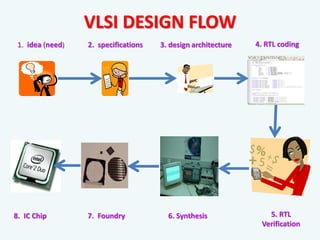
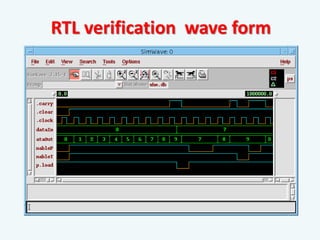
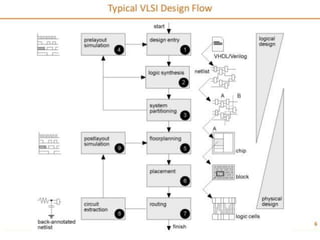
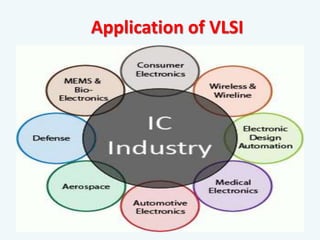
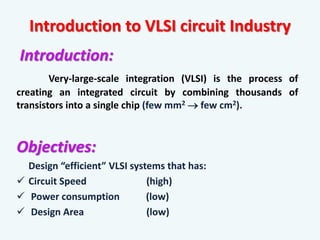
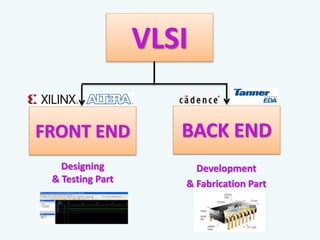
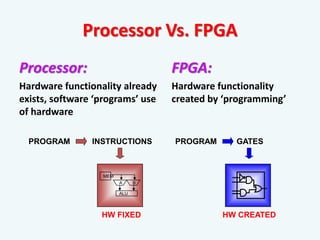
The document discusses the evolution of integrated circuits and their impact on technology, highlighting the transition from discrete components to very-large-scale integration (VLSI). It outlines the VLSI design flow, including idea generation, specifications, design architecture, RTL coding, verification, synthesis, and fabrication, along with tools used in the process. The document also compares ASICs and FPGAs in terms of design time, cost, and flexibility.




![FPGA Vs. ASIC
Category FPGA ASIC
Design time / Time to Market + -
Design Cost + -
Performance [Speed, Power, Density] - +
Size [Area] - +
Total Cost + +
Changes to design + -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nlv-240509080807-a8018a1d/85/Integrated-Circuits-introduction-and-fpga-10-320.jpg)