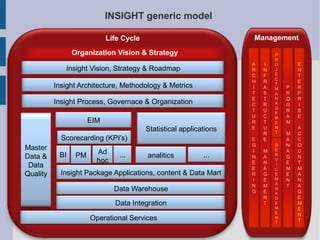
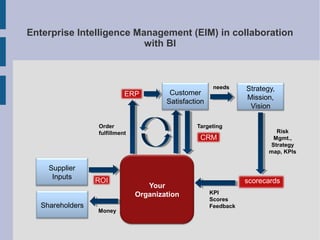
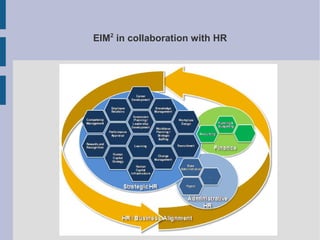
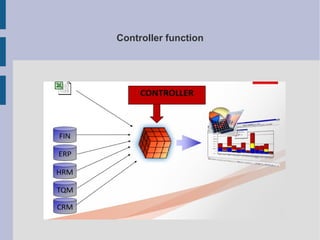
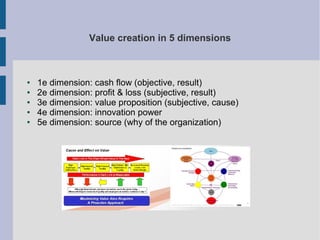
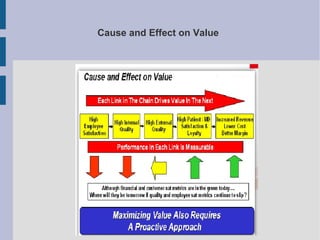
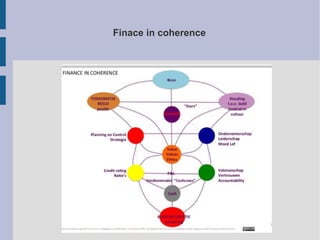
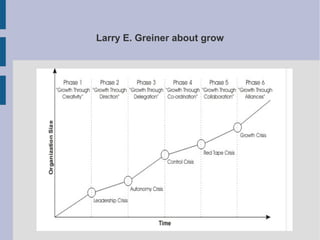
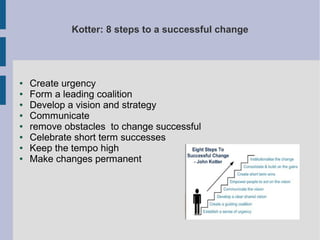
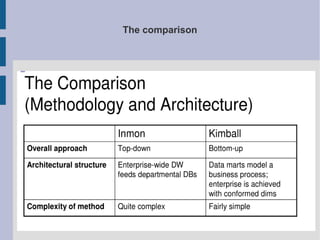
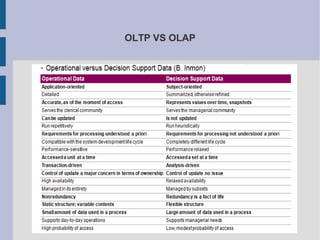
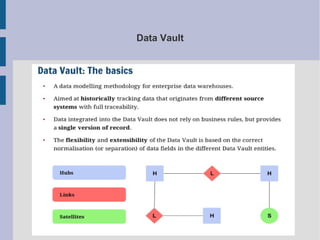
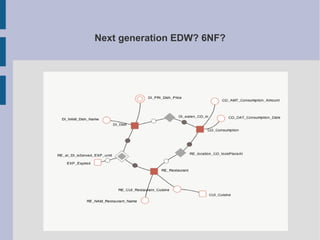
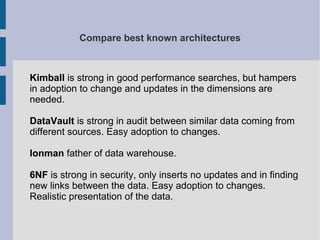
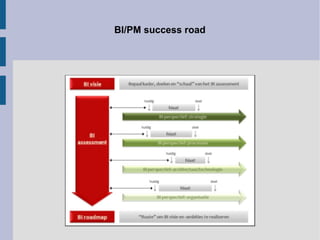
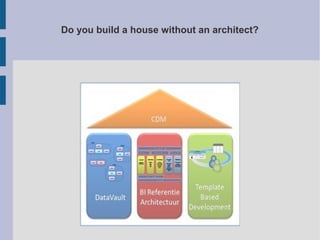
The document discusses the complex nature of business intelligence (BI) and performance management (PM), emphasizing their critical roles in enhancing organizational decision-making and strategic alignment. It presents insights on value creation through various dimensions, effective planning, and control techniques, along with a detailed analysis of ratios and work capital. Additionally, it outlines automation in data warehousing and provides guidance on defining a successful BI/PM roadmap tailored to an organization's needs.