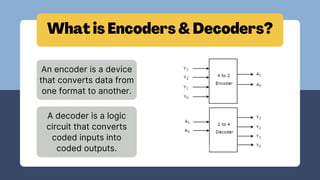
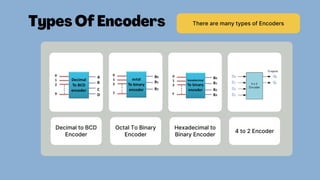
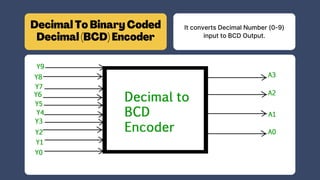
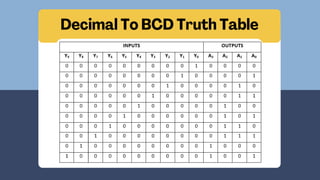
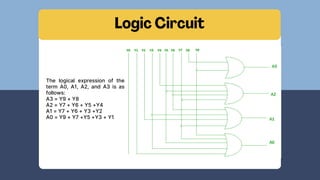
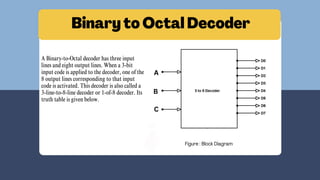
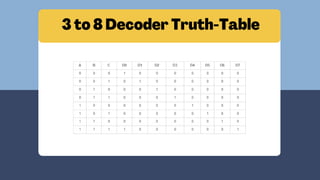
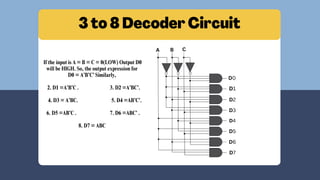
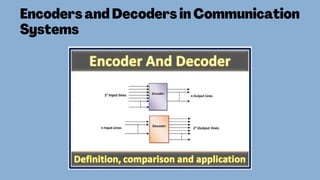
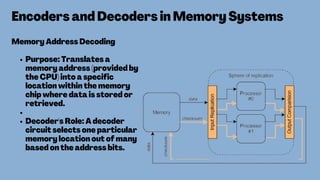
The document discusses the roles and significance of encoders and decoders in digital electronics. Encoders convert data from one format to another, while decoders translate coded inputs into outputs, playing crucial roles in memory address decoding and communication systems. It also highlights advancements in encoding and decoding technologies, such as error correction and data compression.