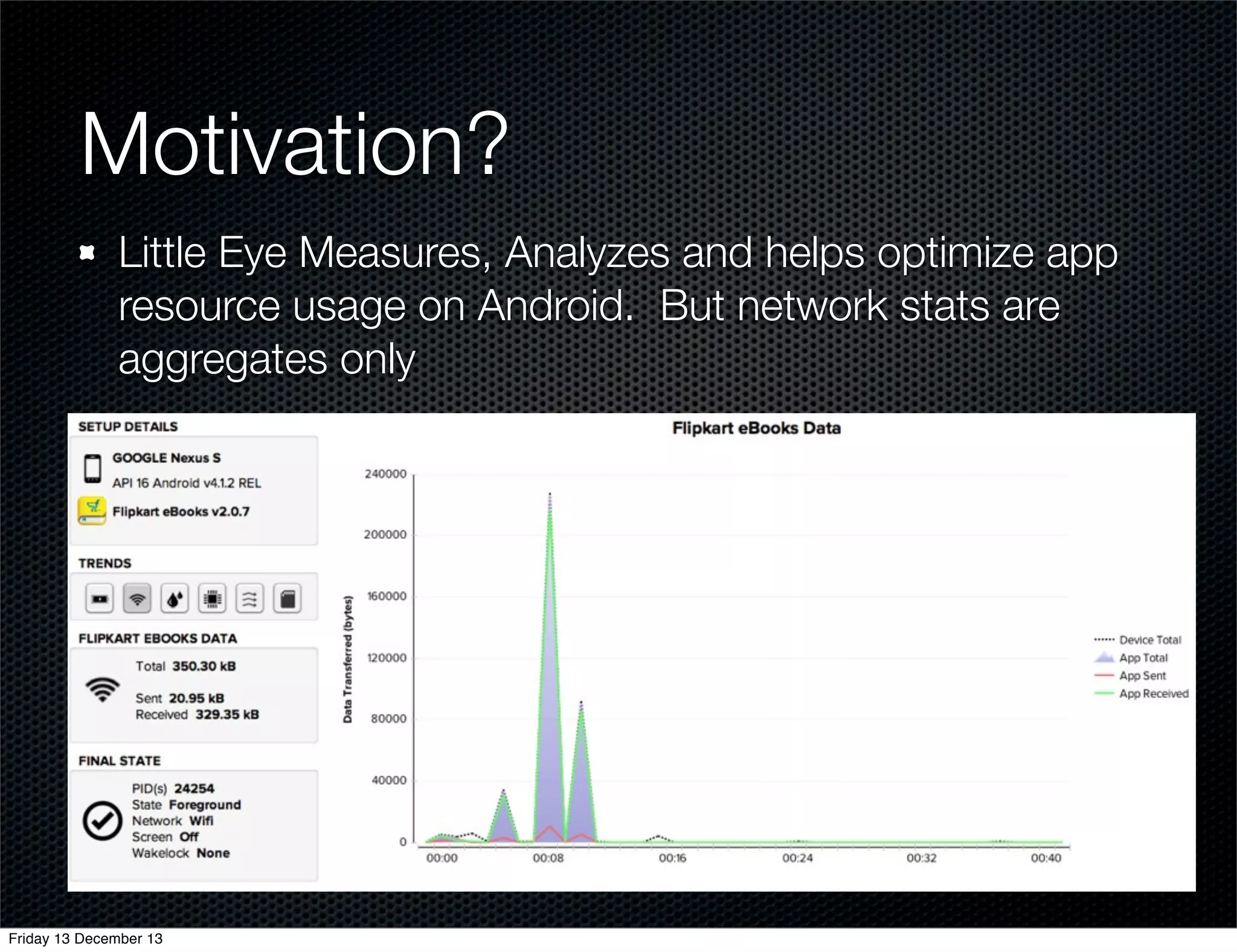
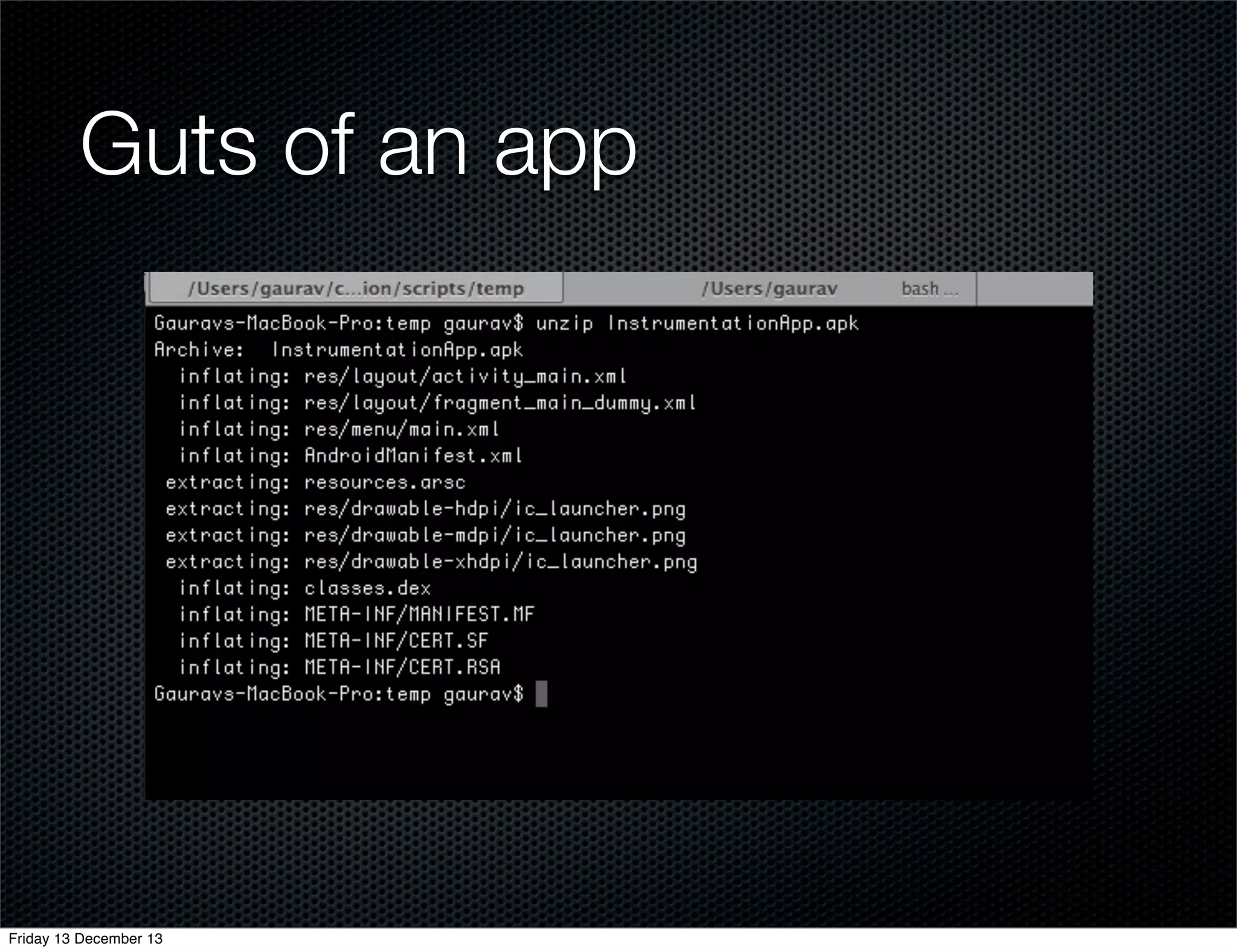
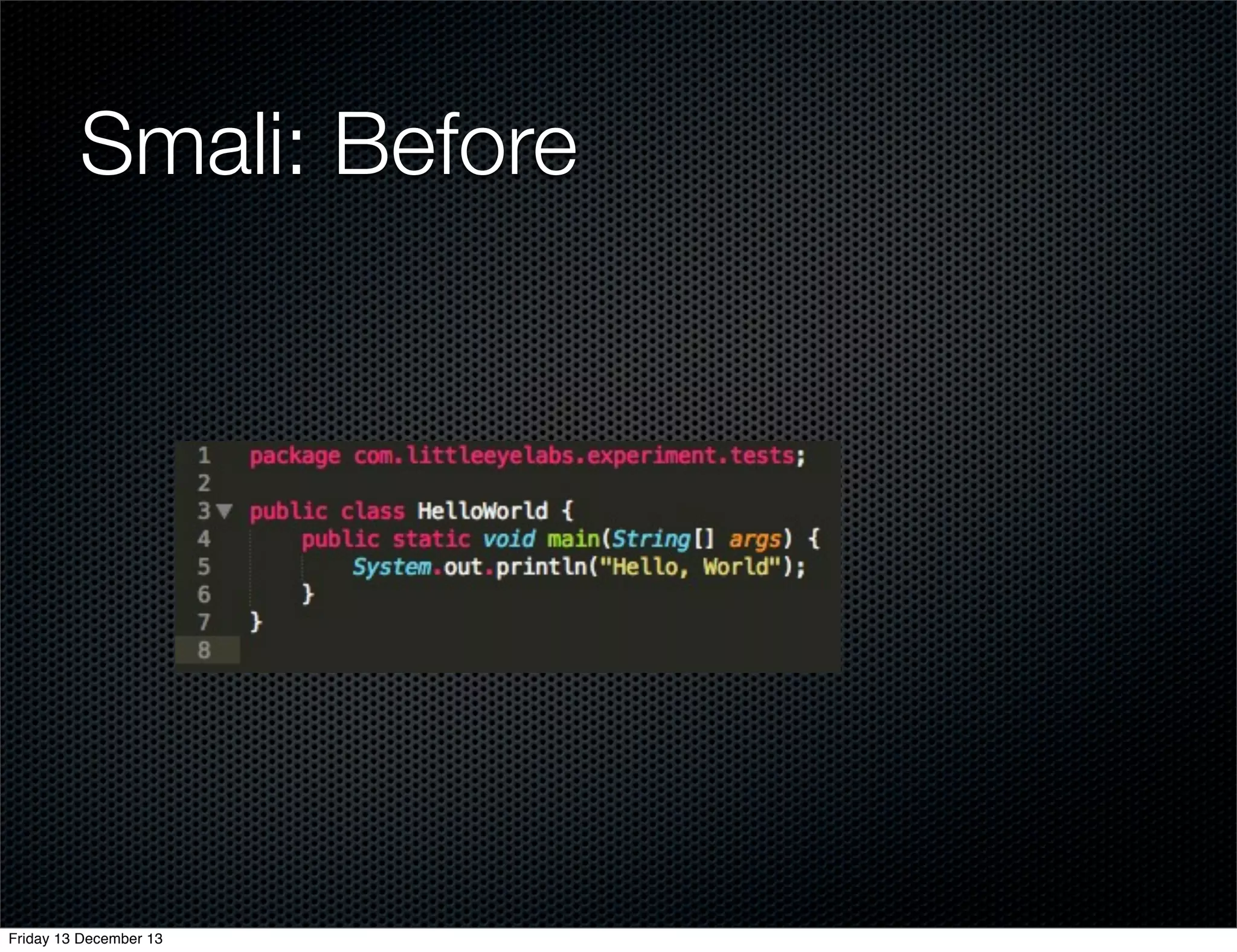
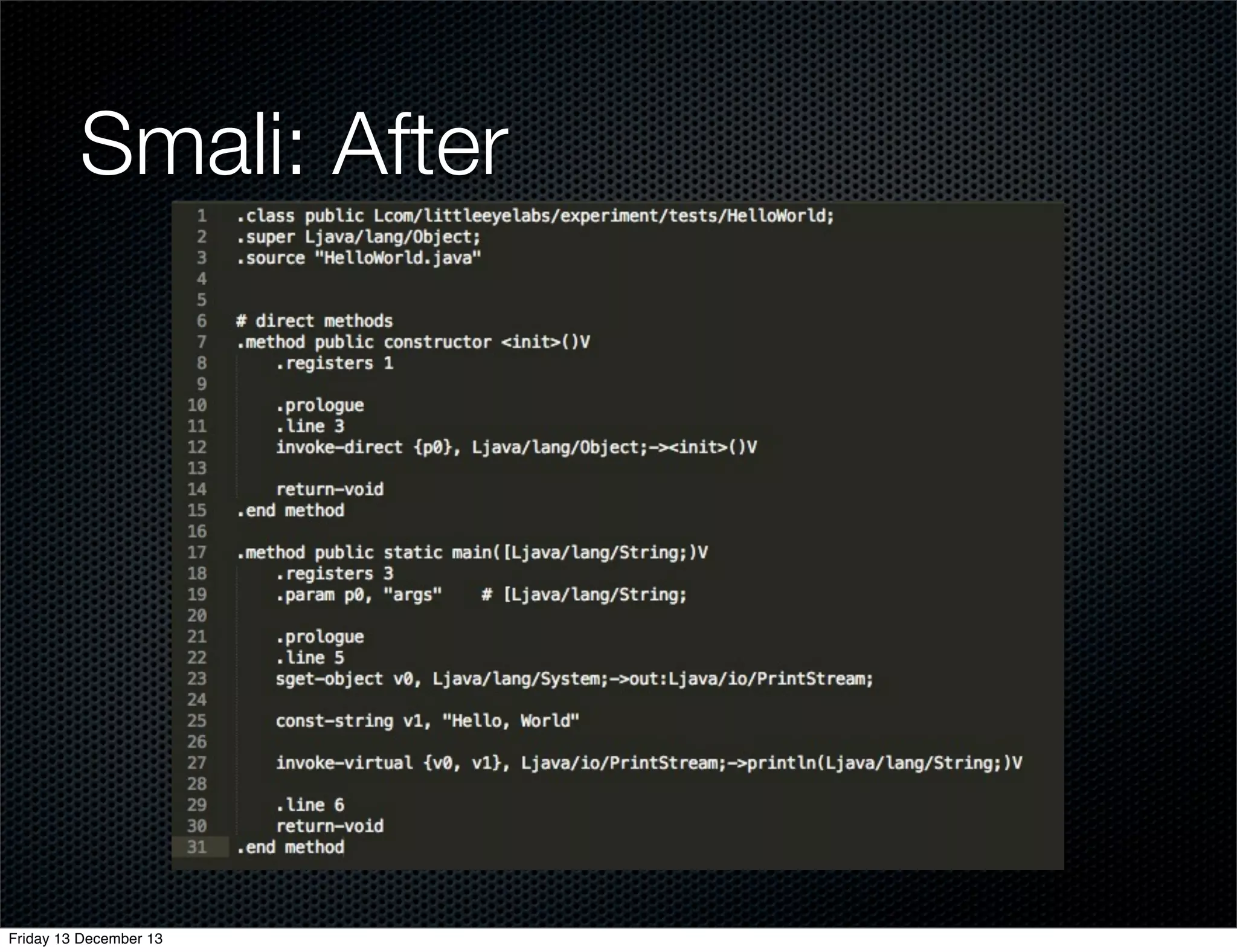
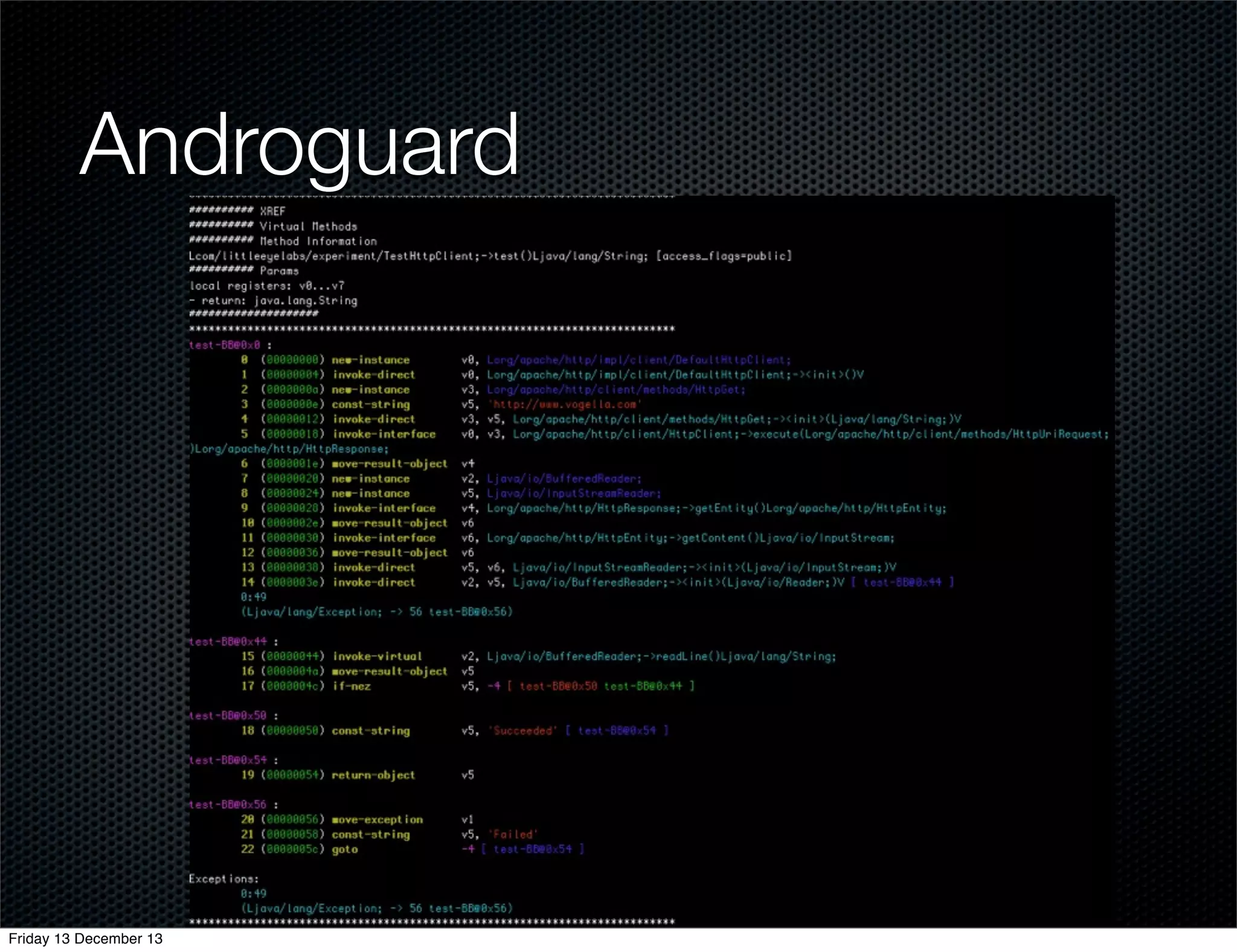
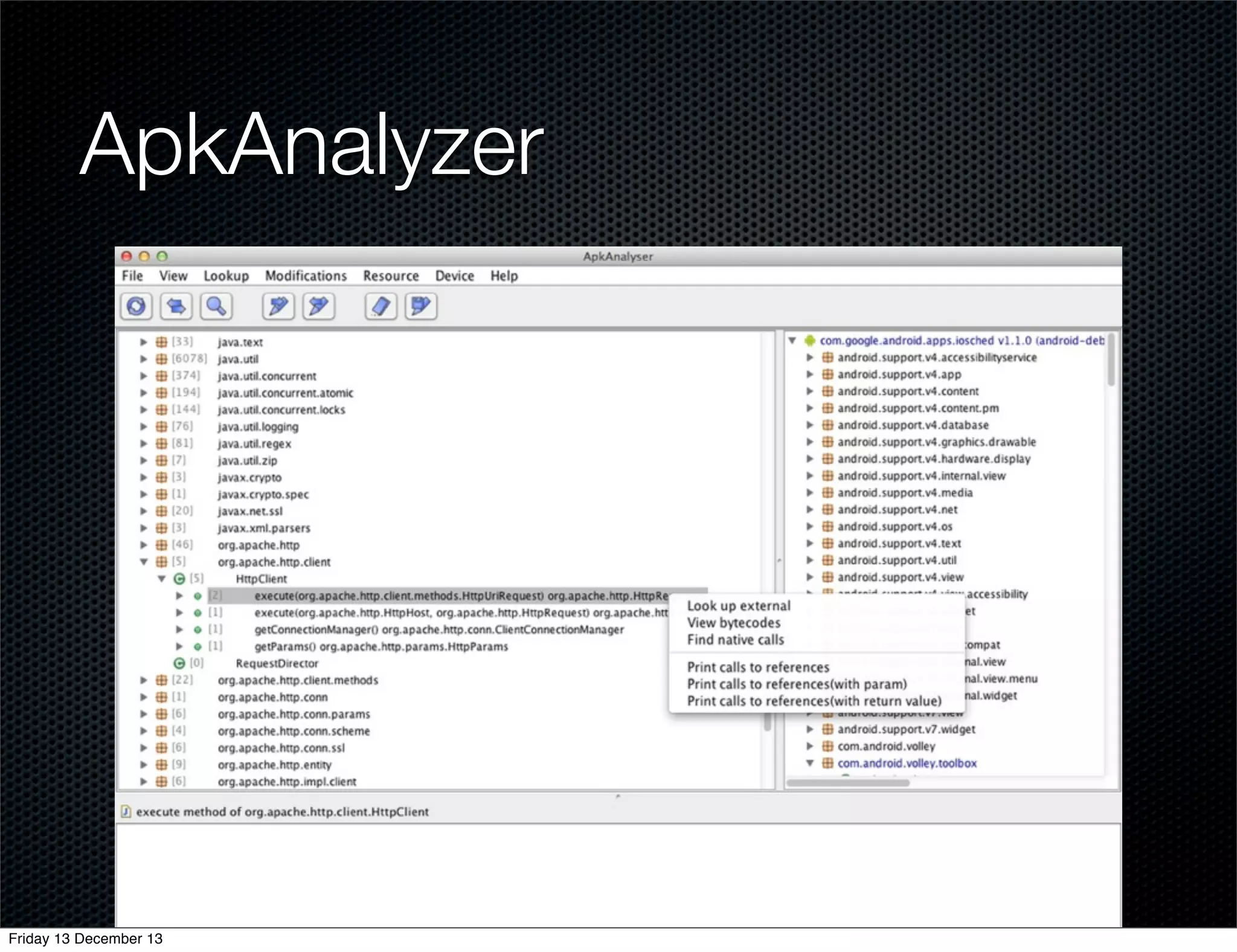
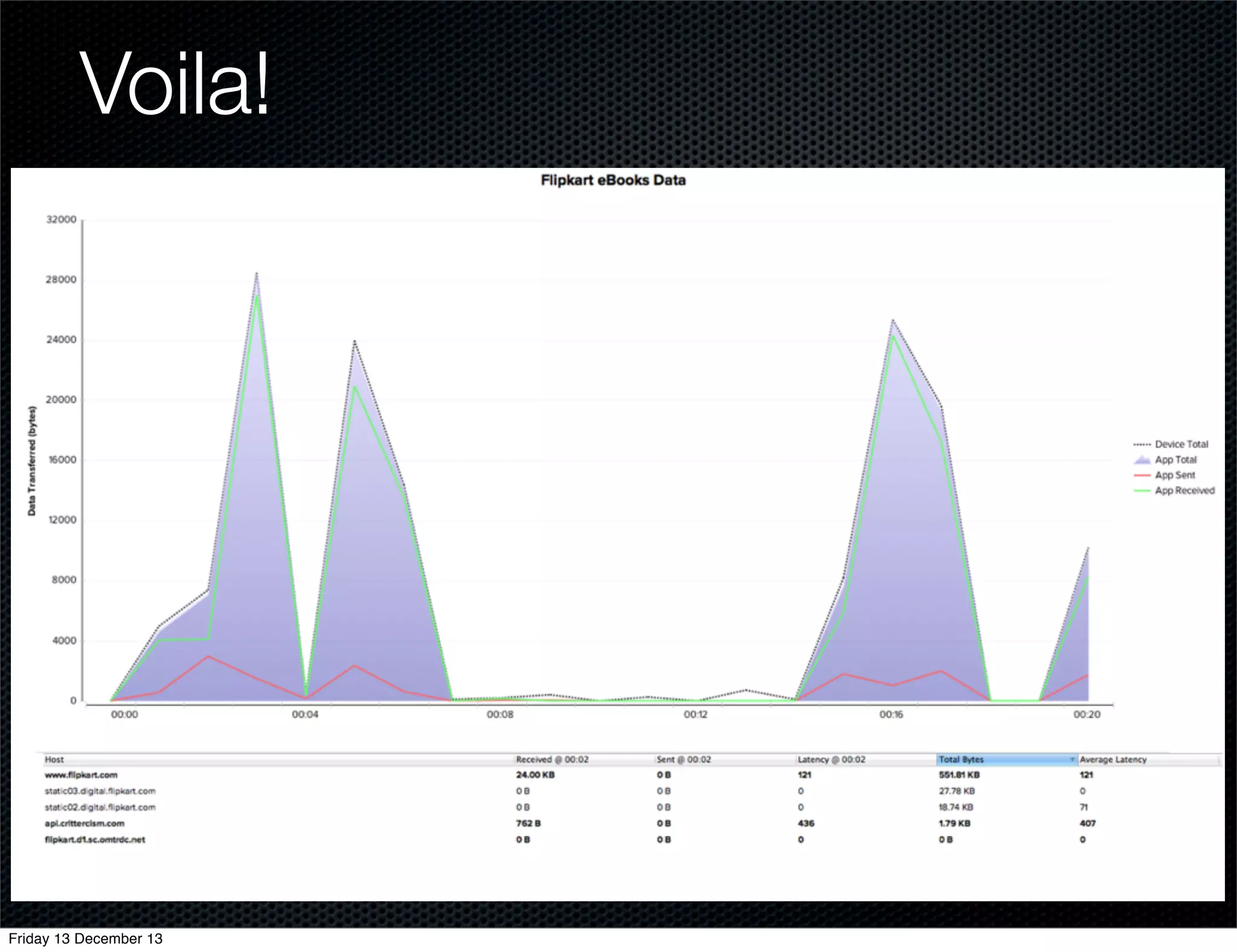
The document discusses different approaches for instrumenting Android apps to add network monitoring capabilities. It describes choosing to modify the app's dex file by disassembling it to Smali code, inserting instrumentation code, and reassembling it. This allows intercepting HTTP calls without requiring access to the app's source code or build process. The key benefits are that it works on any app and Android version without the app's code needing changes.