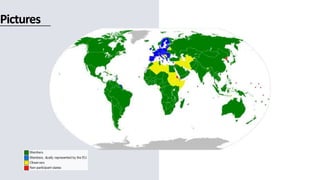
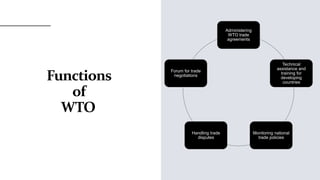
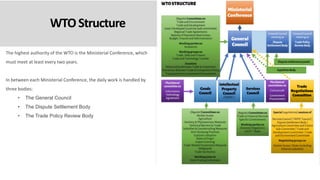
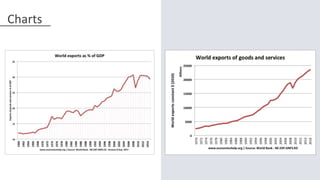
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates international trade between nations. It has 164 member nations and facilitates trade in goods, services, and intellectual property. The WTO was established in 1995 after the Uruguay Round negotiations to further liberalize international trade beyond previous agreements under the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT). The WTO aims to reduce trade barriers and resolve disputes between members through principles of non-discrimination, transparency, reciprocity, and binding commitments.