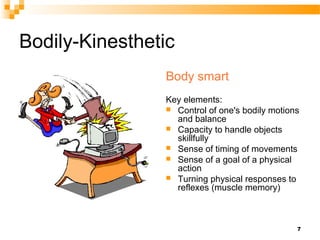
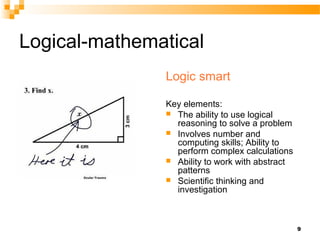
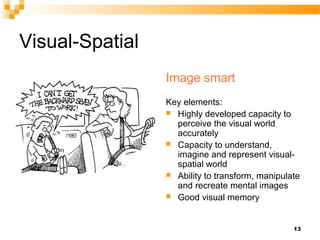
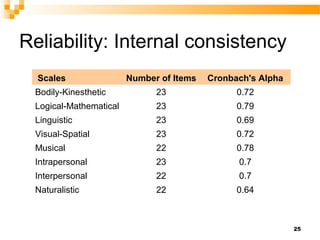
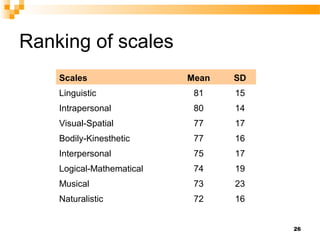
The document discusses Howard Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences and presents an overview of an intelligence types test that measures 8 types of intelligence: bodily-kinesthetic, logical-mathematical, linguistic, visual-spatial, musical, interpersonal, intrapersonal, and naturalistic. It then summarizes validation research on the test which found good internal reliability and differences in scores between men and women.