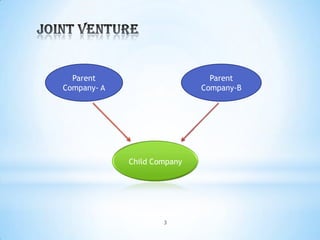
A joint venture is a business arrangement where two or more parties pool their resources for a specific project or business activity. In a joint venture, each participant shares in profits, losses, and costs of the venture, which operates as a separate entity from the participants' other business interests. Joint ventures can be domestic or international. They allow partners to share financial resources, reduce business risks through diversification, achieve economies of scale, and directly manage functional activities. However, joint ventures also carry investment risks and potential conflicts around profit sharing, use of shared technologies, and management difficulties.