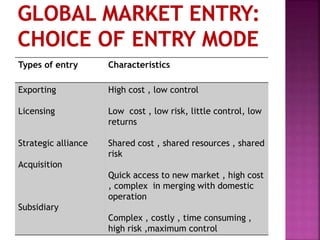
The document discusses the strategies companies use to achieve superior performance through resource allocation and international diversification. It highlights the importance of balancing global efficiency with local market responsiveness, and outlines various entry strategies such as exporting and acquisitions, along with their associated costs and controls. Additionally, it addresses the risks involved in international operations, including political and economic uncertainties.