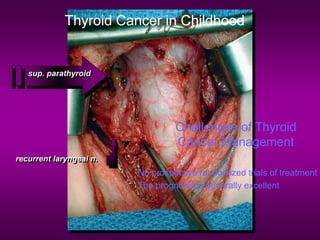
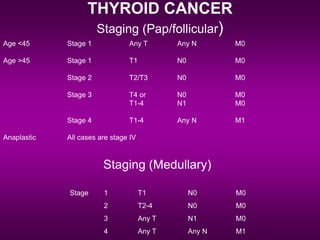
1) Thyroid cancer in children has distinct characteristics compared to adults, with papillary carcinoma being much more common and follicular carcinoma rarer. Children also often present with more advanced disease.
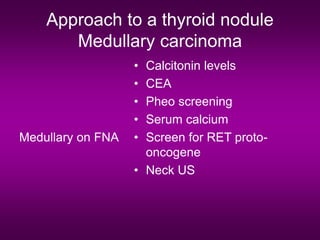
2) Fine needle aspiration is important for diagnosis, but distinguishing benign from malignant follicular lesions can be difficult.
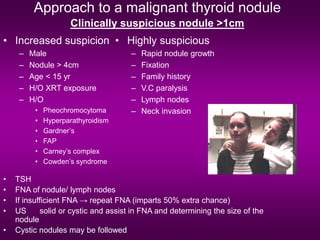
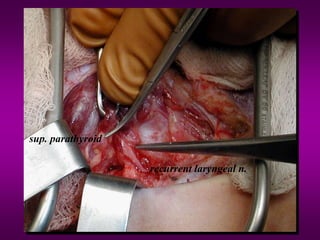
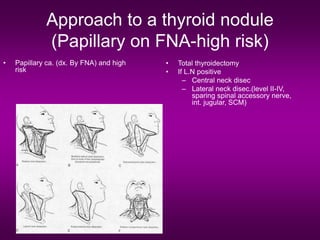
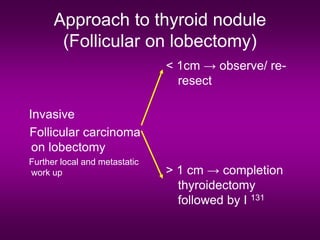
3) Treatment involves surgery, with total thyroidectomy recommended for high-risk cases and lobectomy sometimes sufficient for low-risk papillary carcinoma under 1cm.
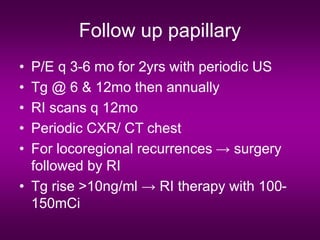
4) Outcomes are generally excellent even with metastases, though management challenges exist due to lack of prospective trials. Careful long-term follow-up is important.








![Thyroid nodules
• By far most thyroid nodules are benign
and are either colloid nodules,
adenomas or manifestations of
thyroiditis
• They may be cystic or solid
• Most cystic are generally benign
(degenerated colloid)
• They may be toxic or non toxic
Thyroid Cancer
Pediatric vs. Adult
• Thyroid masses more likely to be cancer
– 50% of solitary nodules are malignant
– More often larger, multicentric
• Higher rate of metastasis at diagnosis
– regional lymph nodes: 65% (35% adult [papillary])
– distant: 20% (10% adult [follicular])
• Higher rate of recurrence
– 40% <20y (also >60y); 20% adults
– 80% locoregional, 20% distant (similar)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10-230823081404-1319e109/85/thyroid-cancer-10-320.jpg)