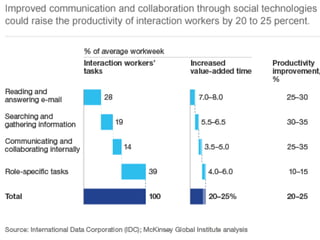
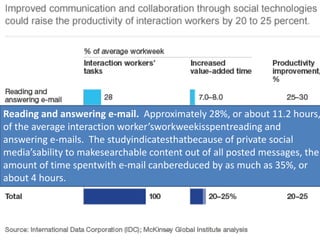
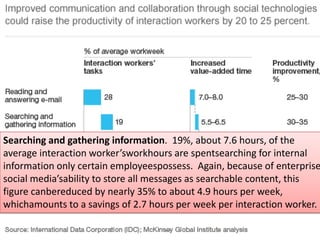
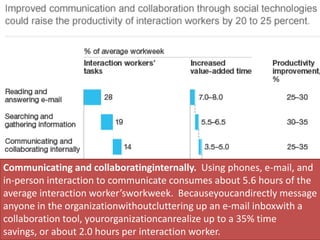
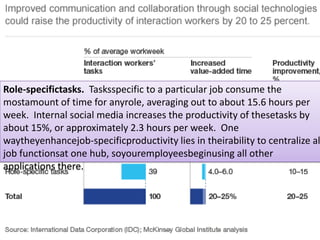
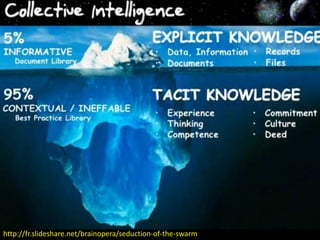
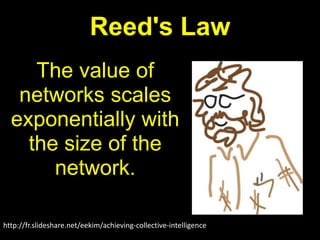
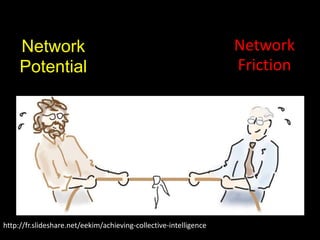
The document discusses risks and opportunities of internal social networks. It identifies several risks including: [1] data privacy and ensuring personal data is collected and processed legally; [2] data security and protecting information from accidental or unlawful access; and [3] intellectual property issues around copyright infringement and ownership of employee work. It also notes potential opportunities for internal social networks including improved knowledge management, communication and collaboration between employees, and increased productivity. The document recommends developing an internal code of conduct to help manage these risks and realize the added values of internal social networks.