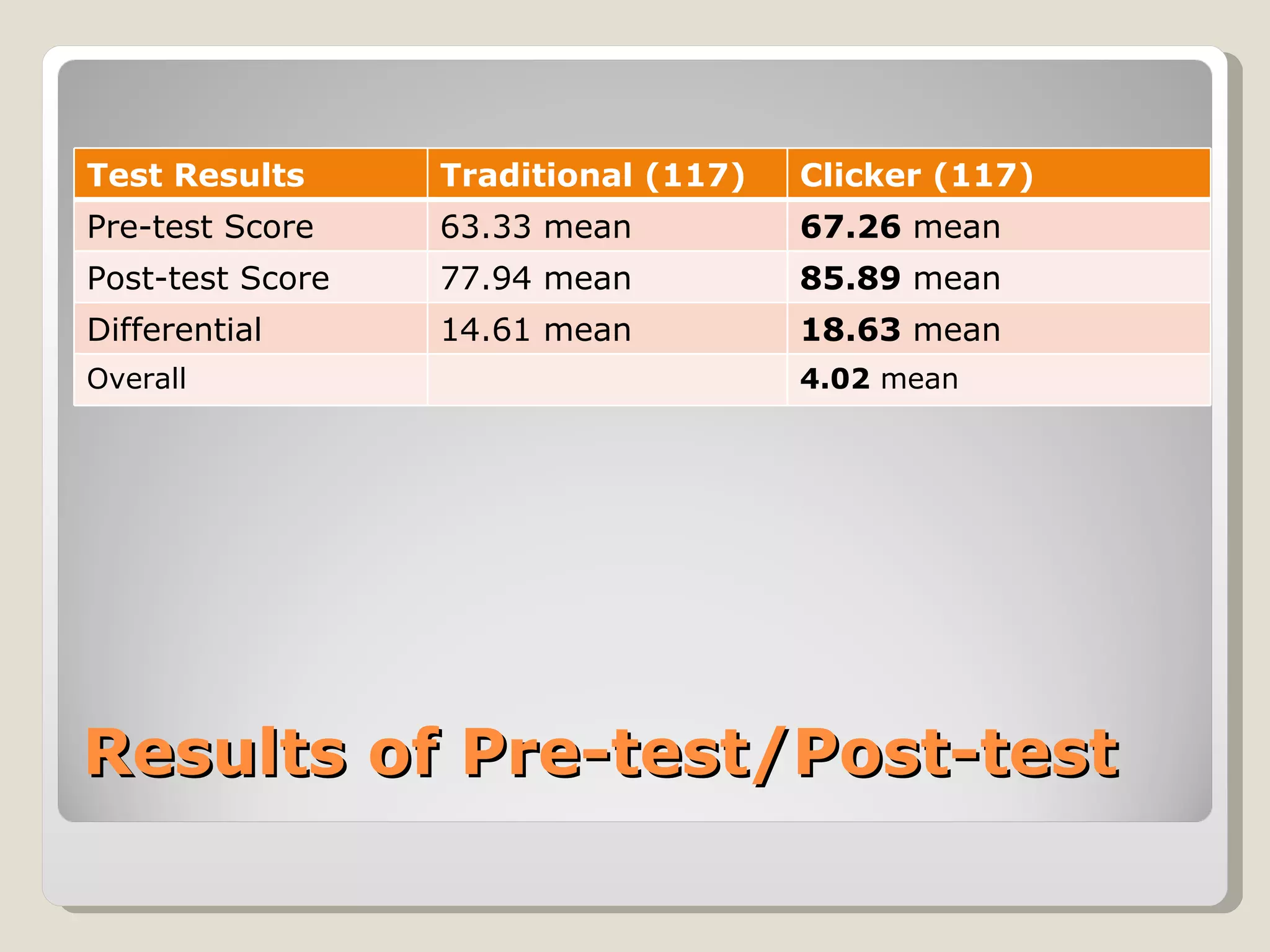
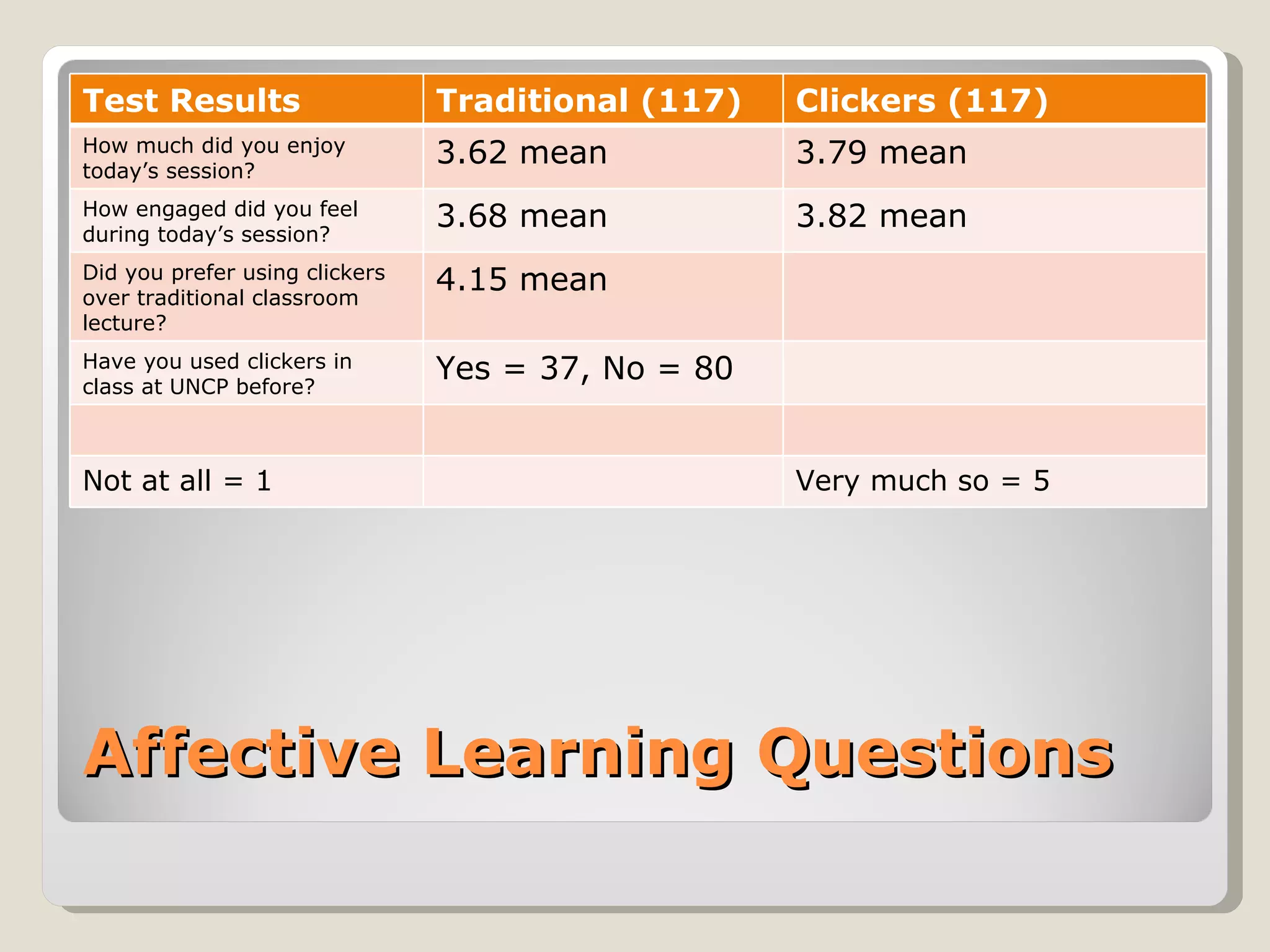
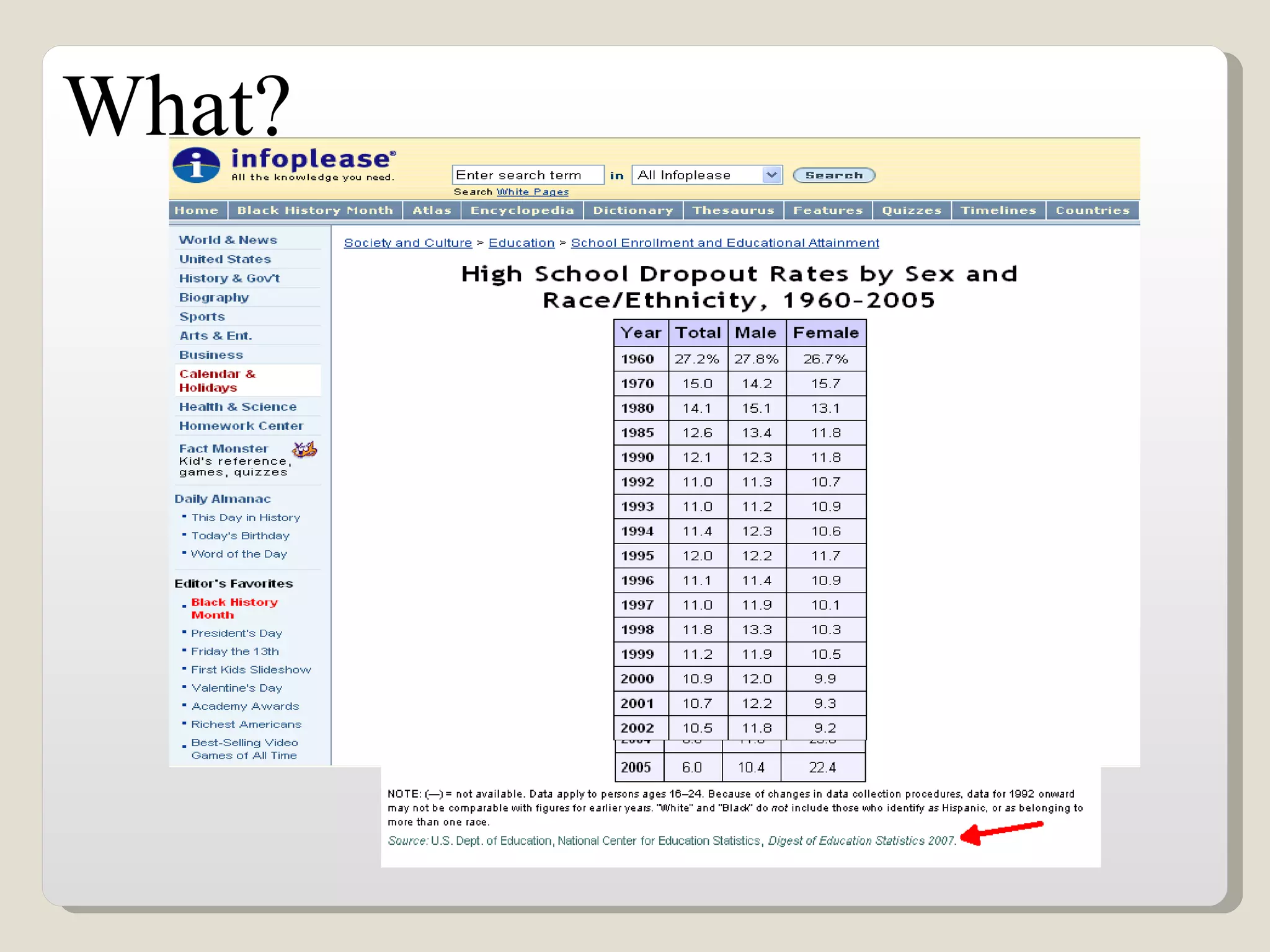
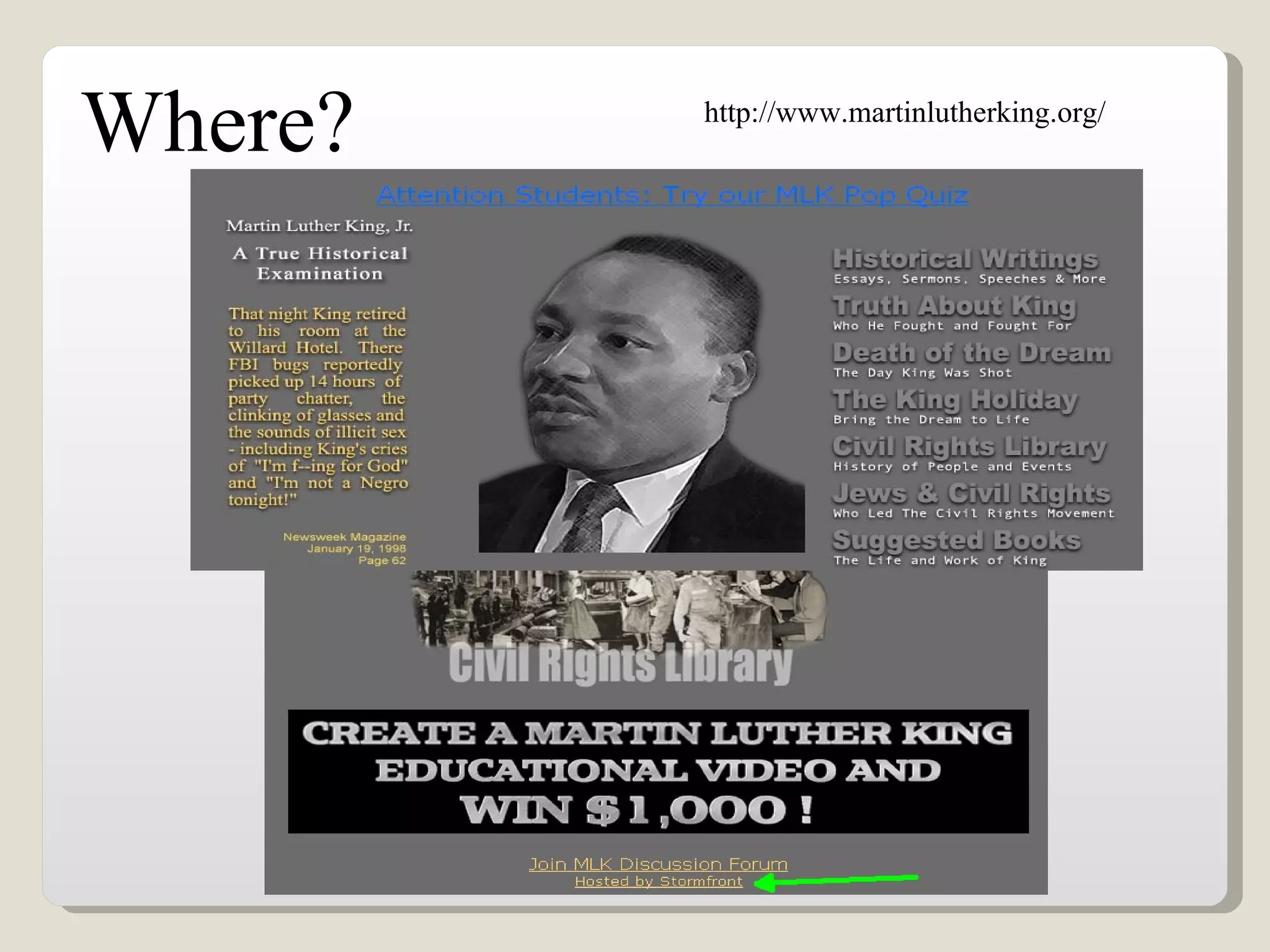
This document discusses using interactive technologies and active learning exercises to enhance library instruction. It describes student response systems (clickers), interactive whiteboards, and wireless slates/document cameras. It provides information on what active learning is, characteristics of active learning, and how clickers can actively engage students. The document also shares a case study on using clickers in an English research methods class, including test results. Best practices for using clickers and characteristics of good clicker questions are outlined. Interactive whiteboards and their uses in the classroom are also examined.