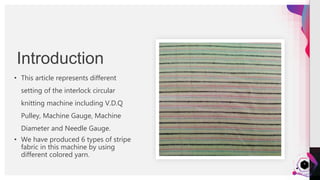
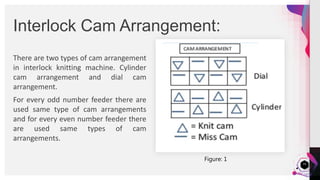
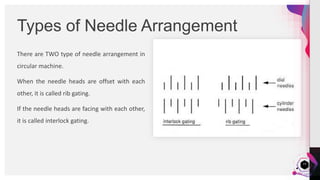
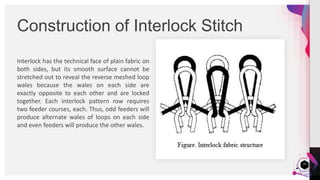
The document provides a practical analysis of interlock circular knitting machines, detailing various settings and parameters for producing stripe fabrics. It outlines the machine's specifications, including components like needles and cams, as well as the effects of different yarn counts and stitch lengths on fabric weight (gsm). The study demonstrates the production of six types of stripe fabrics using different yarn colors and examines the influence of machine settings on quality and output.