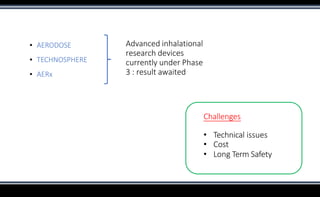
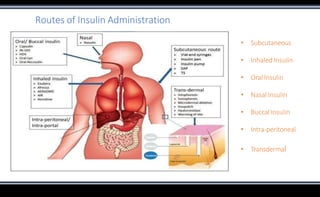
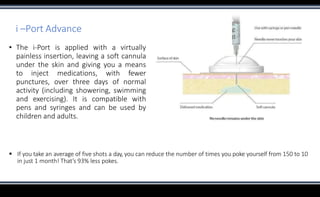
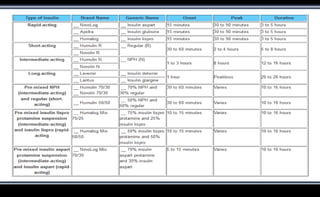
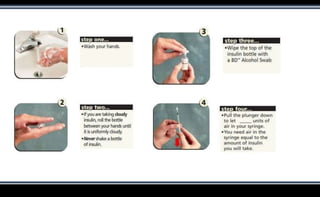
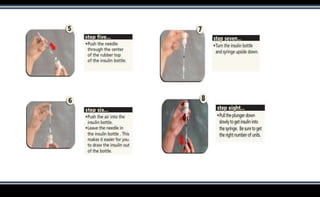
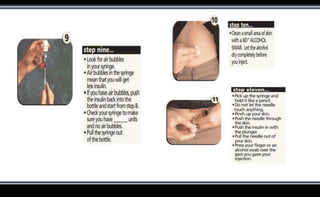
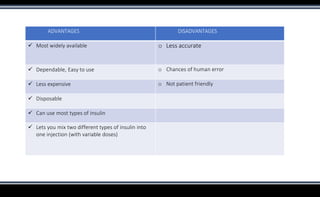
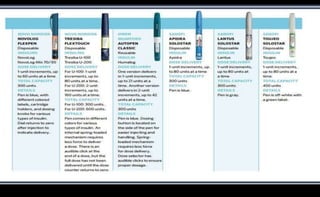
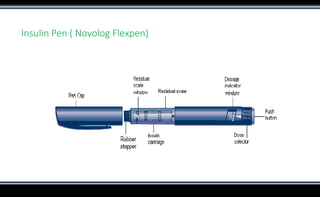
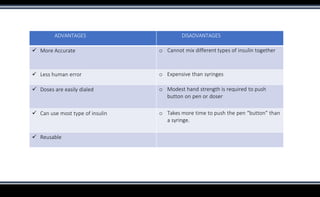
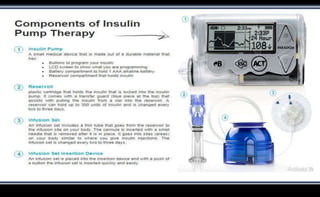
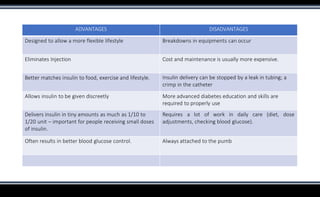
This document discusses various methods of insulin delivery including subcutaneous, inhaled, oral, nasal, buccal, intra-peritoneal, and transdermal routes. Subcutaneous delivery via insulin pens and pumps is currently the standard method but is associated with pain and non-compliance. Newer devices like the i-Port aim to reduce injections. Inhaled insulins like Afrezza offer non-invasive delivery but have limitations. Future areas of research include oral/buccal insulin, islet cell and stem cell transplantation, and gene therapy to better regulate insulin levels.




















![CONTRAINDICATIONS
AFREZZA is contraindicated in patients:
▪ During episodes of hypoglycemia.
▪ With chronic lung disease (such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
[(COPD)] because of the risk of acute bronchospasm.
▪ With hypersensitivity to regular human insulin or any of the AFREZZA excipients.
SIDE EFFECTS
• Hypoglycemia (sweating, confusion, headache, blurred vision, slurred speech etc)
• Decreased Lung function
• Severe allergic reactions
• Hypokalemia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/insulindeliverymethods-230528105227-70cdfb53/85/INSULIN-DELIVERY-METHODS-pptx-33-320.jpg)