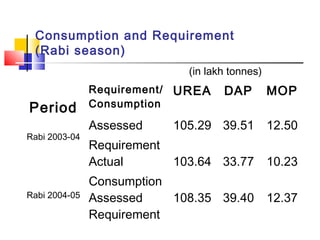
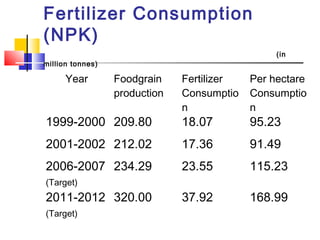
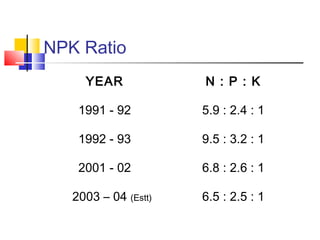
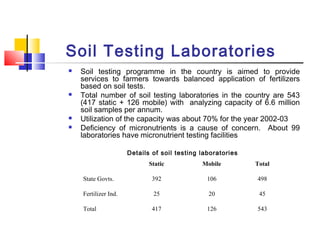
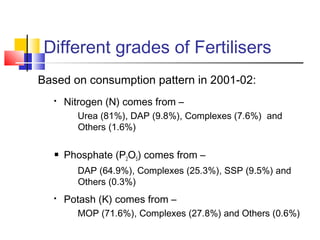
This document discusses integrated nutrient management in India. It provides statistics on fertilizer consumption from 1999-2000 to 2011-2012, showing consumption increasing from 18 million tonnes to a target of 37.92 million tonnes. It also compares India's per hectare fertilizer consumption to neighboring countries in 2001-2002, showing India's was lower than China, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Pakistan. The document outlines the components of integrated nutrient management and provides details on soil testing laboratories, fertilizer grades, fortified fertilizers, biofertilizers production, and the national project on organic farming.