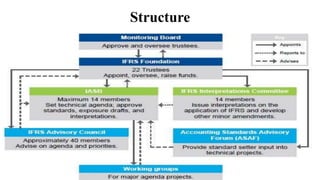
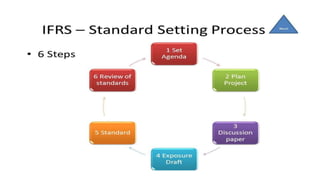
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are issued by the International Accounting Standards Board to establish consistent, transparent, and comparable financial reporting around the world. IFRS address record keeping, financial reporting, and other aspects of financial reporting. While not universal, with the US using GAAP, IFRS are used in the European Union, India, Hong Kong, Australia, and other countries. The objectives of IFRS include bringing uniformity to accounting practices, expanding global capital markets, enhancing transparency, and reducing reporting costs. Financial statements prepared under IFRS include a statement of financial position, statement of comprehensive income, statement of changes in equity, and cash flow statement.