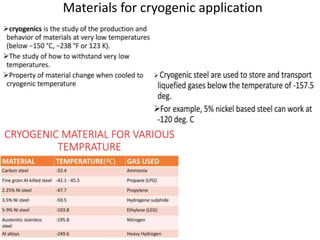
This document discusses intermetallic materials, materials for cryogenic and space environments, and evaluation of materials for extreme conditions. It provides details on intermetallic compounds, including that they are generally hard and brittle but can have good high-temperature properties. Intermetallics exhibit a mix of metallic and ceramic properties and have applications in areas like batteries, superalloys, and microelectronics. The document also introduces materials for cryogenic use, extreme environments, and metallic foams, which have gas-filled pores and can be open-celled or closed-celled.