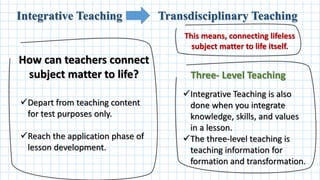
The document discusses constructivist teaching methodologies, emphasizing that learning is a socially constructed, active process where students build knowledge based on prior experiences. It covers various interactive and collaborative teaching techniques that engage students in problem-solving, critical thinking, and real-world applications through inquiry-based and project-based learning. Additionally, it highlights the importance of integrating knowledge, skills, and values in order to connect academic content to real-life contexts.