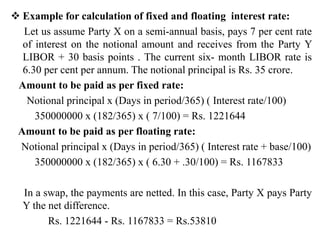
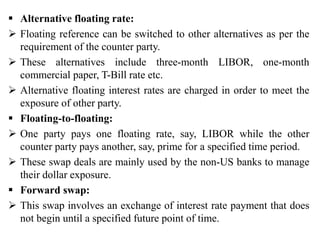
The document discusses the origins and evolution of swap markets. It began in the 1970s when countries imposed exchange controls in response to instability from the collapse of Bretton Woods. This led banks and corporations to develop swap agreements as a more flexible way to exchange cash flows compared to loans. Standardization of documentation in the 1980s by ISDA helped the market grow. The document then defines key swap types like interest rate, currency, and debt-equity swaps. It describes the mechanics of how they work and motivations for counterparties to enter swap agreements like hedging risks or accessing cheaper funding.