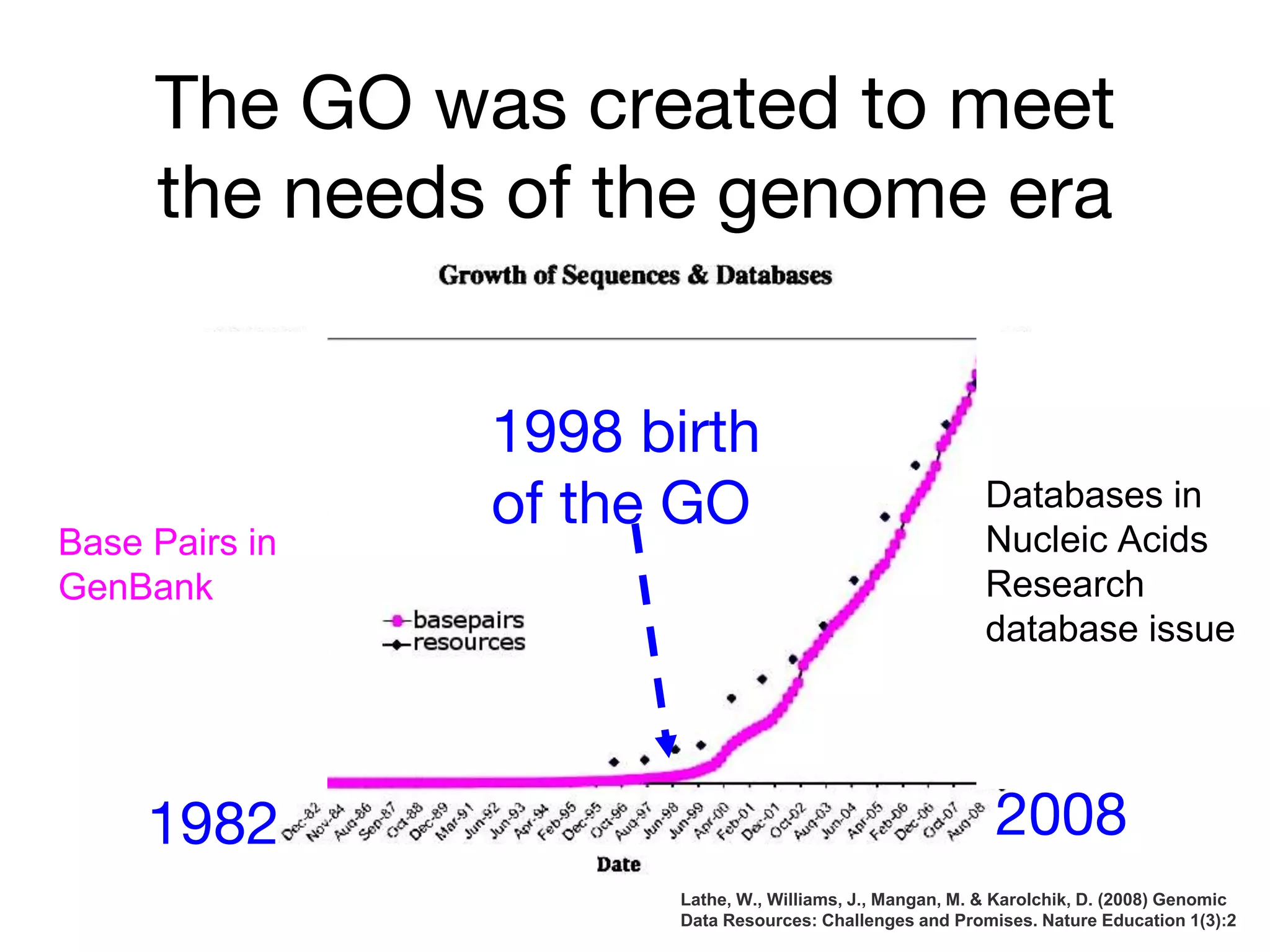
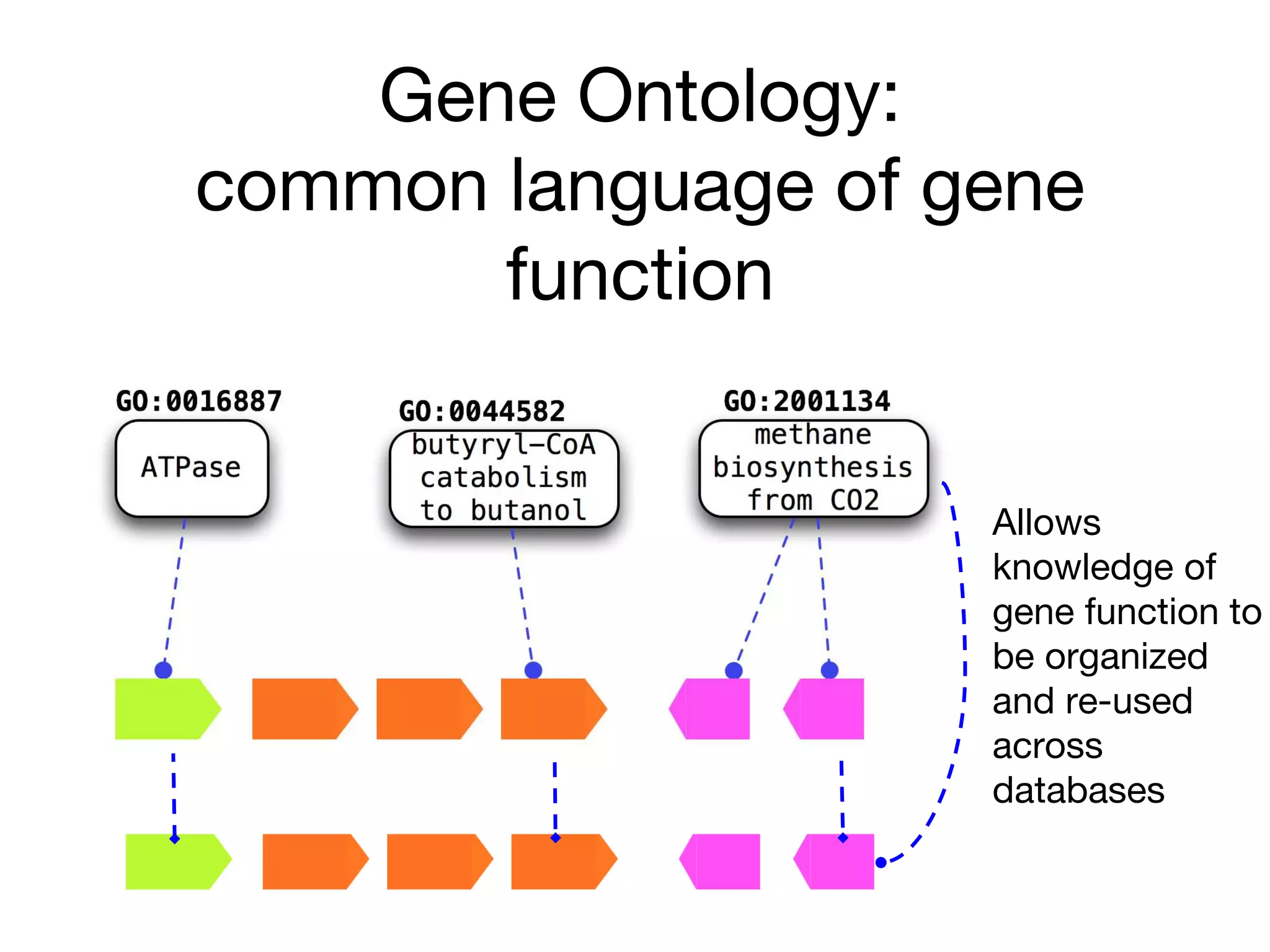
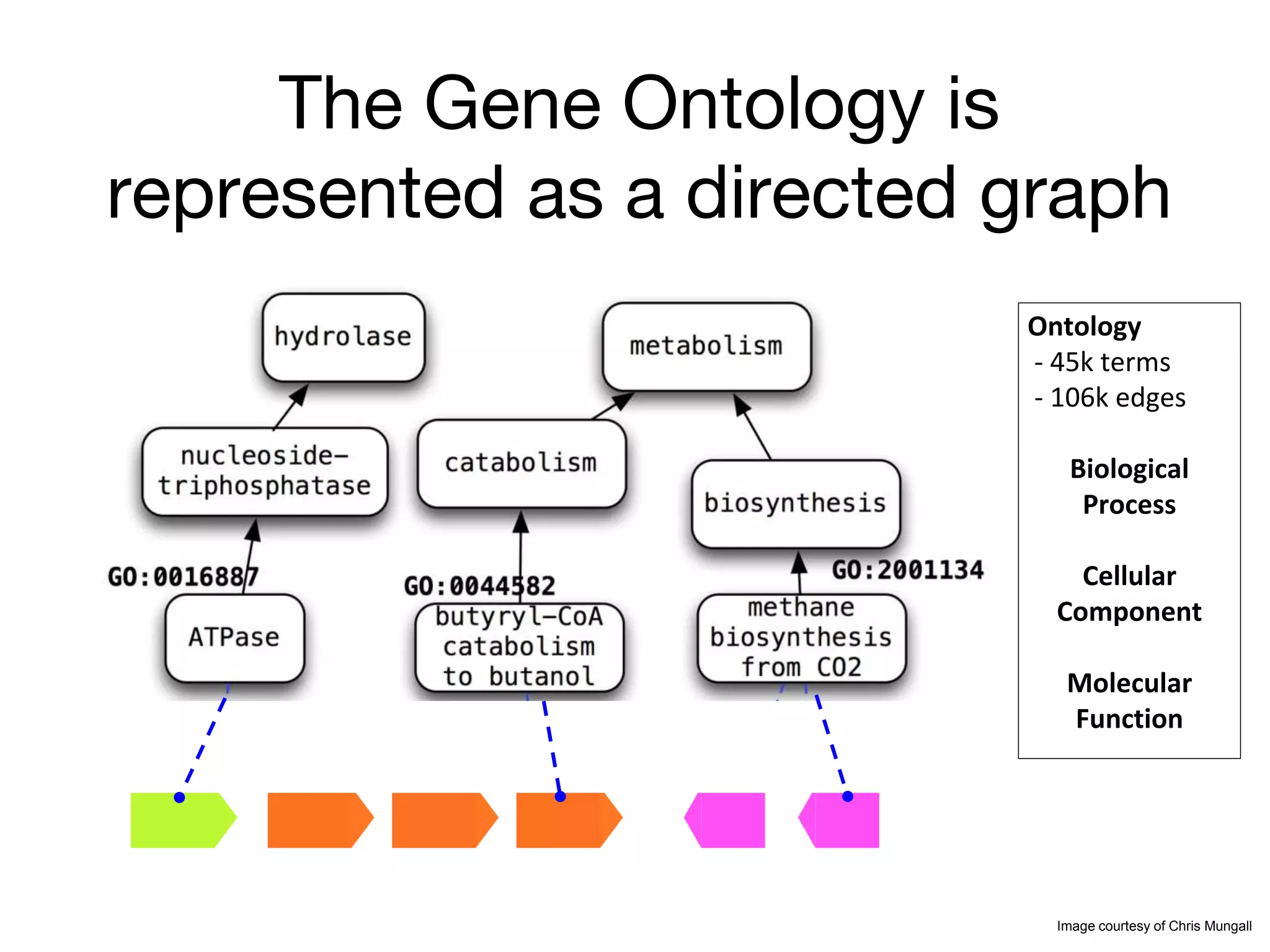
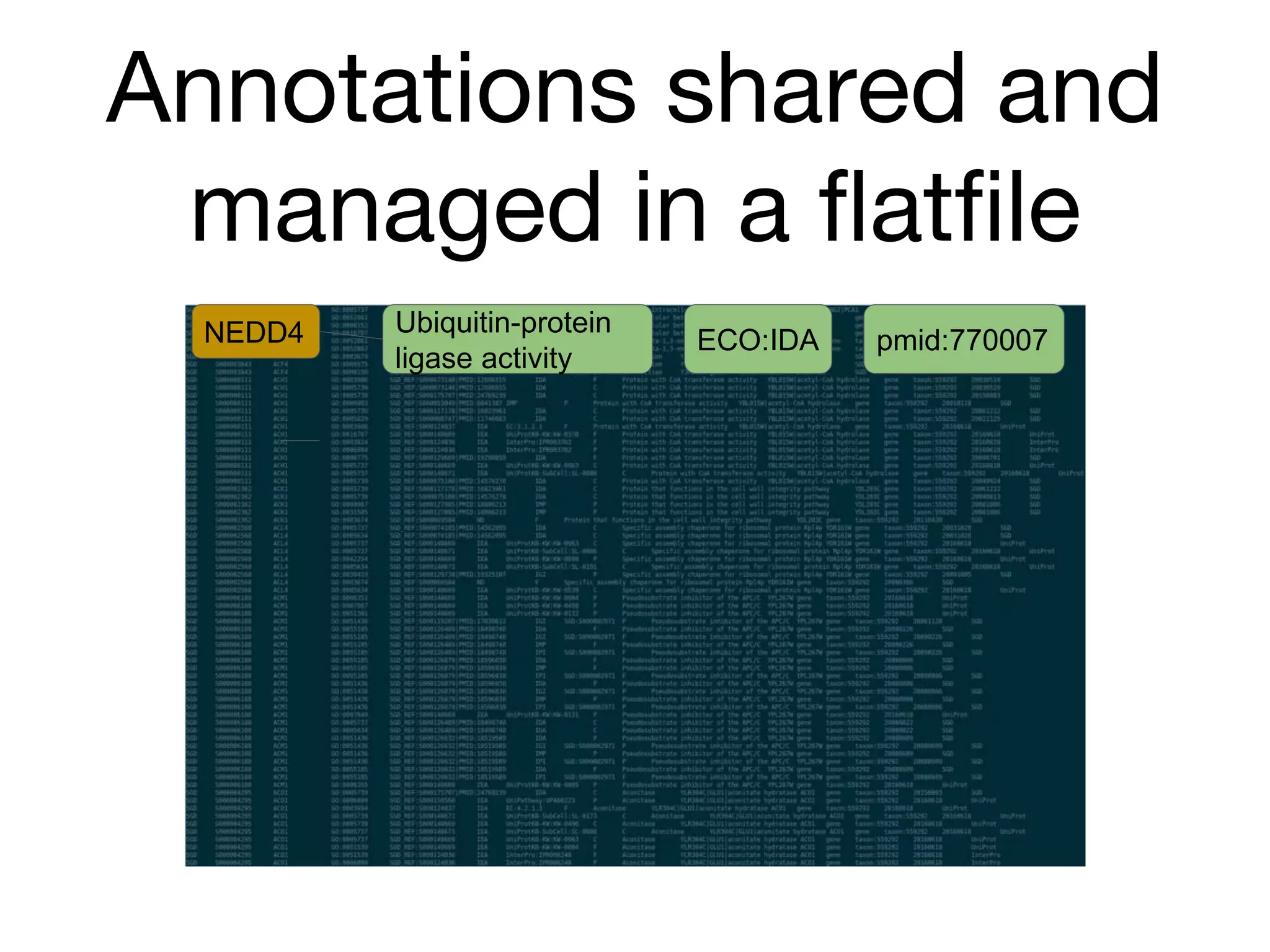
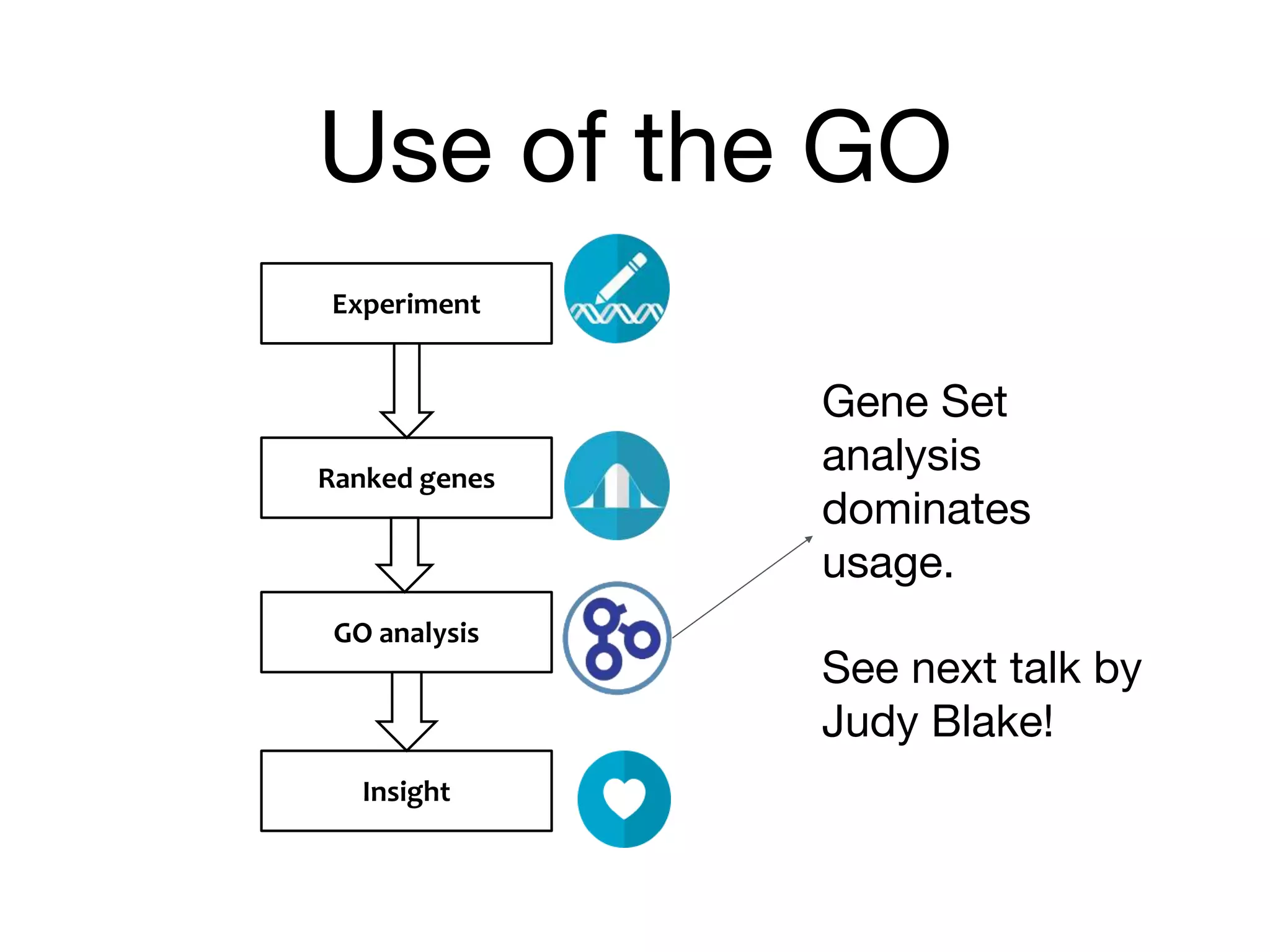
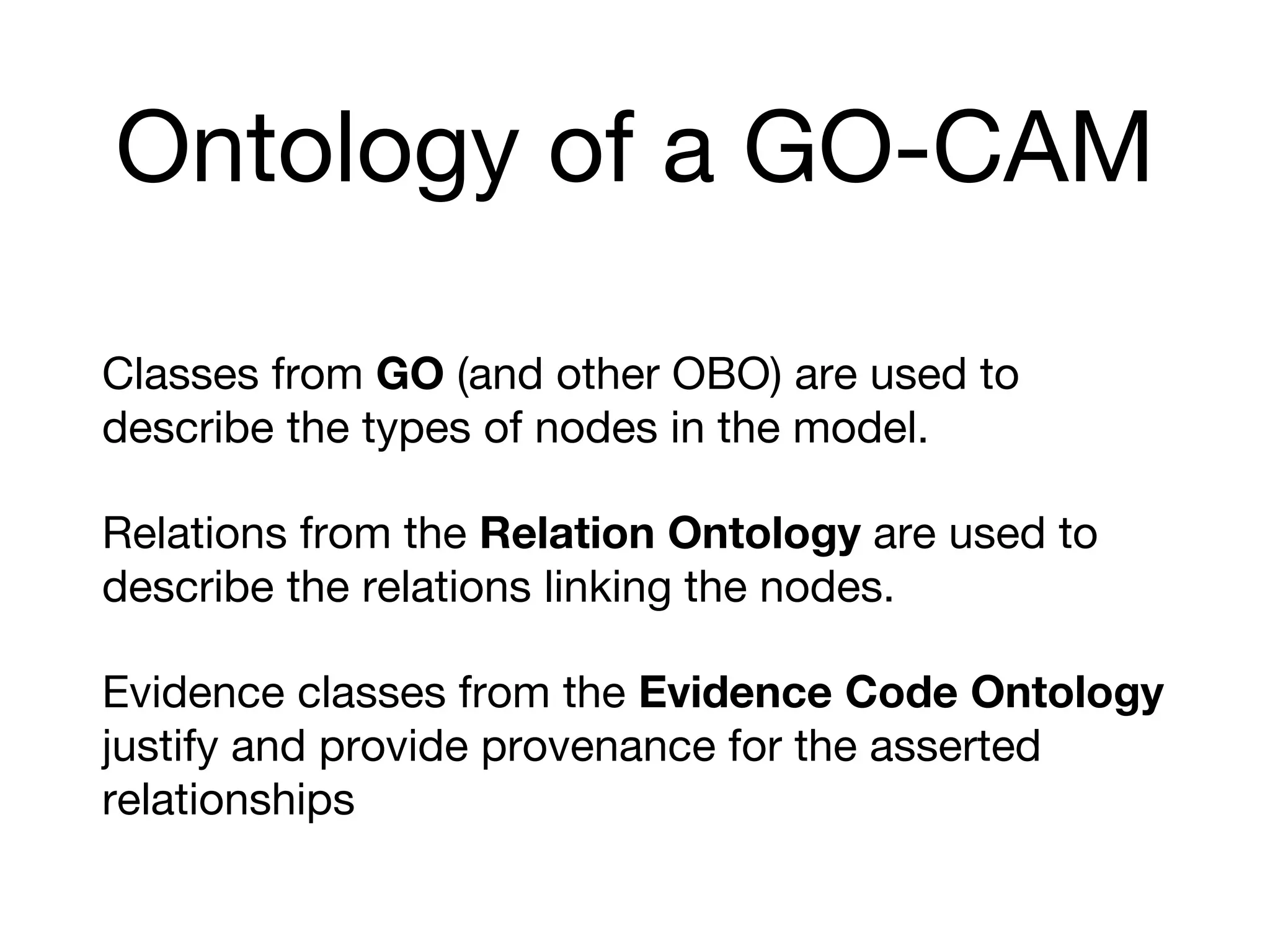
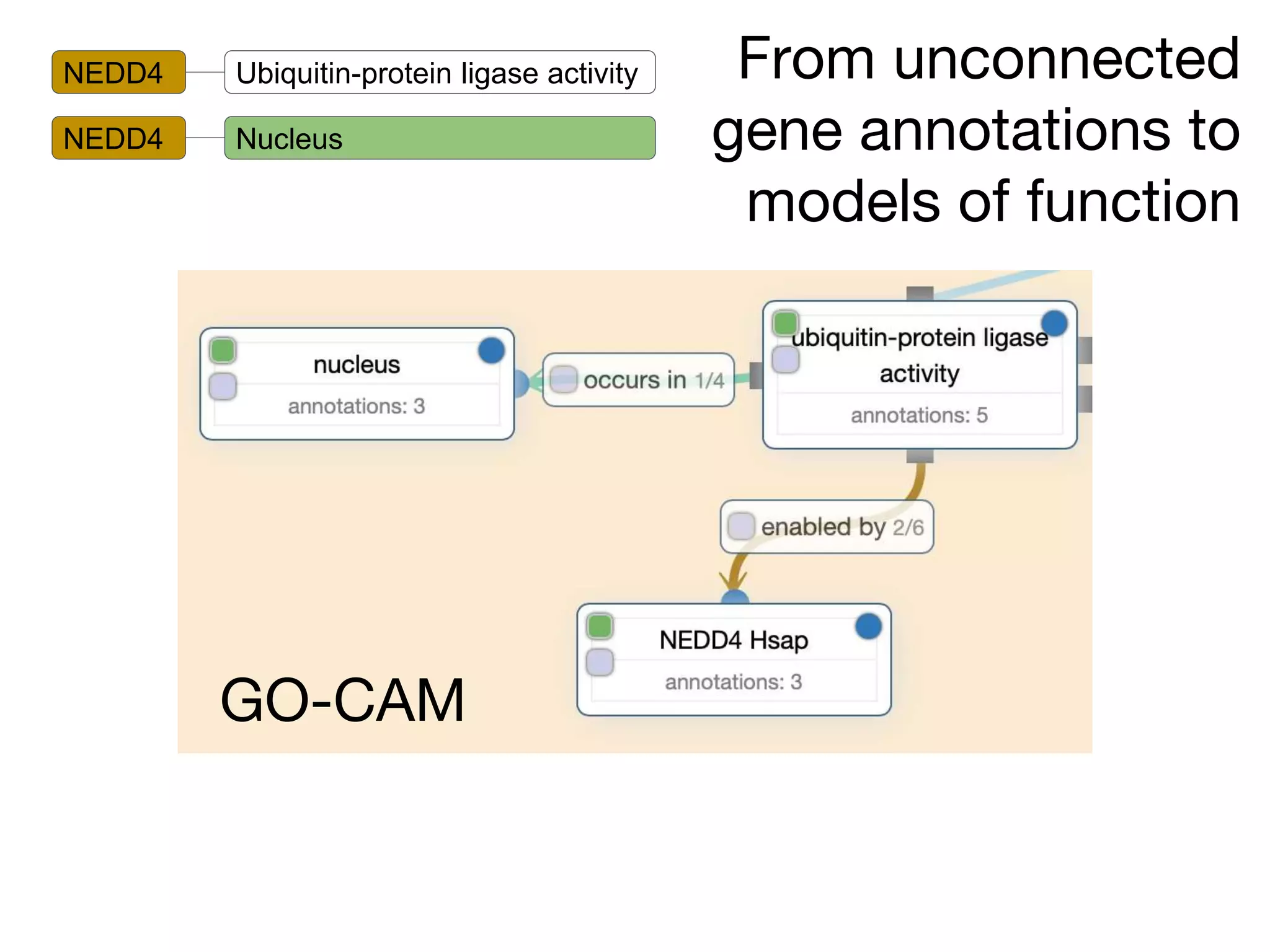
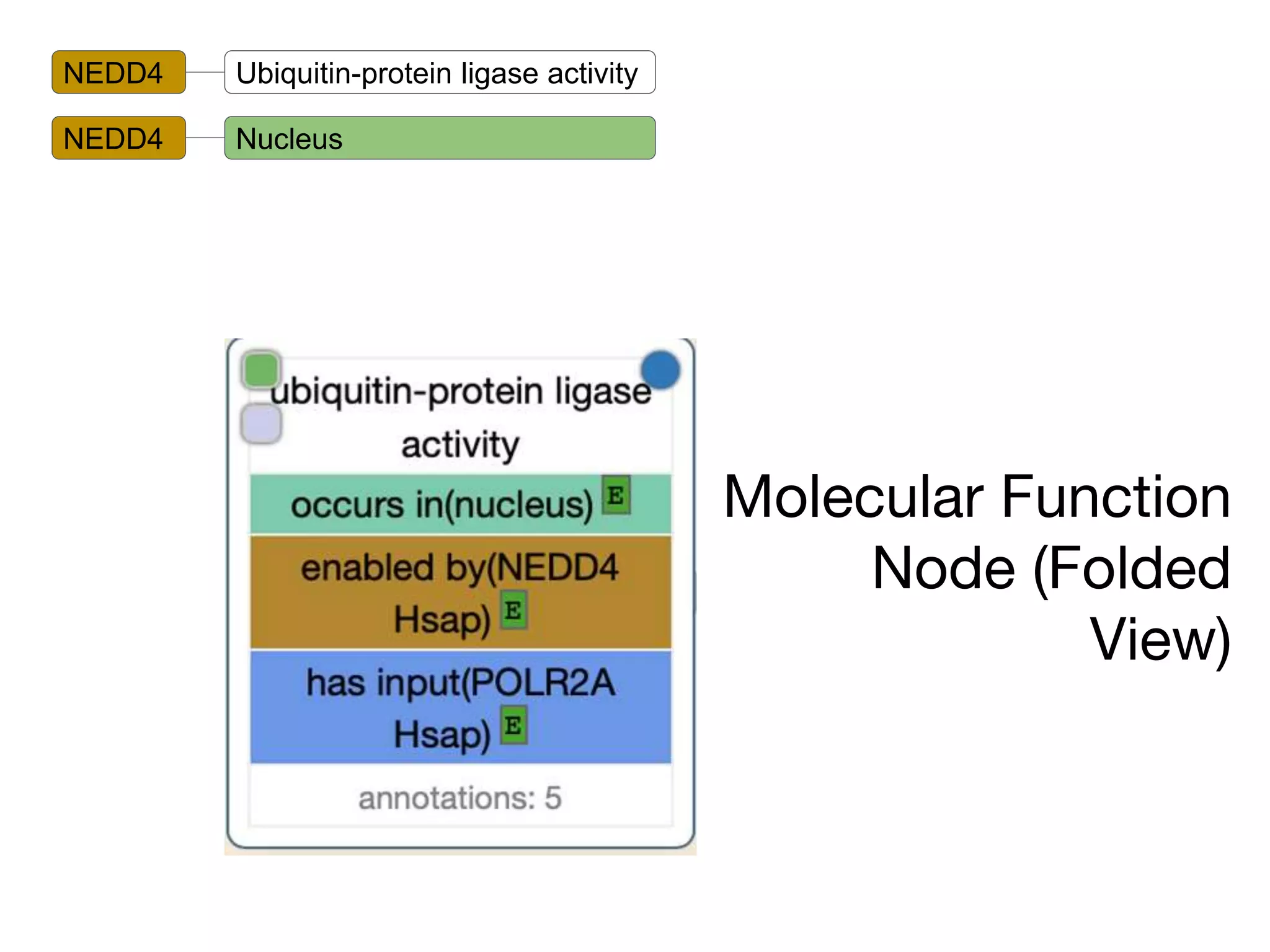
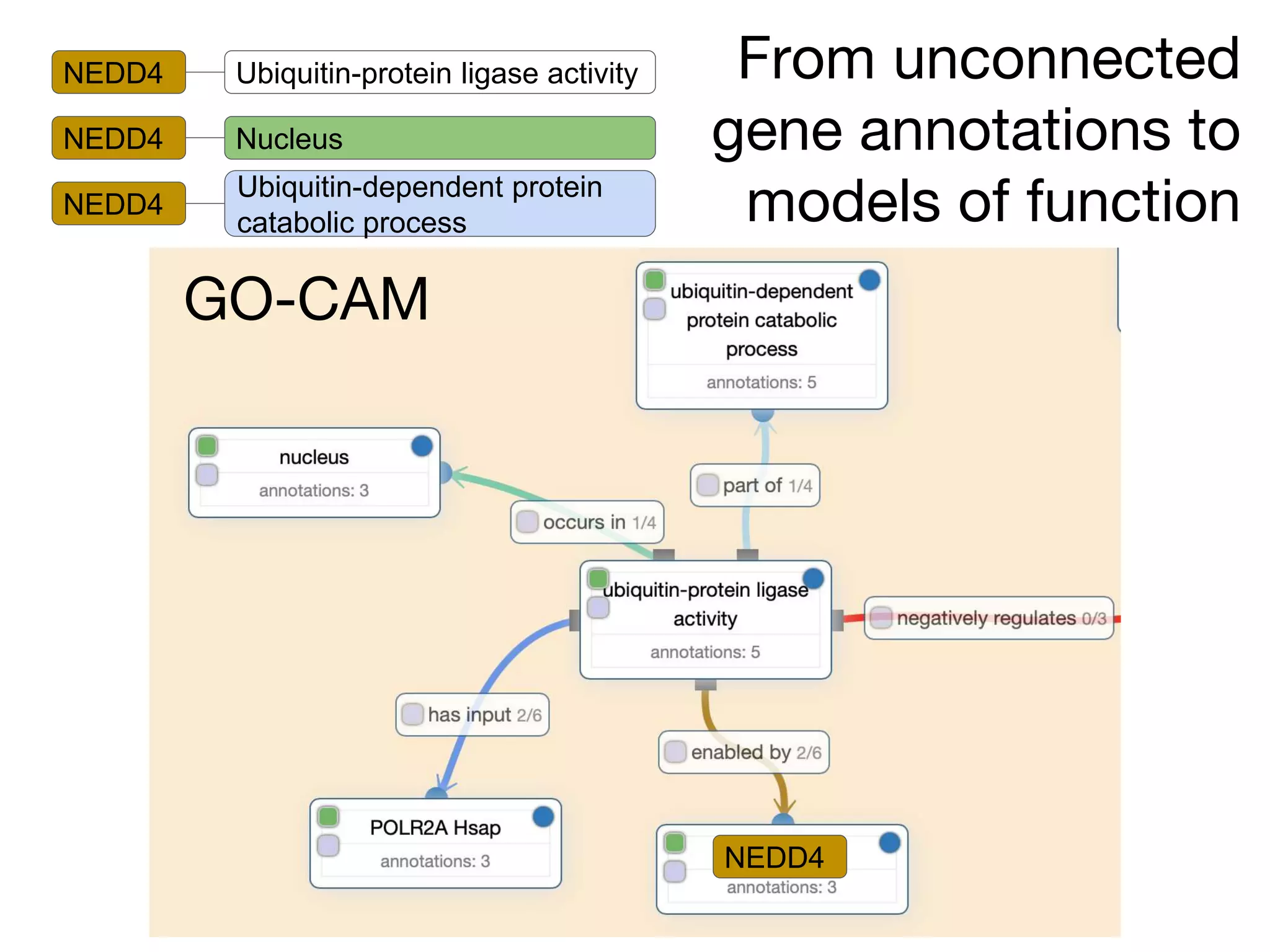
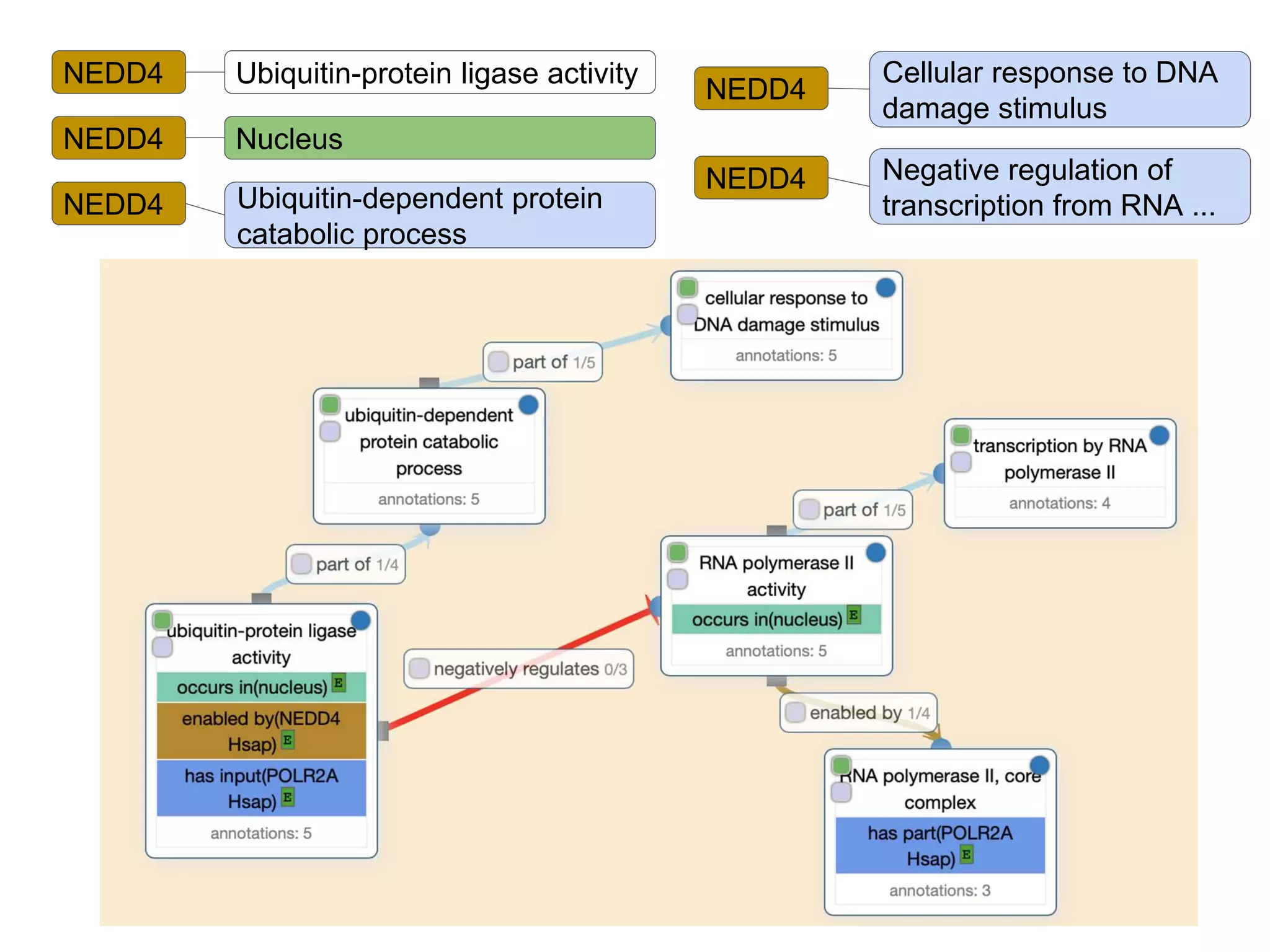
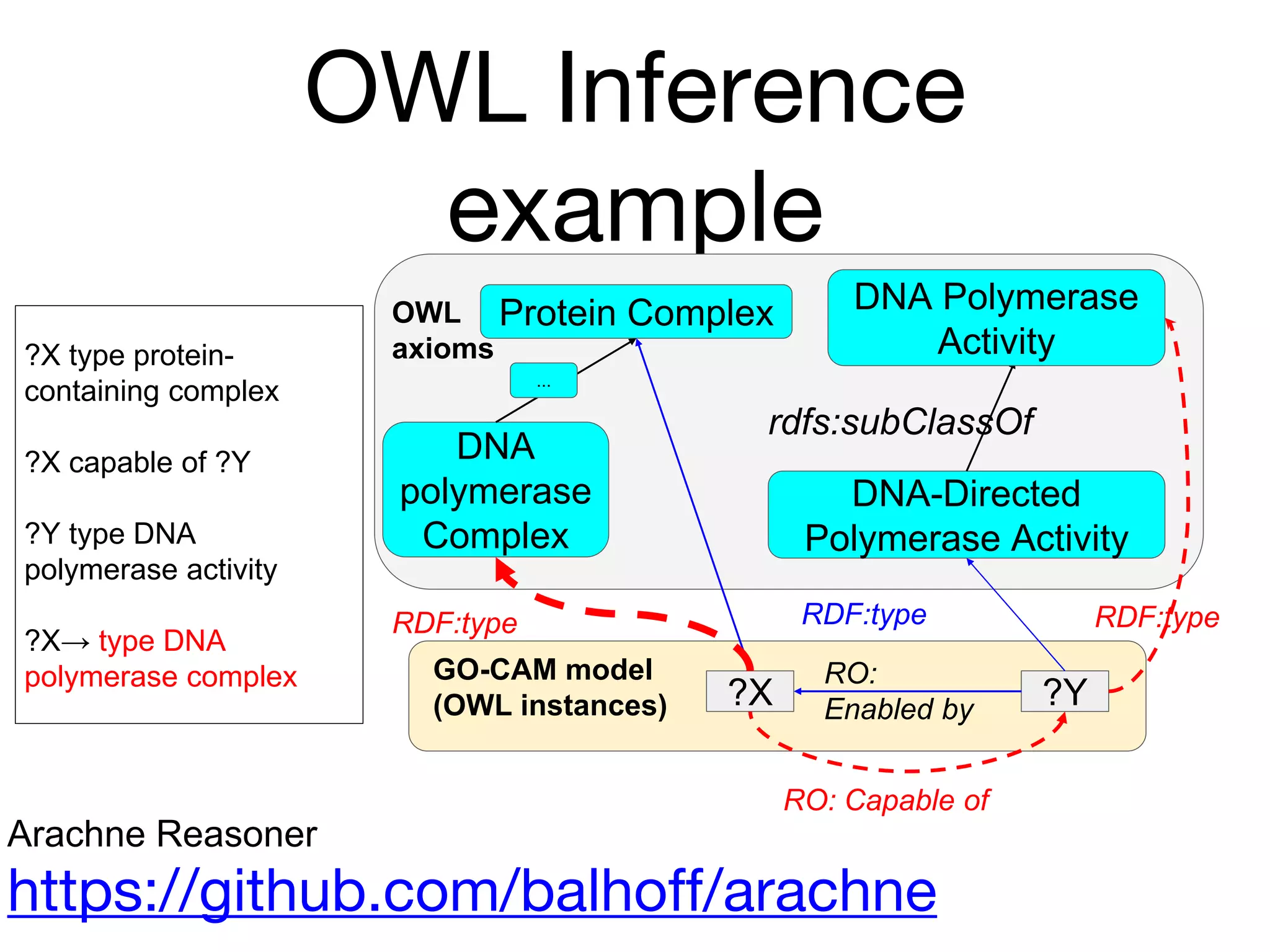
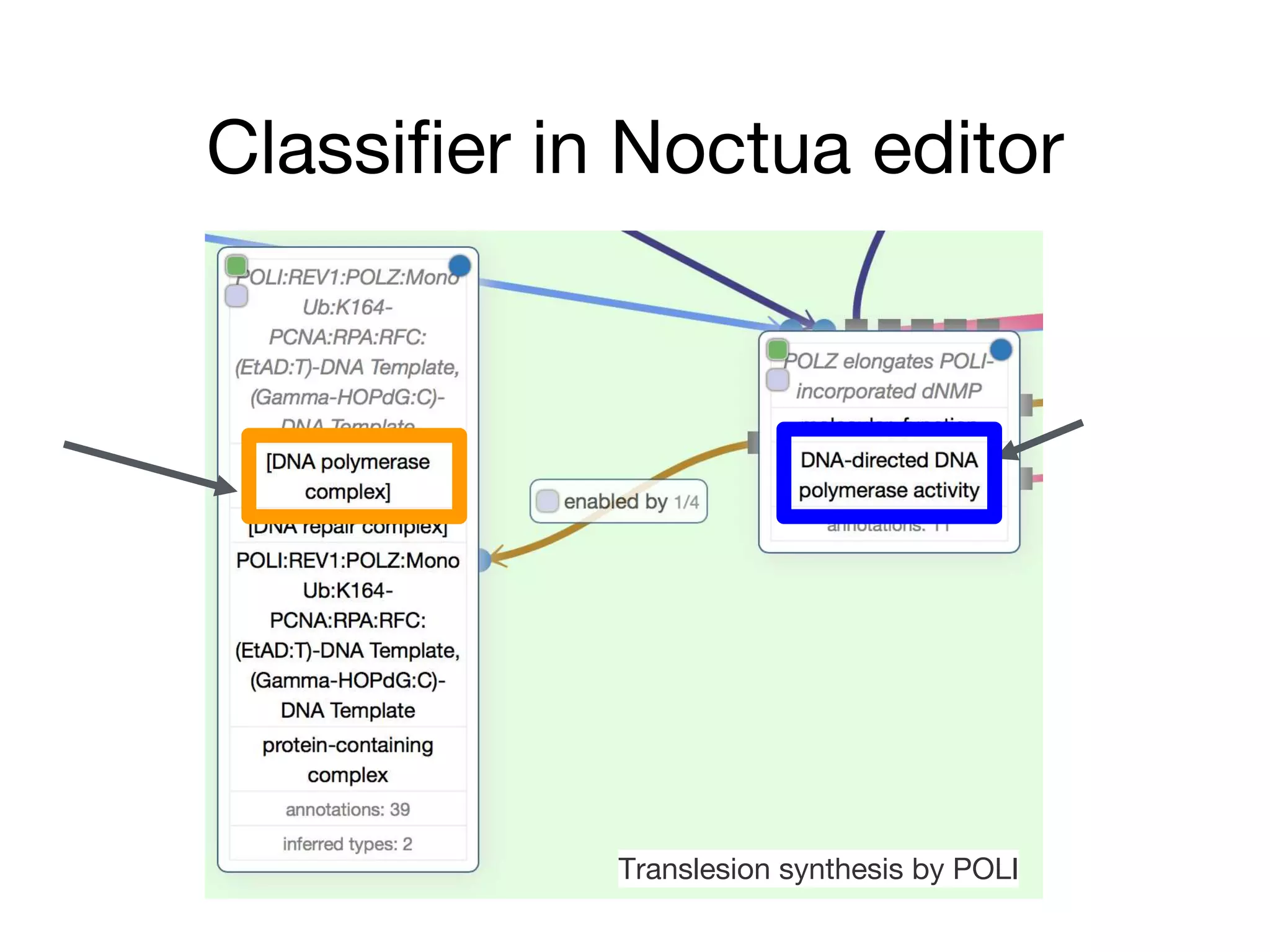
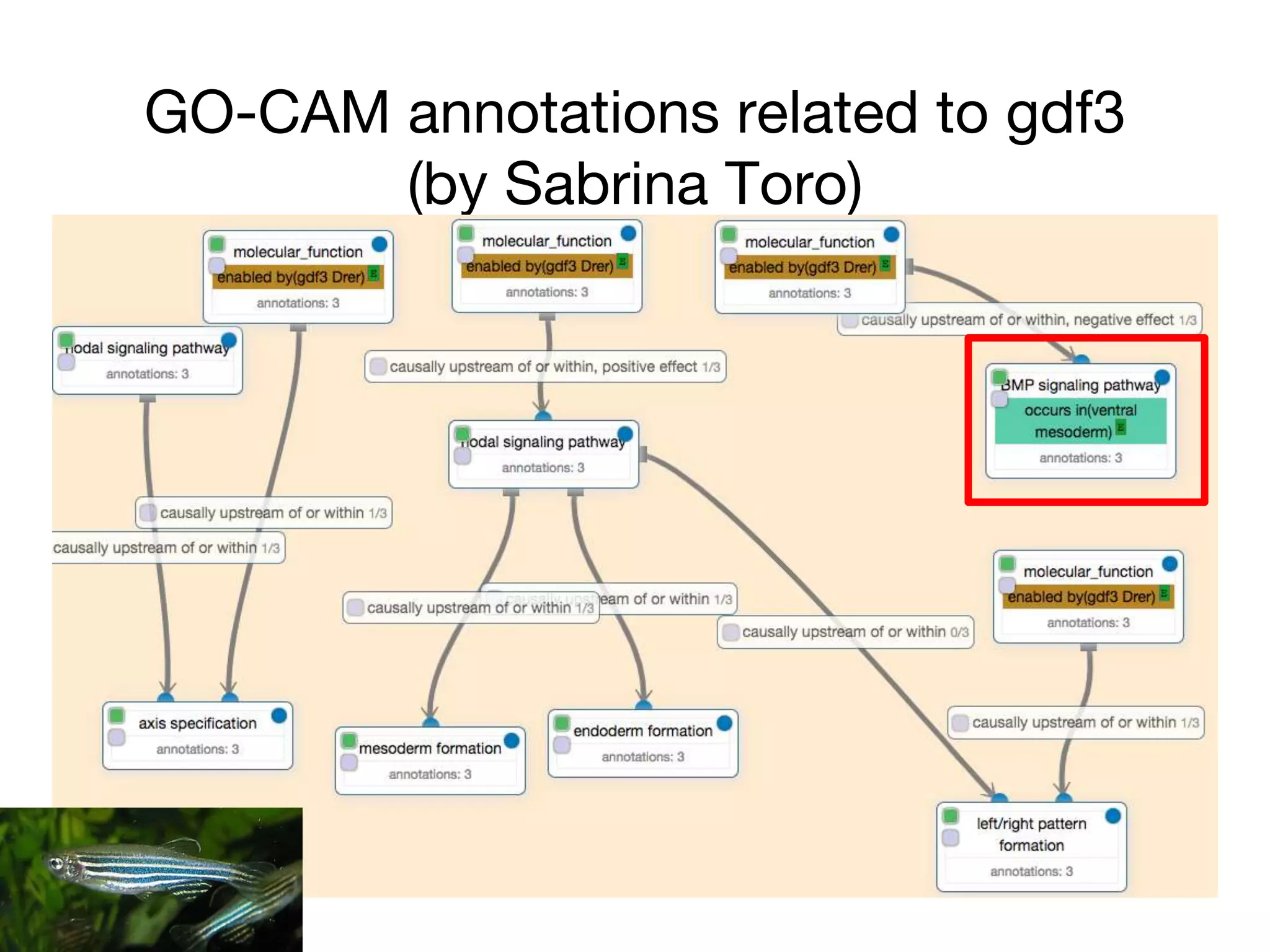
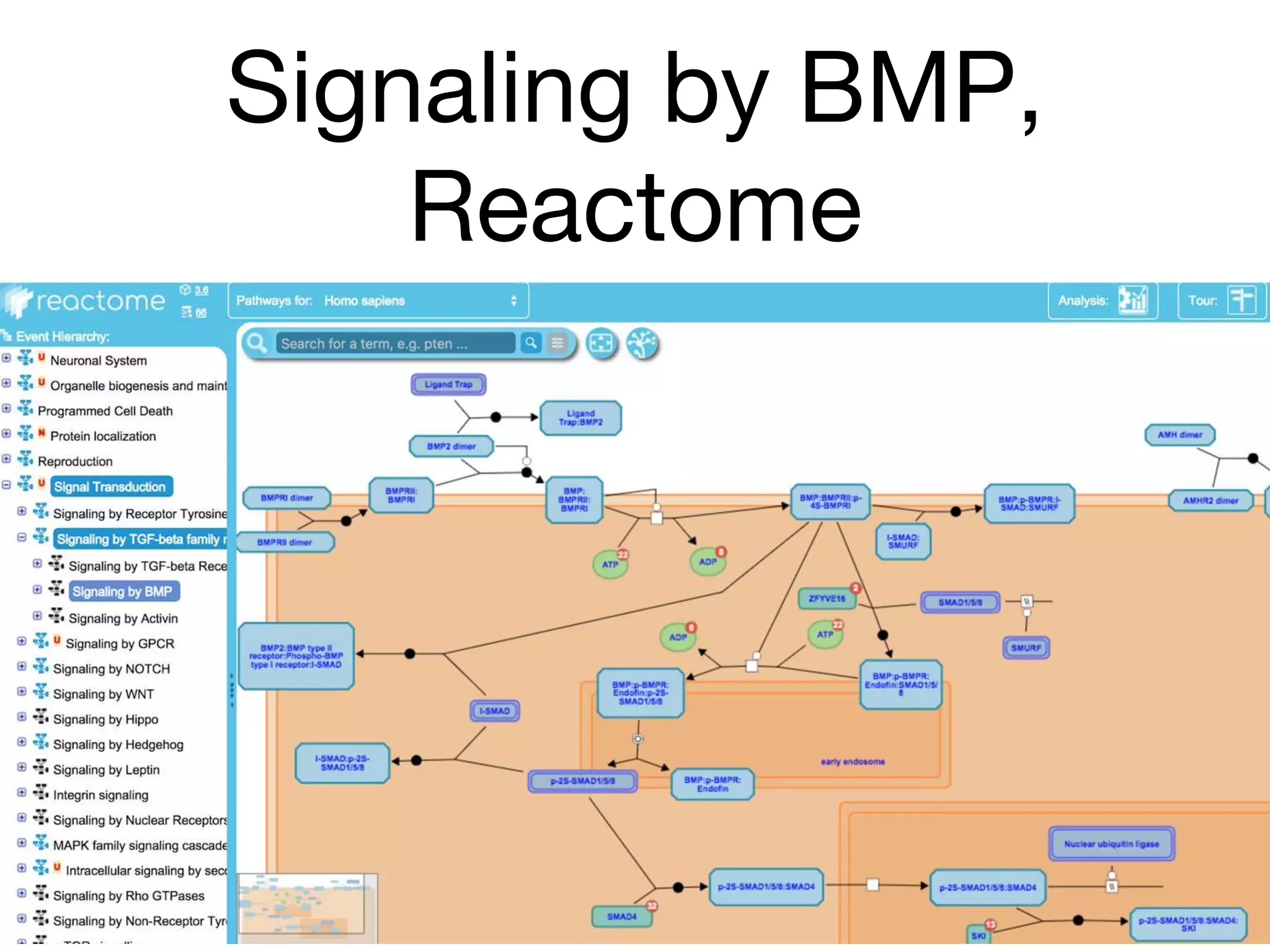
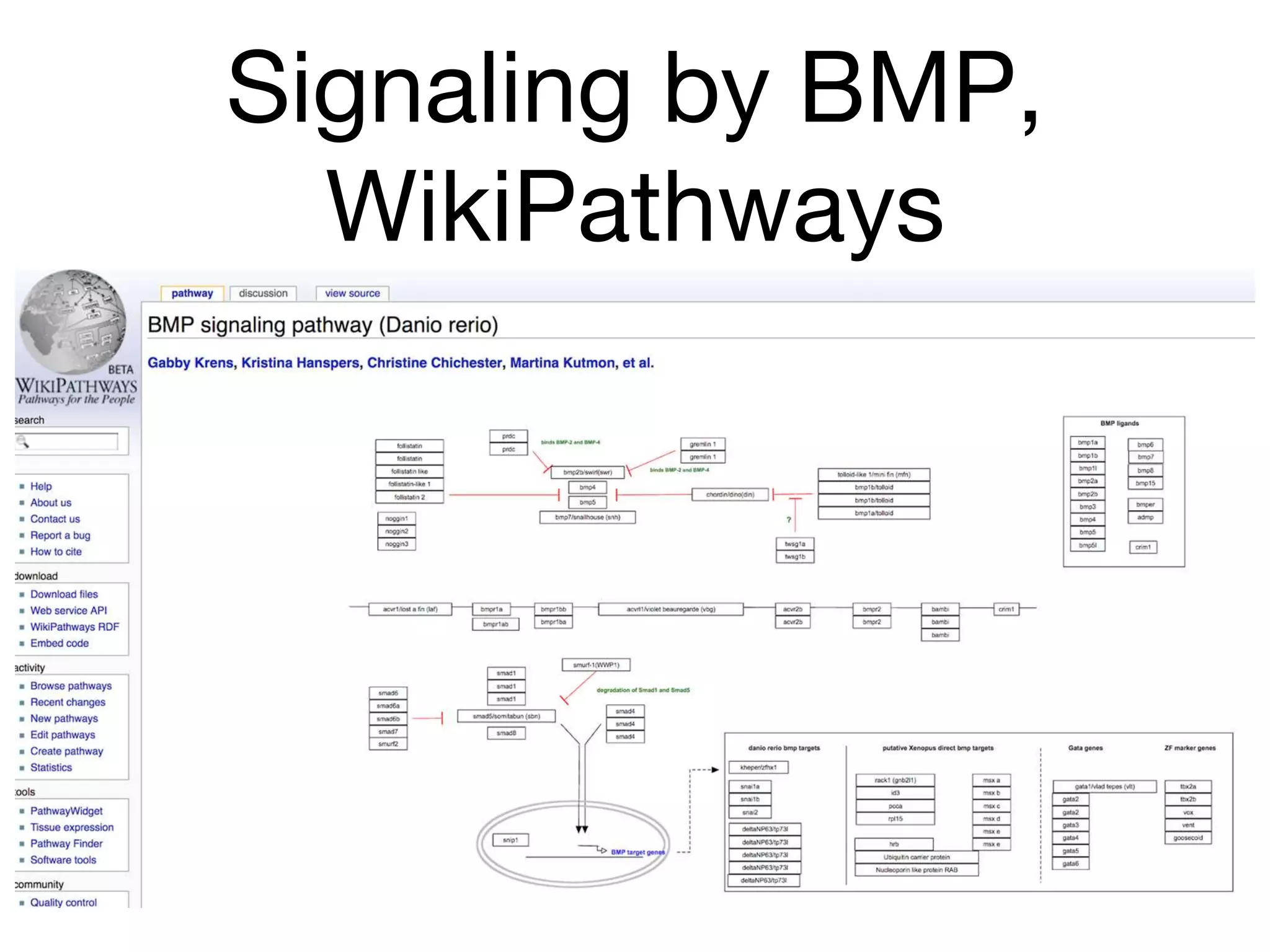
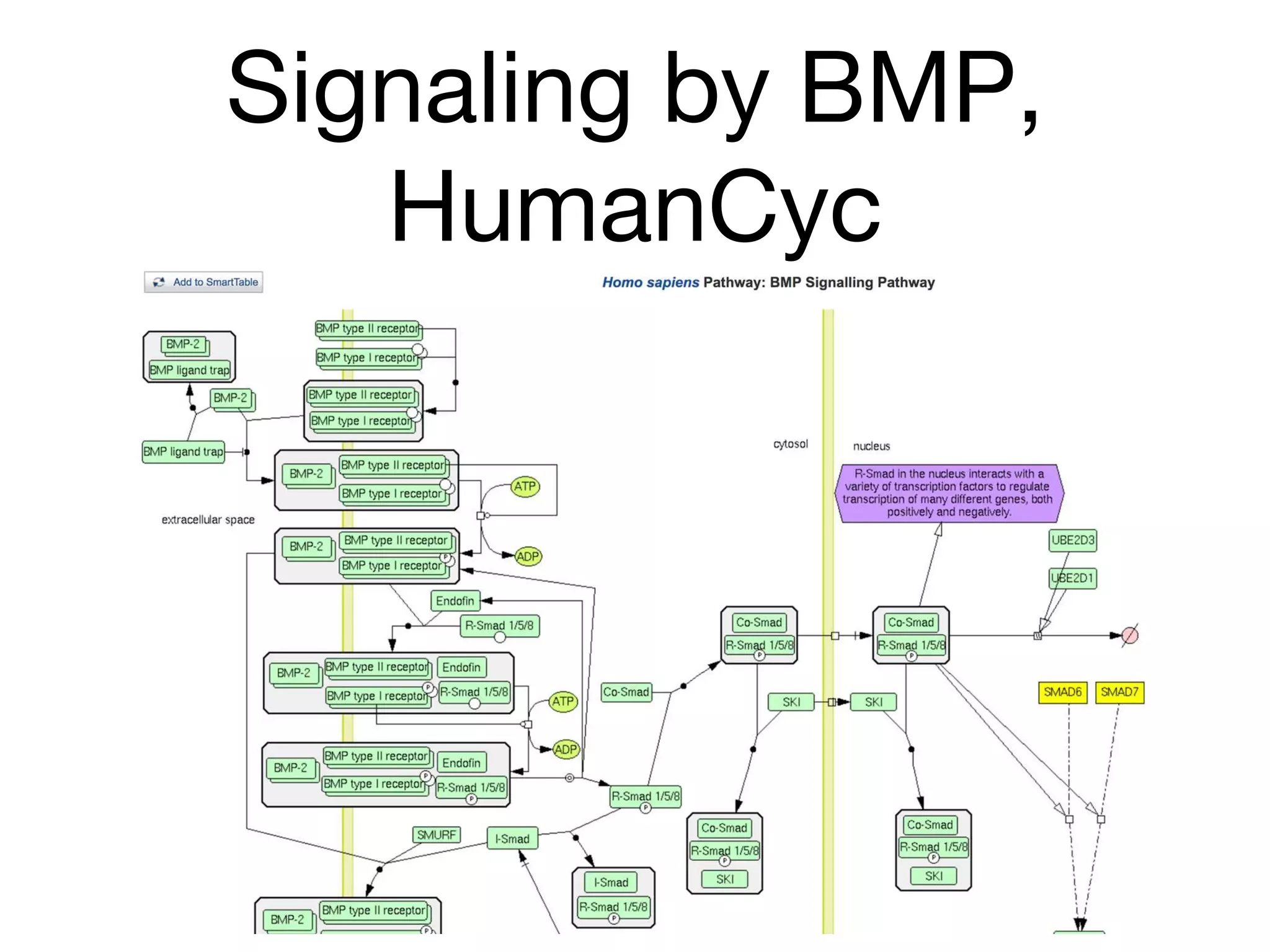
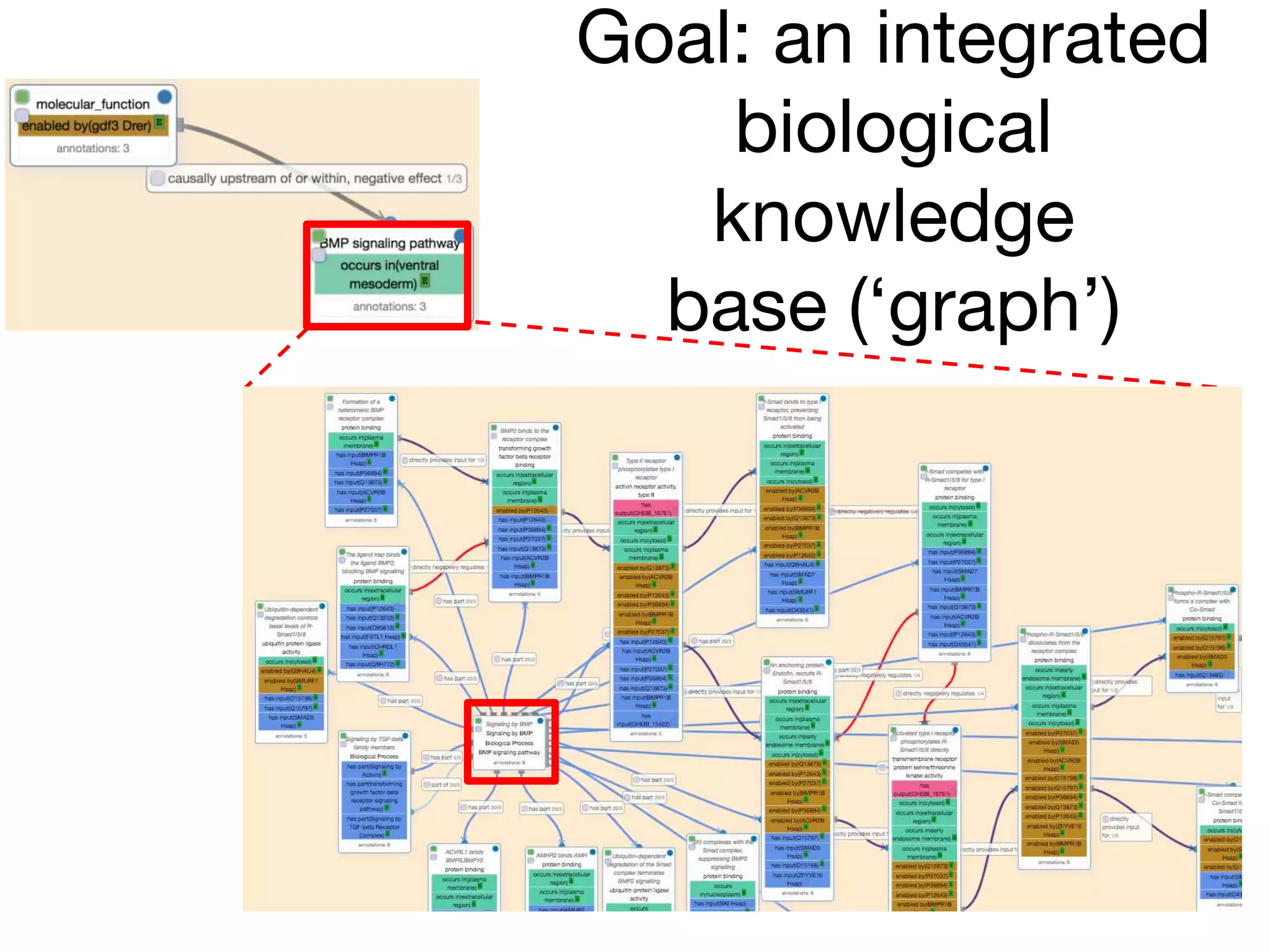
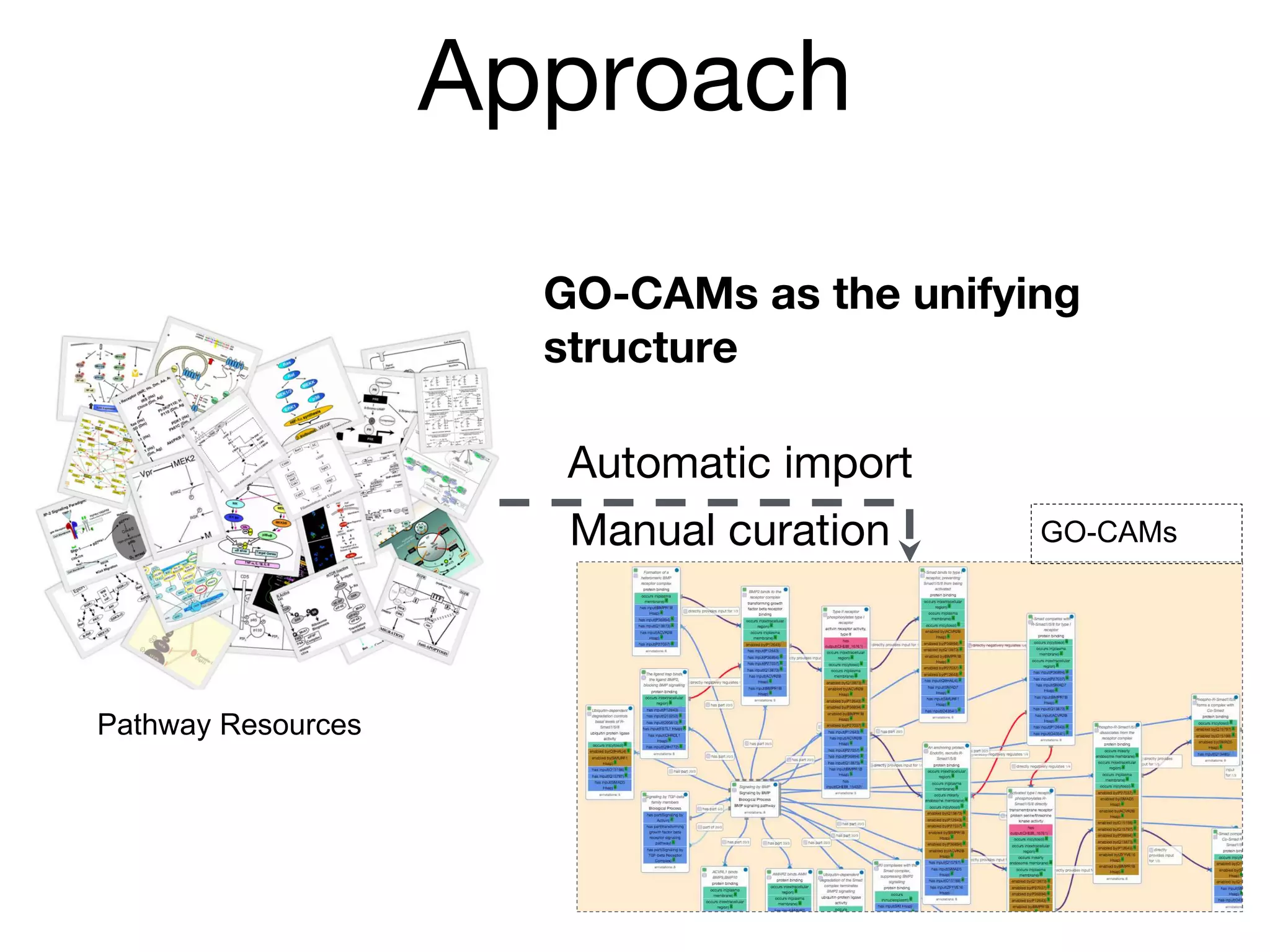
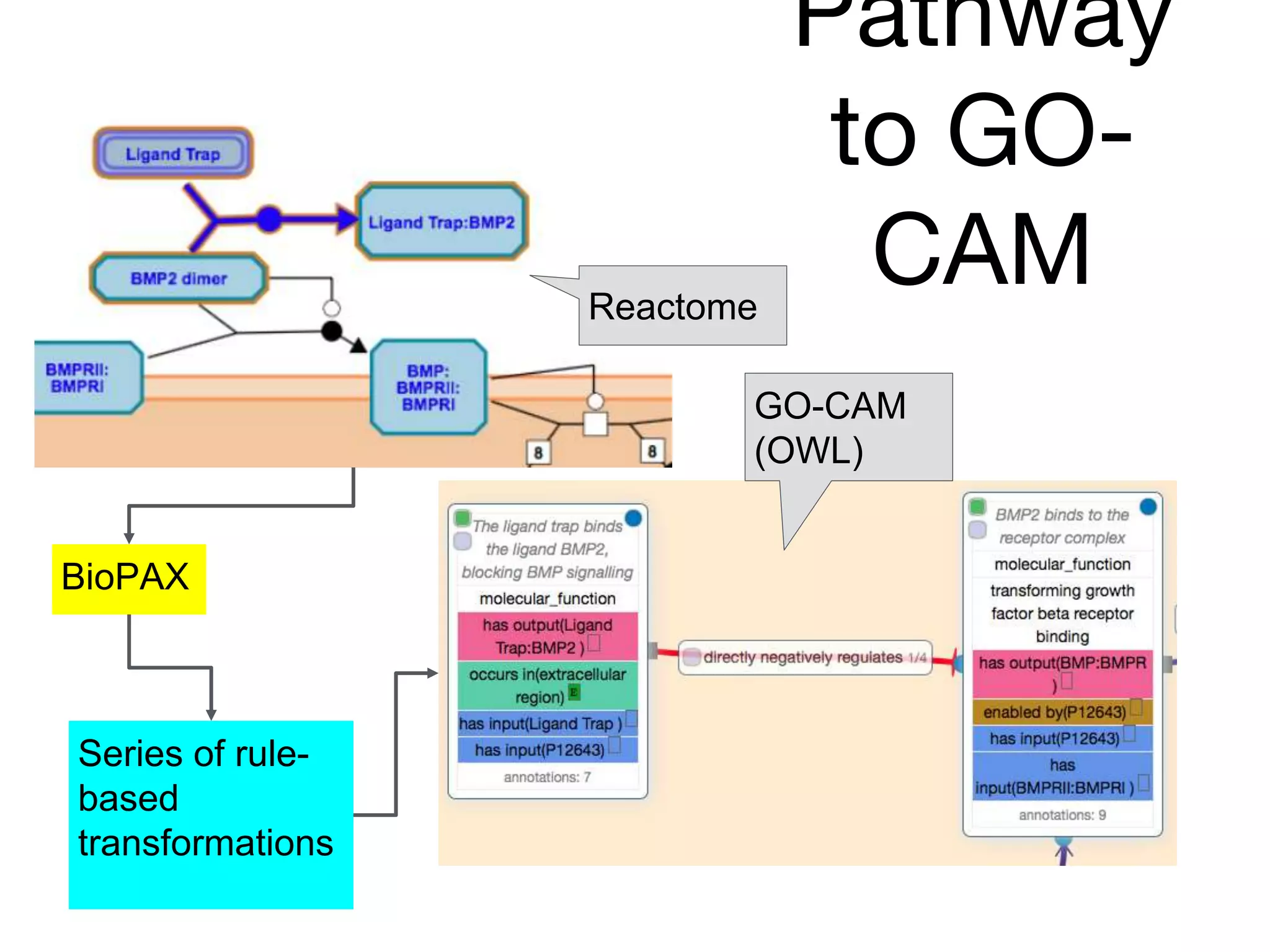
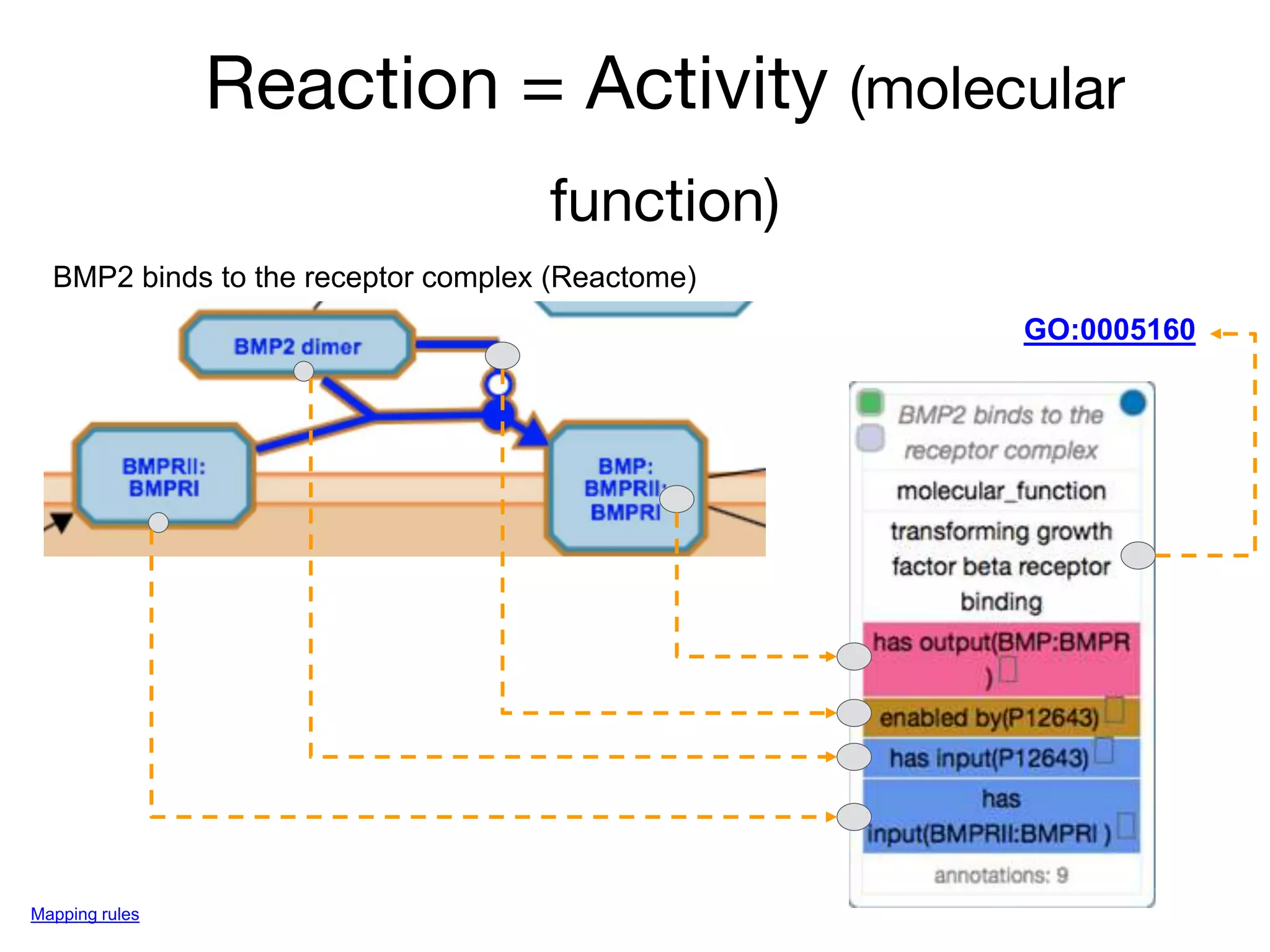
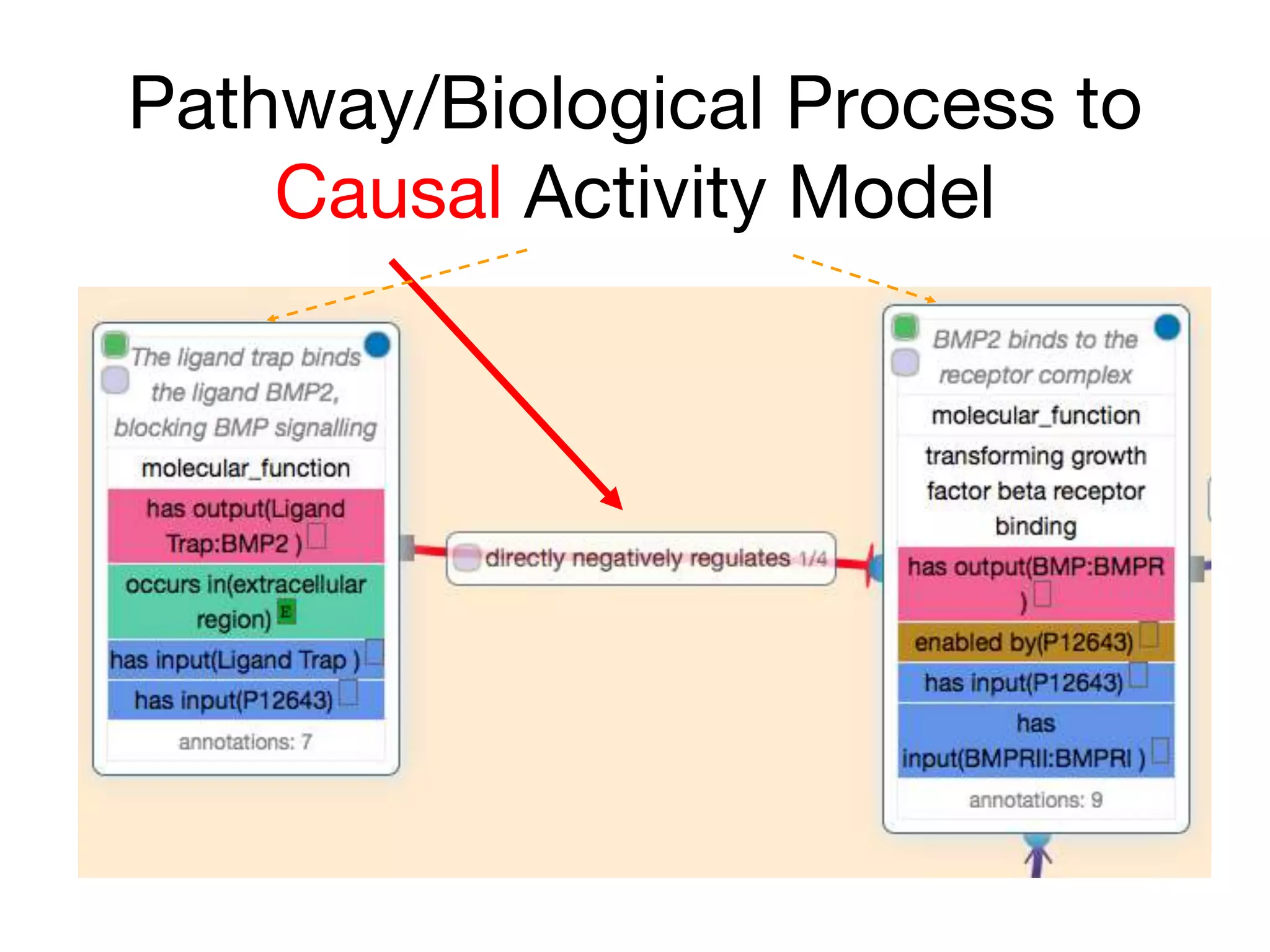
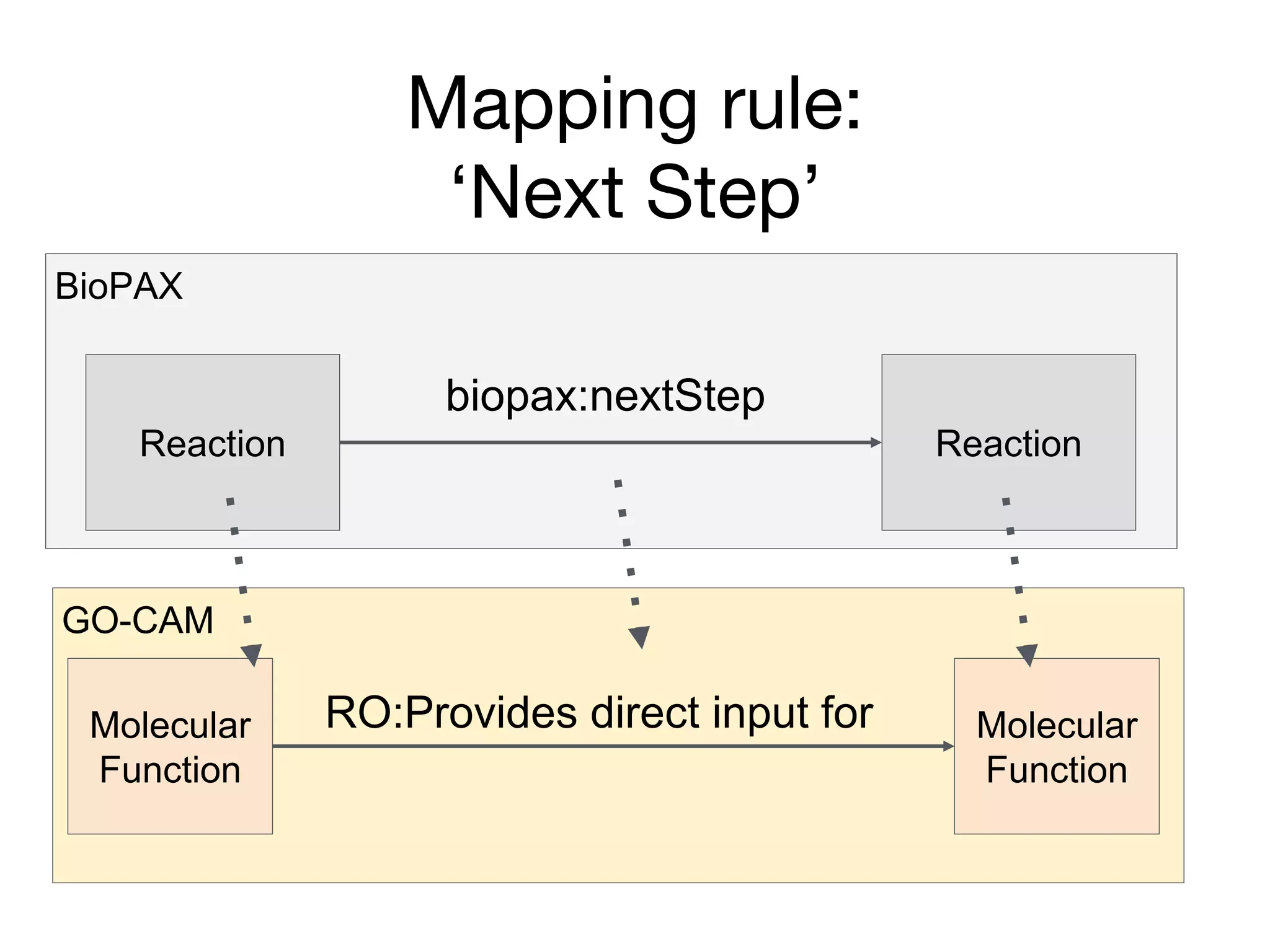
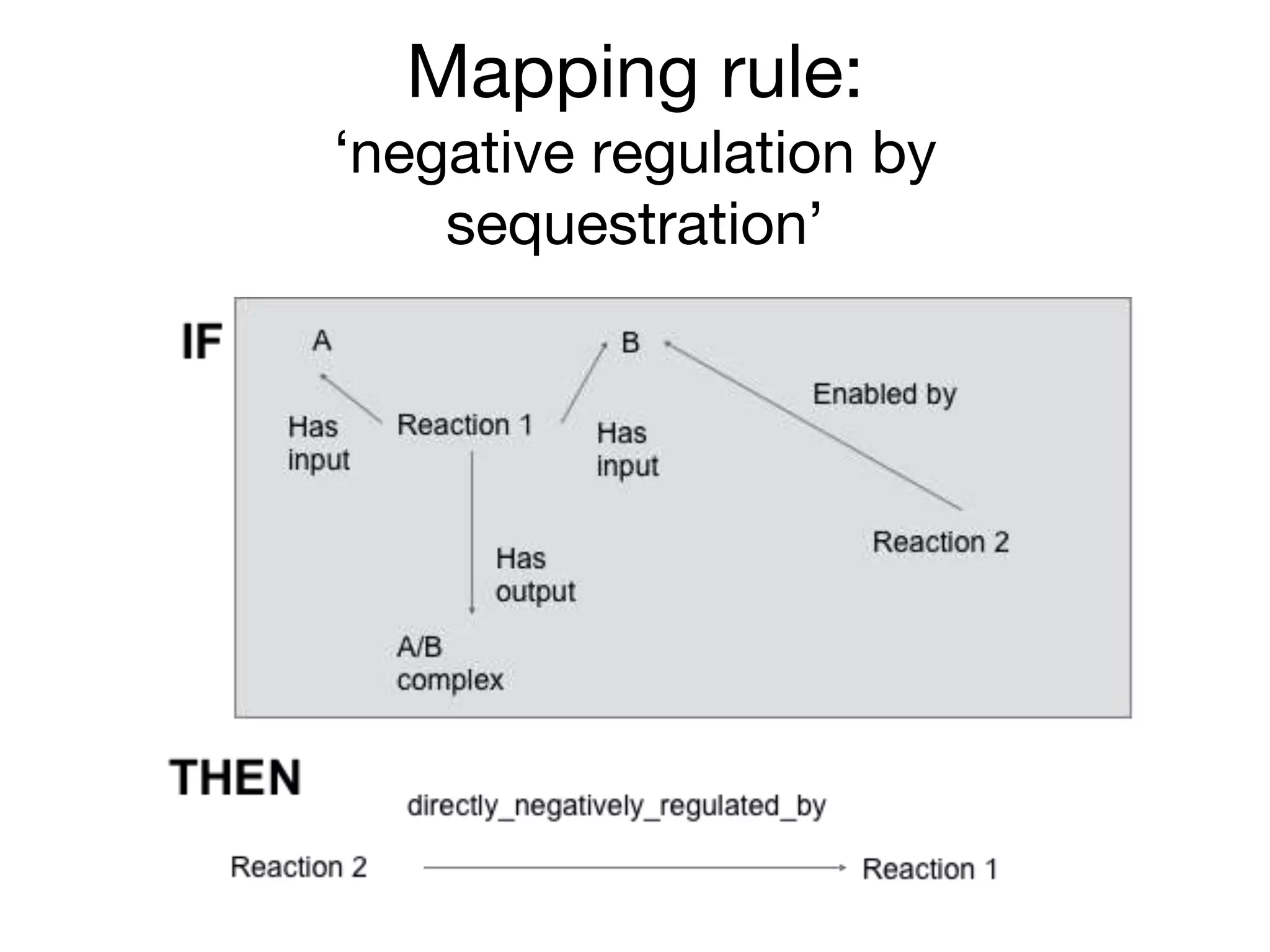
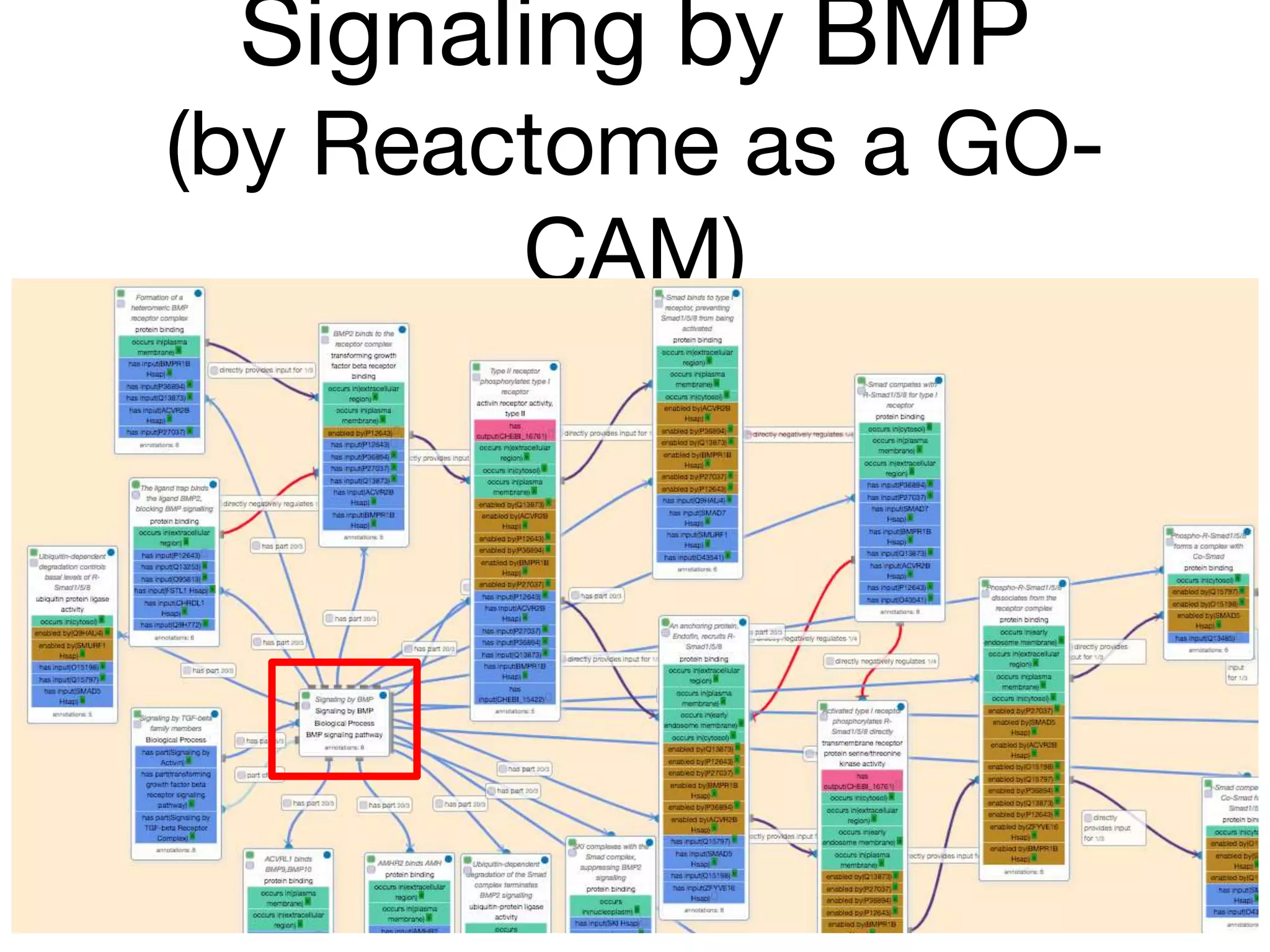
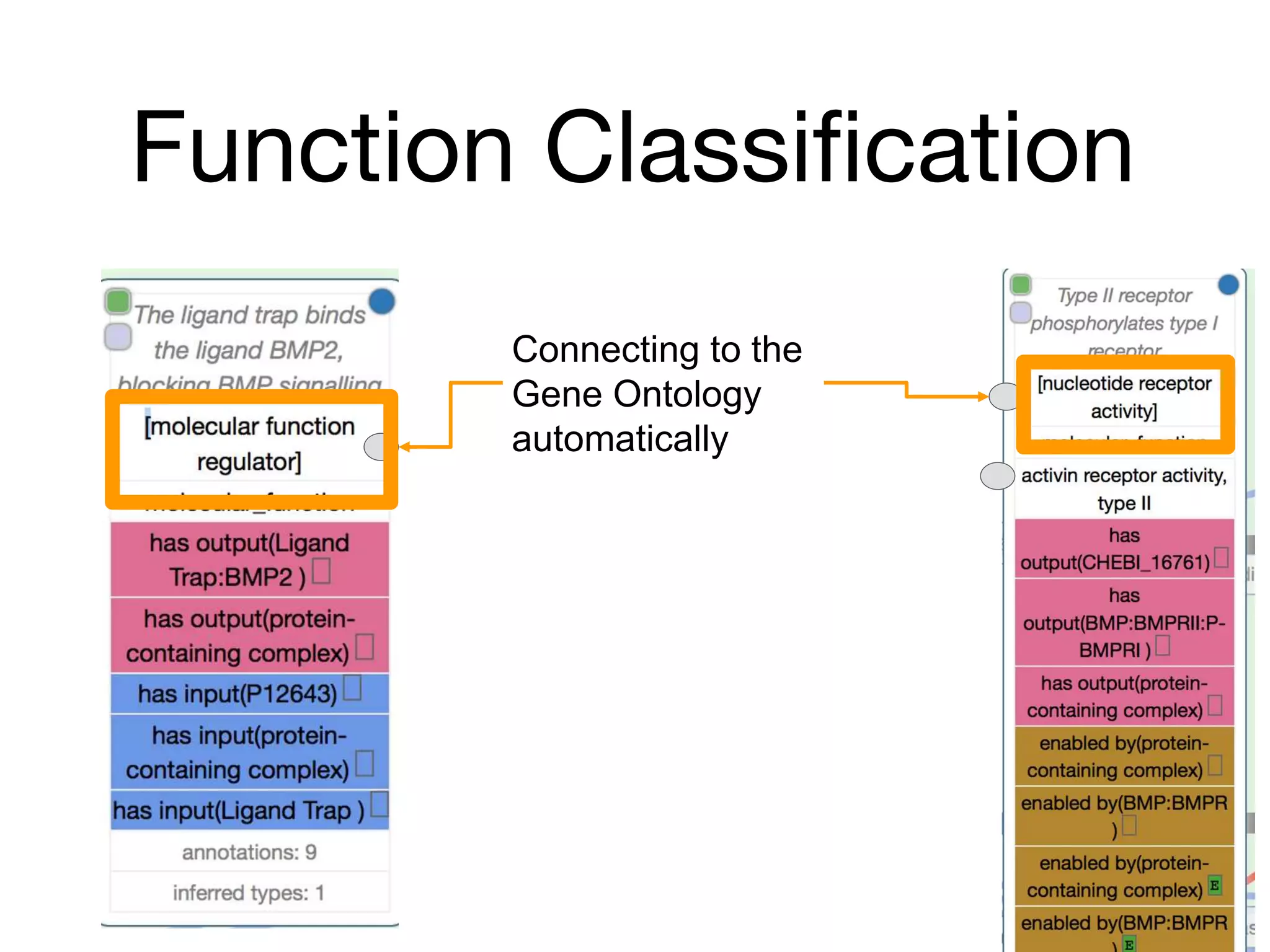
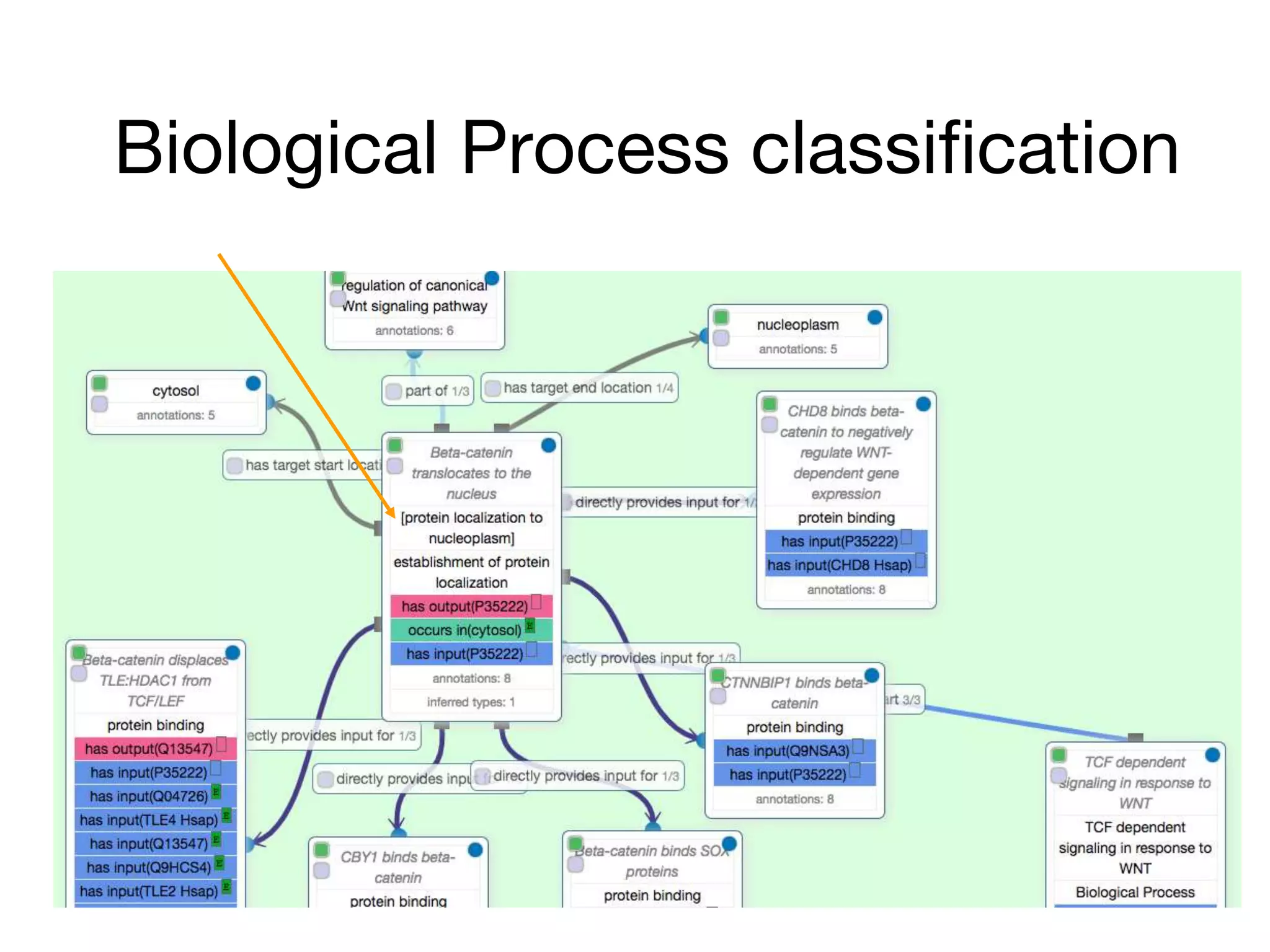
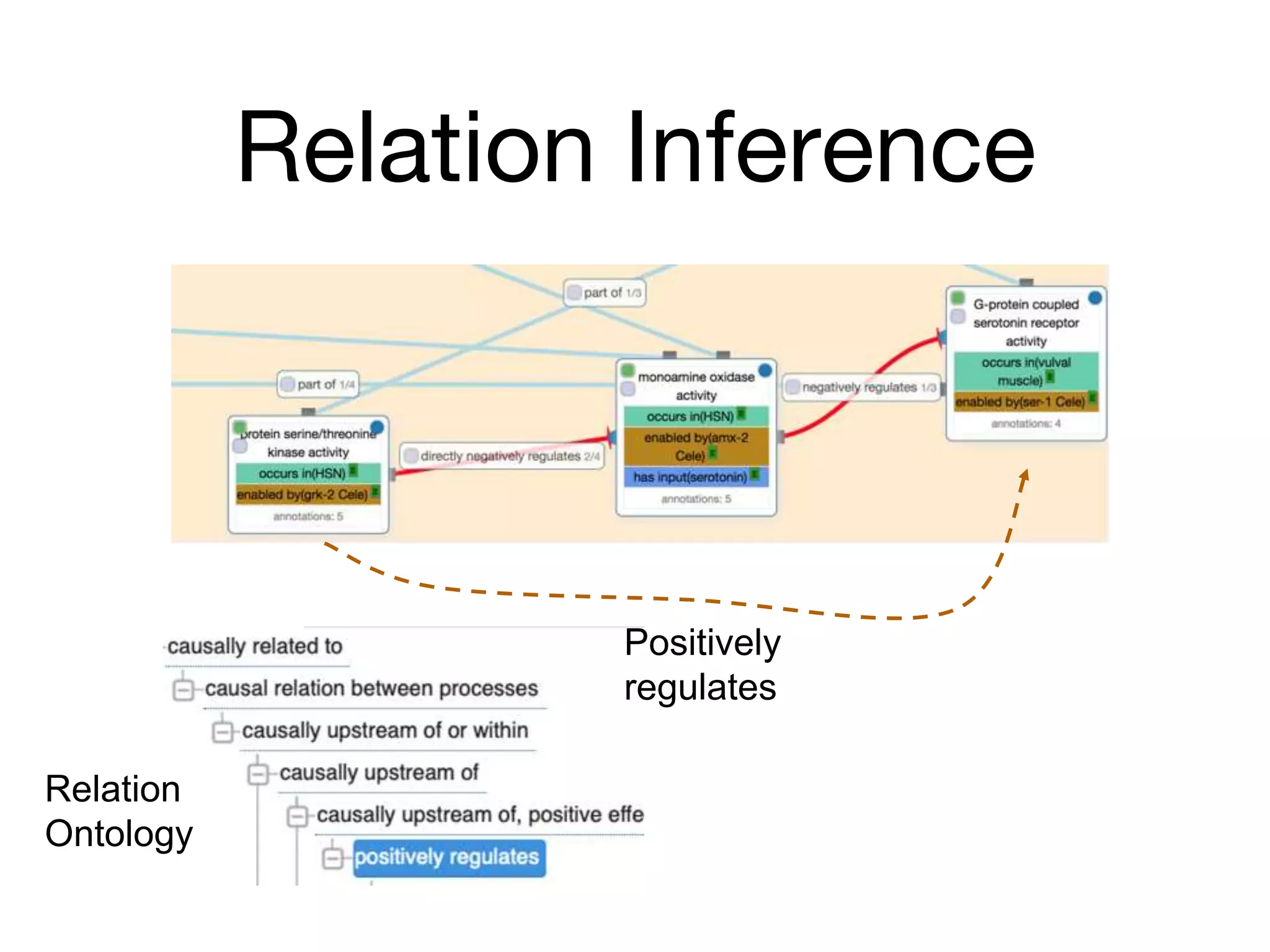
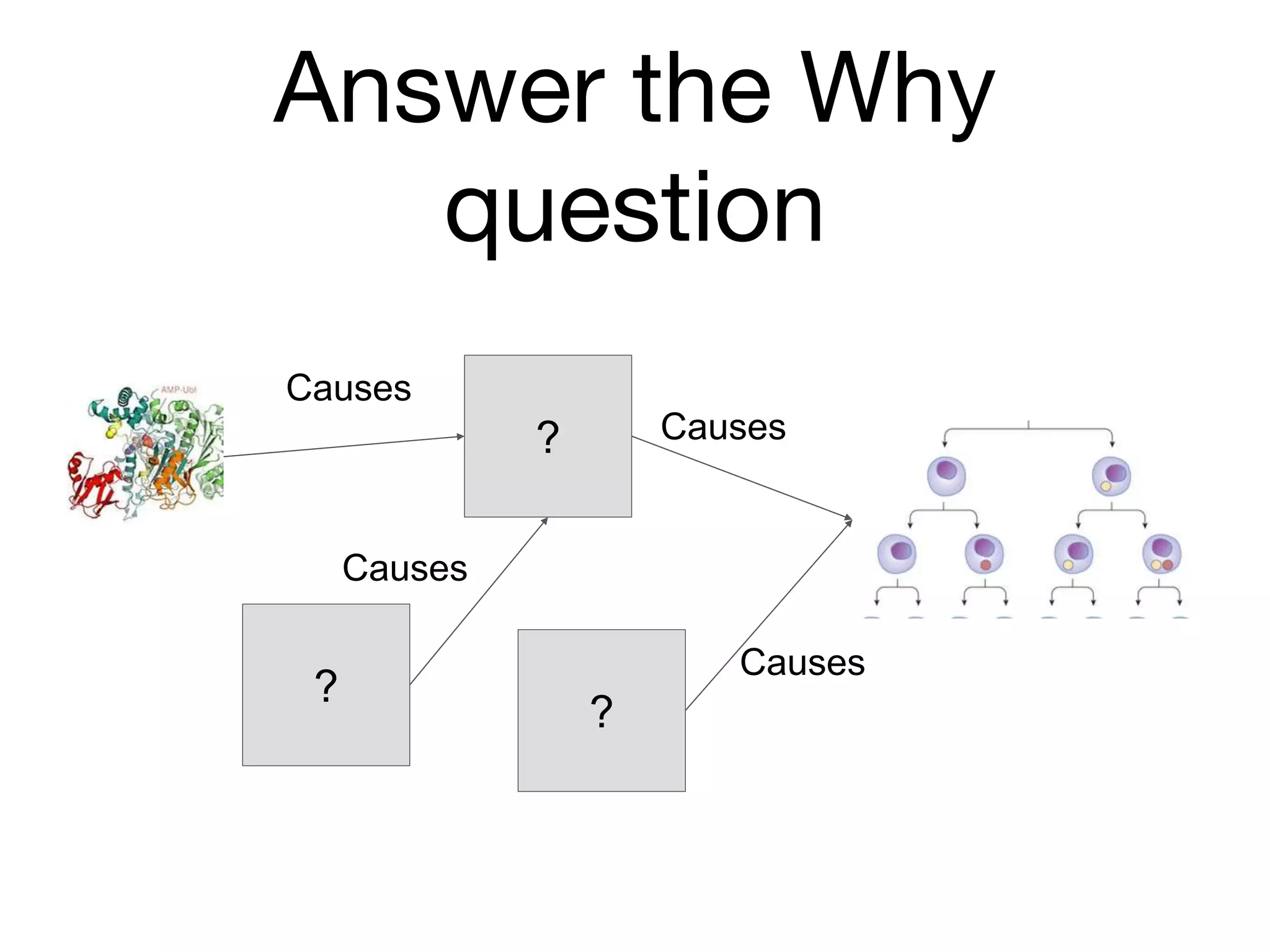
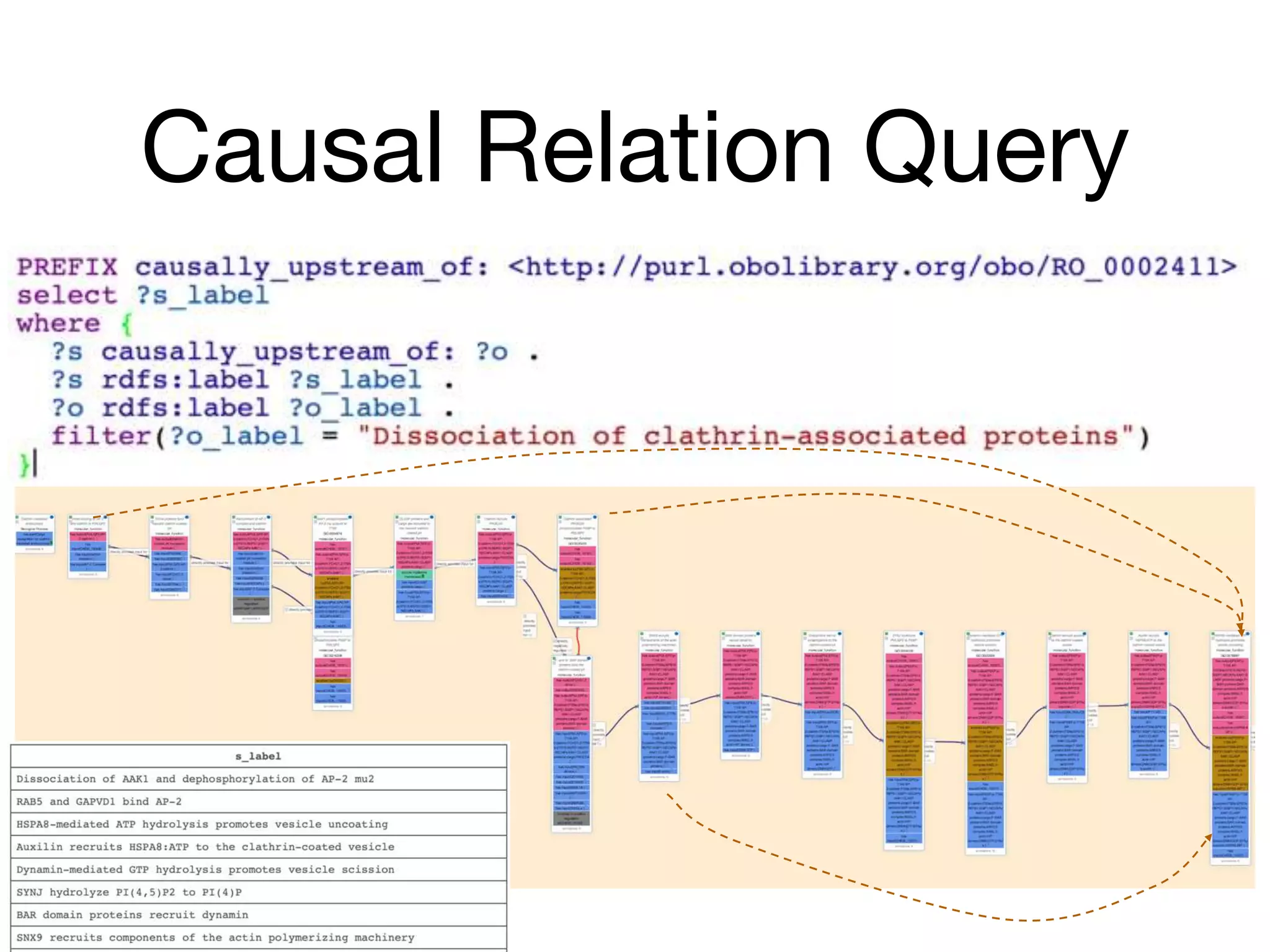
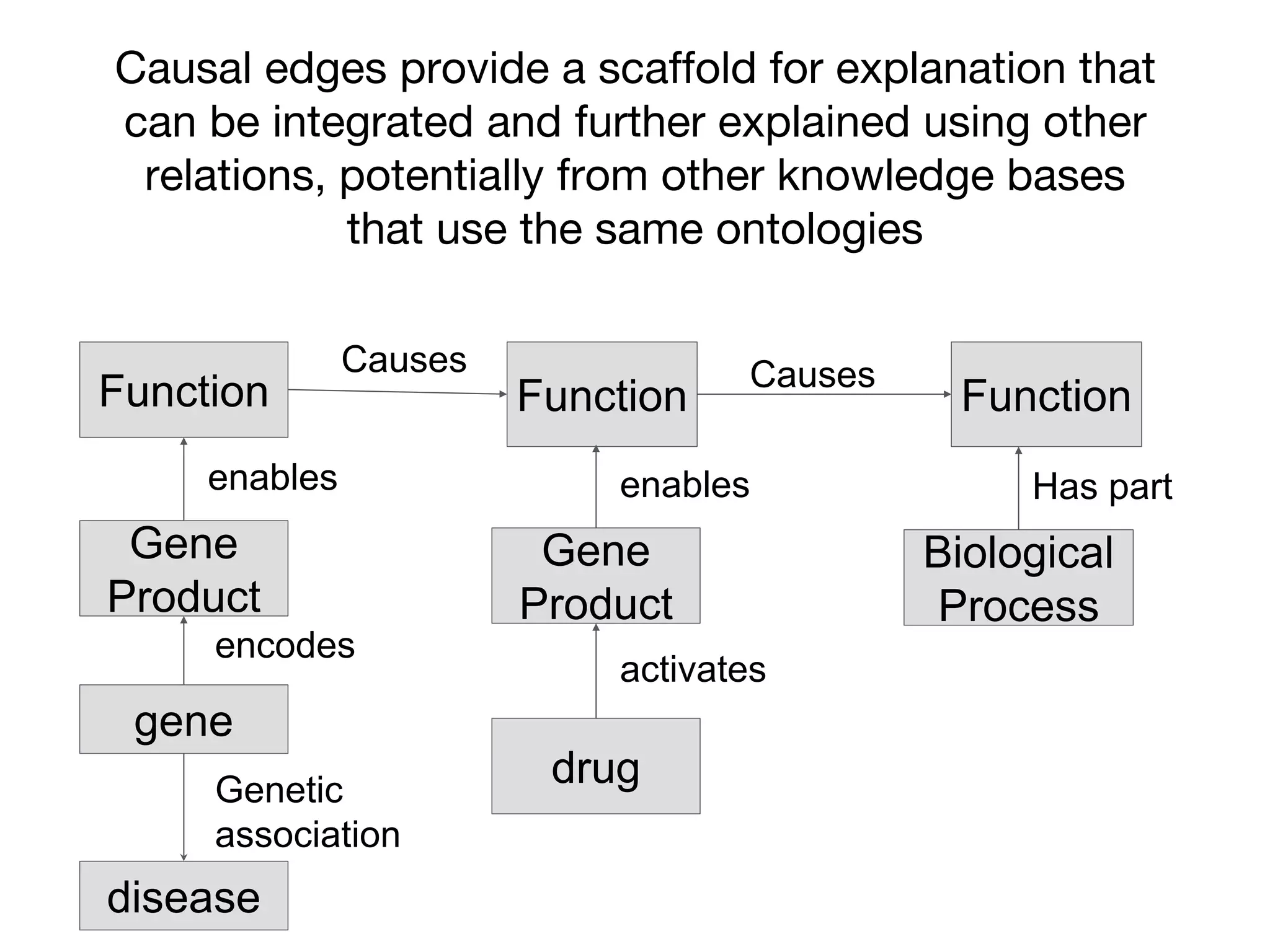
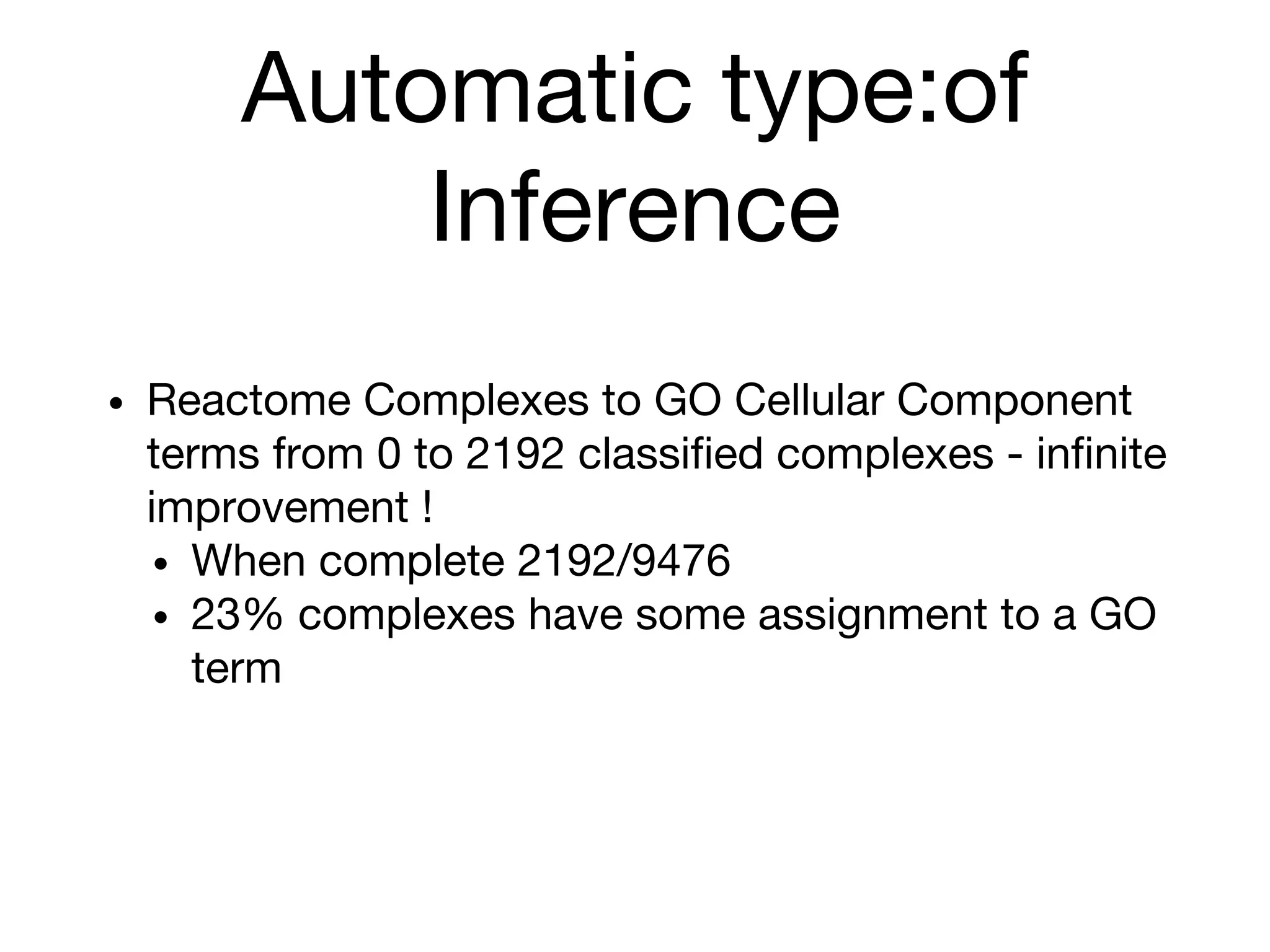
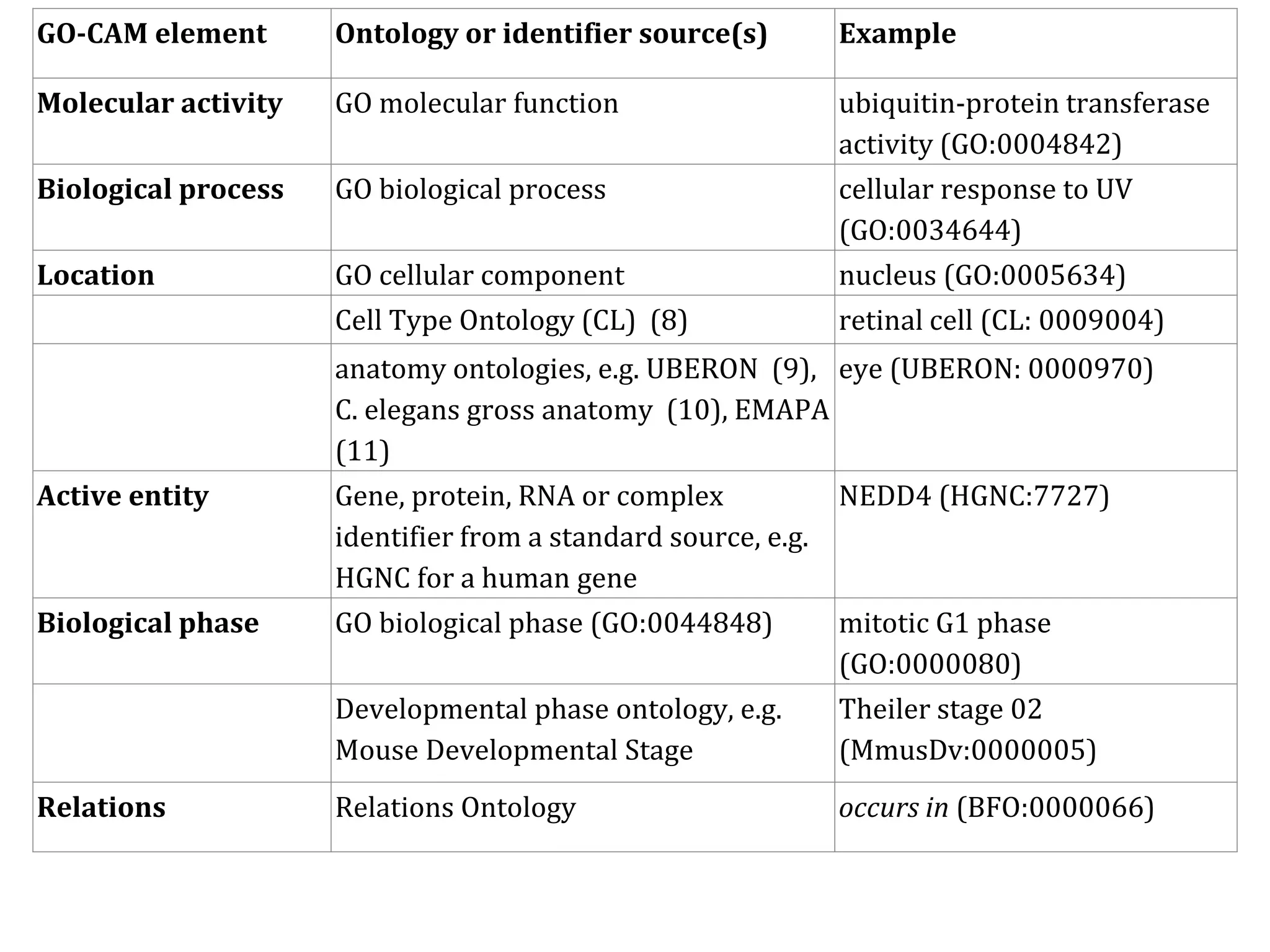
The document discusses the integration of pathway databases with Gene Ontology Causal Activity Models (GO-CAMs) to create a comprehensive computational model for biological systems. It highlights the challenges of managing the extensive Gene Ontology, which consists of over 45,000 terms, and how GO-CAMs can provide a structured approach to annotate gene functions and relationships in context. The presentation details current efforts to transition to GO-CAMs for improved biological knowledge representation and analysis.