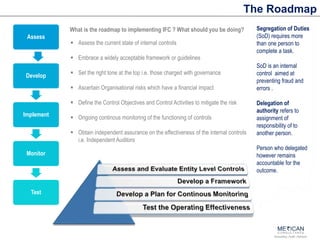
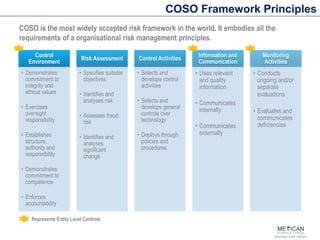
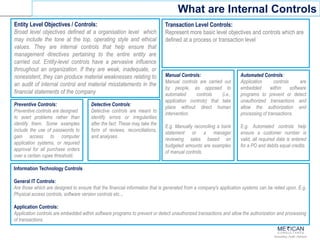
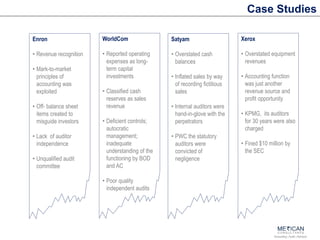
The document discusses internal financial controls (IFC) as mandated by the Companies Act of 2013 in India. It provides an overview of key aspects of IFC including definitions, requirements for boards of directors, audit committees and independent auditors. It also discusses the COSO framework that is widely used for IFC and provides a roadmap for implementing IFC including assessing current controls, developing a framework, implementing controls, monitoring and testing. Case studies of control failures at companies like Enron, Worldcom and Satyam are also summarized.