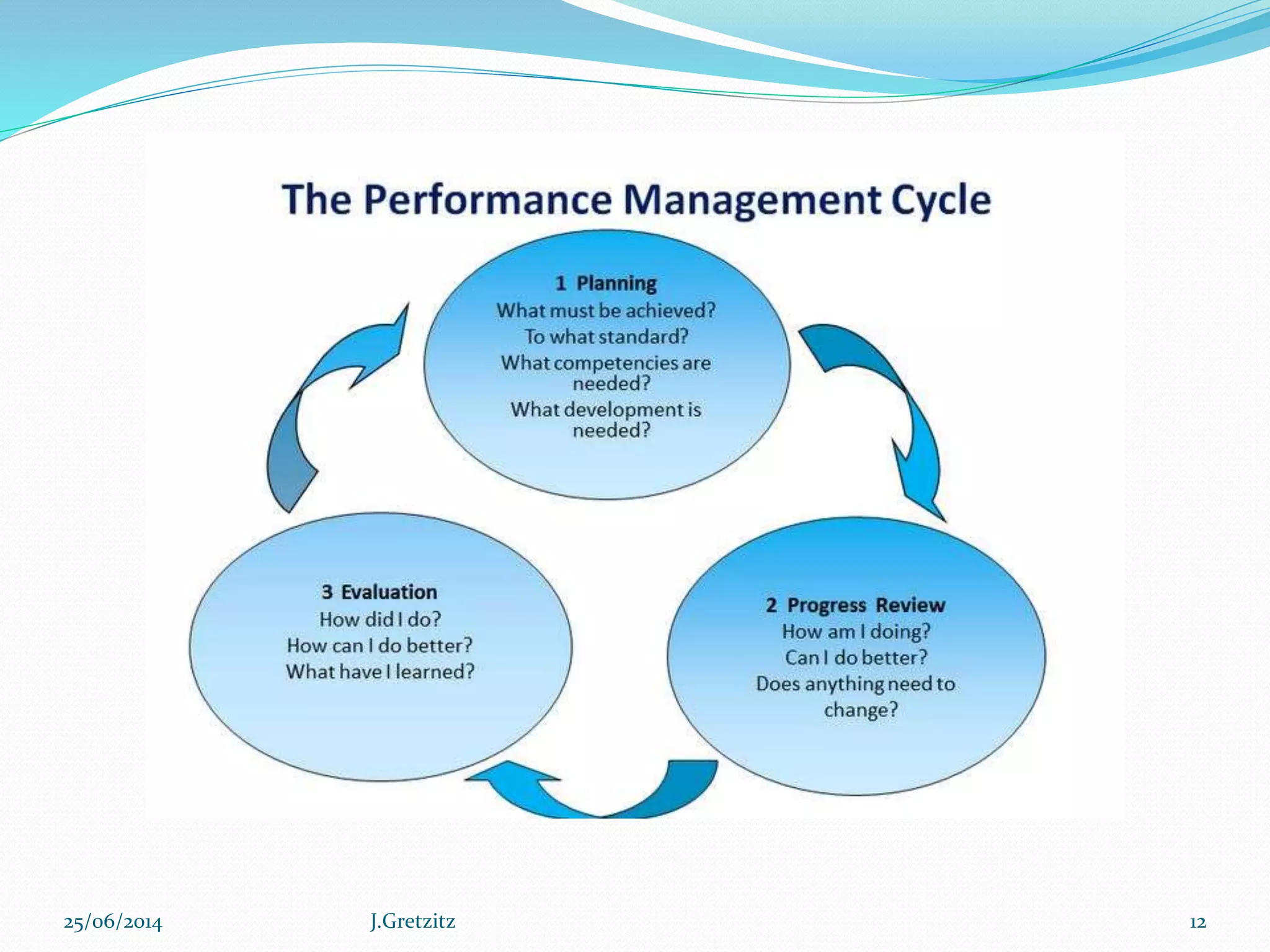
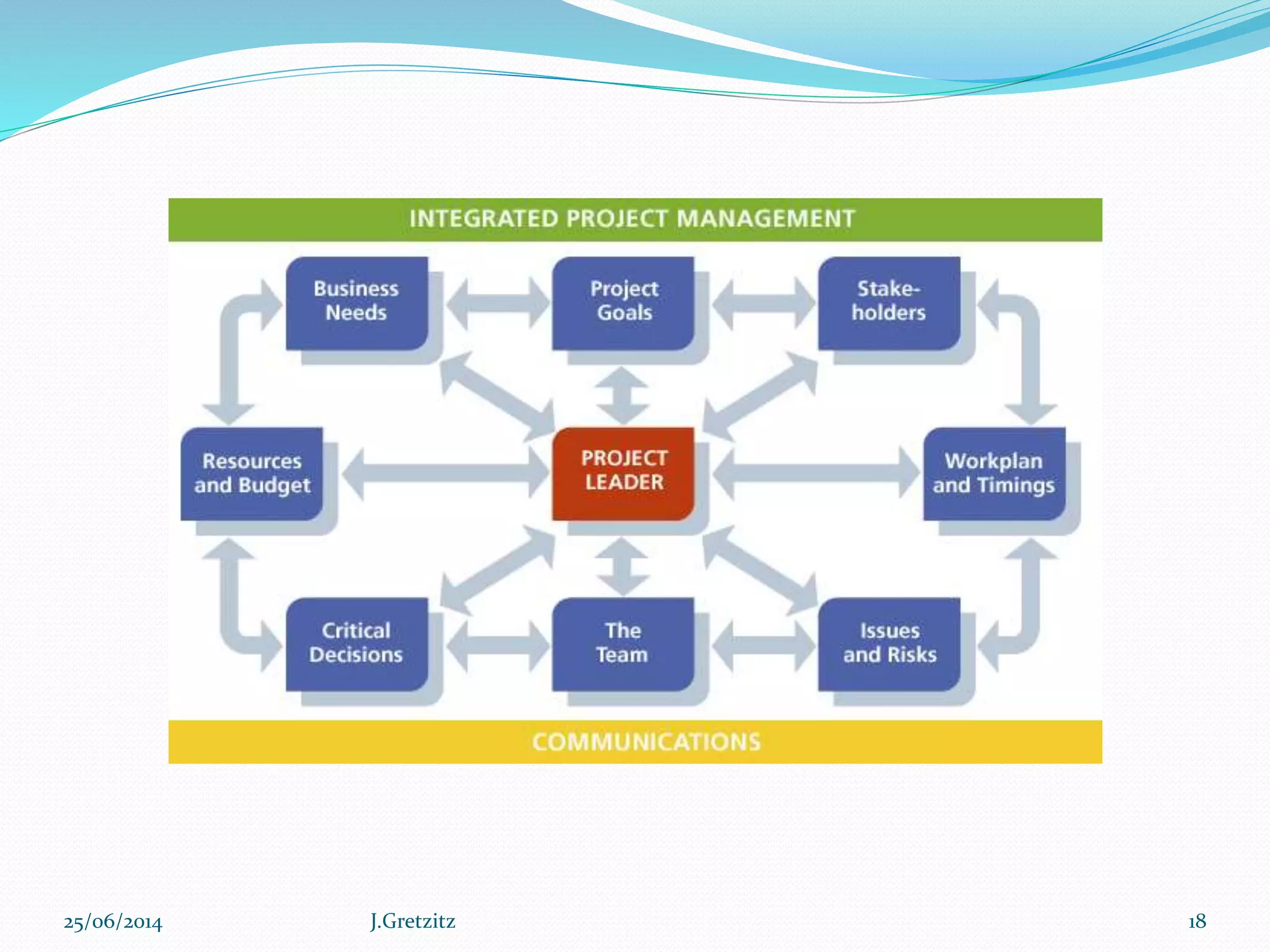
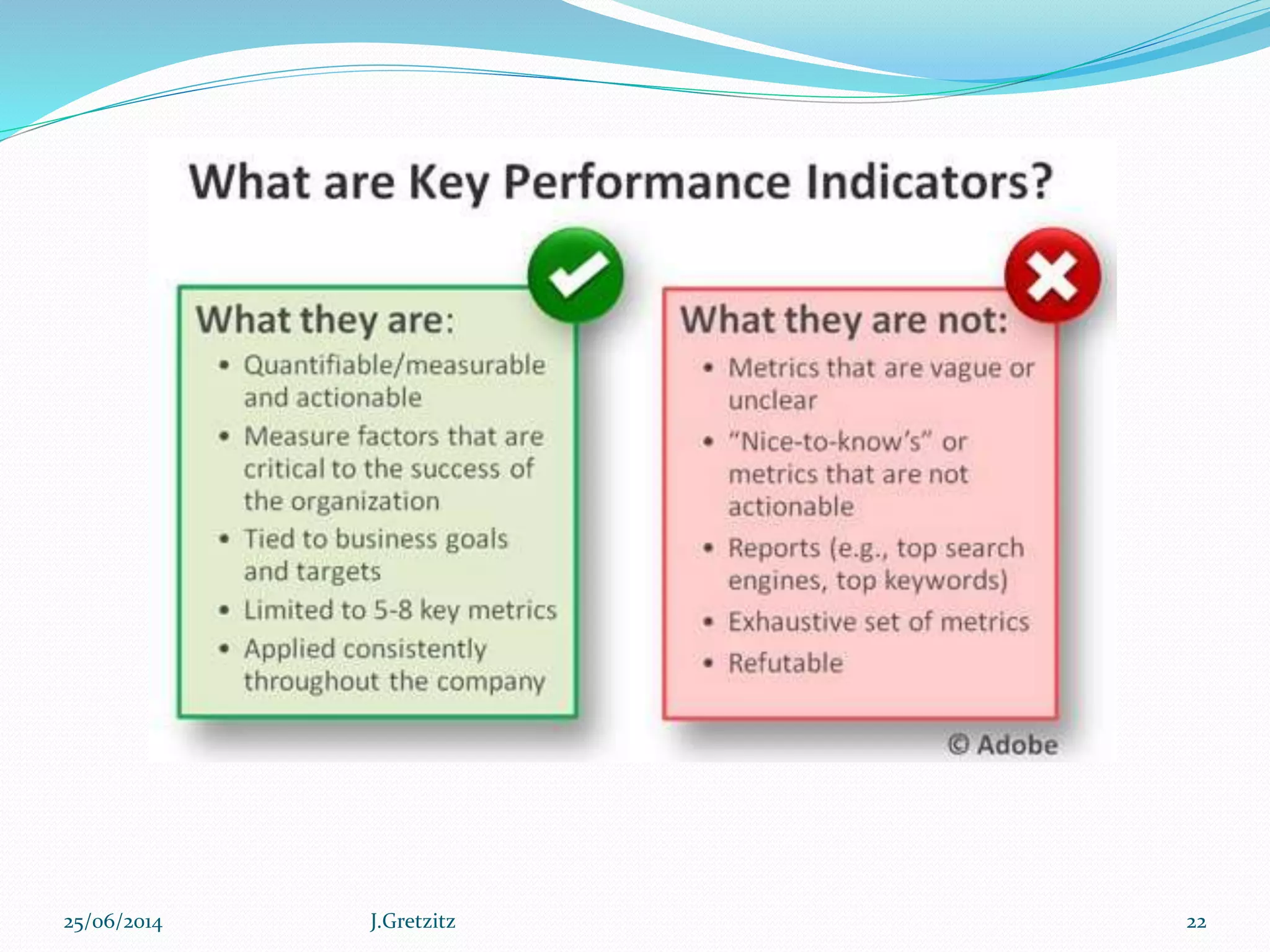
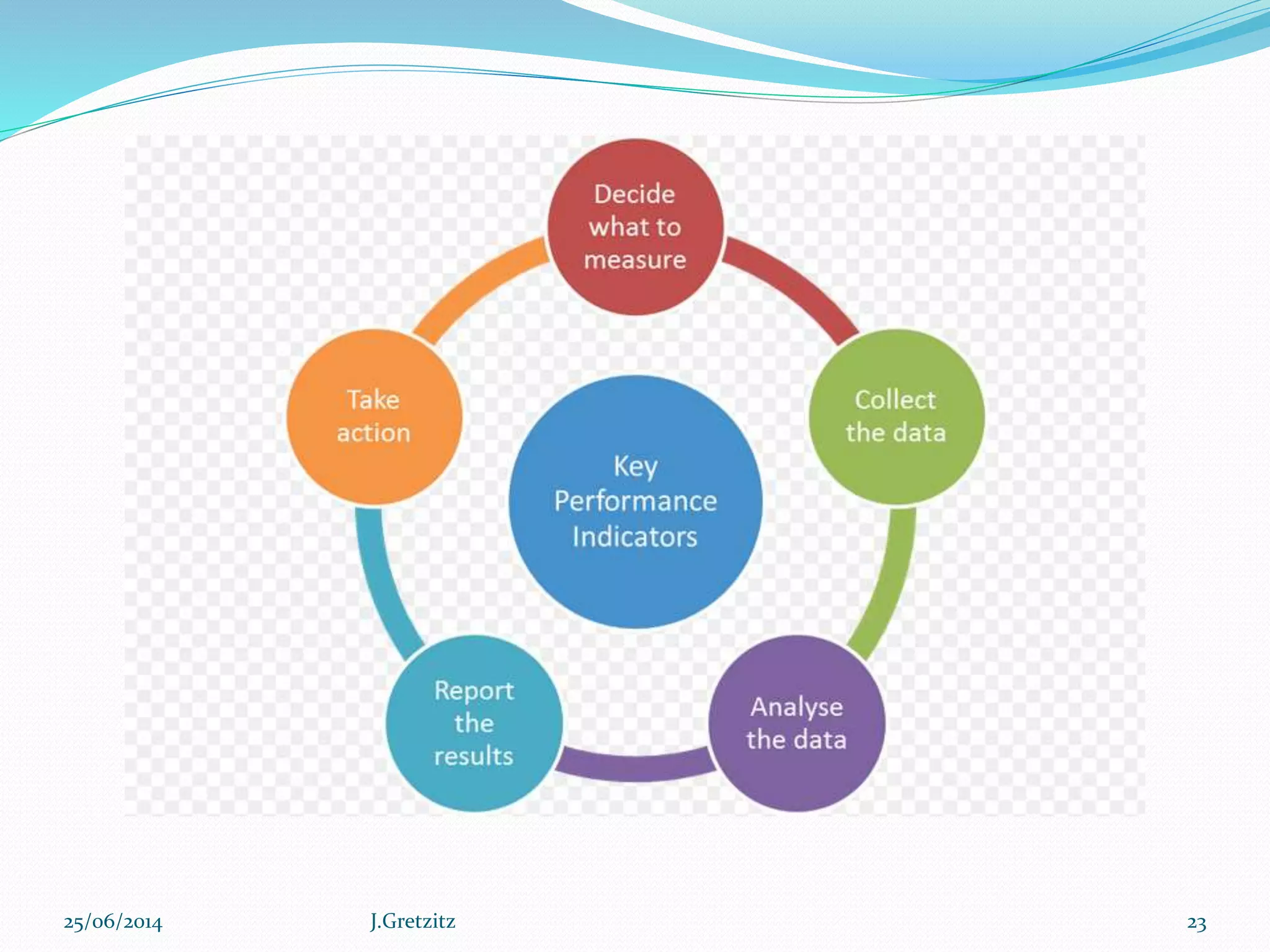
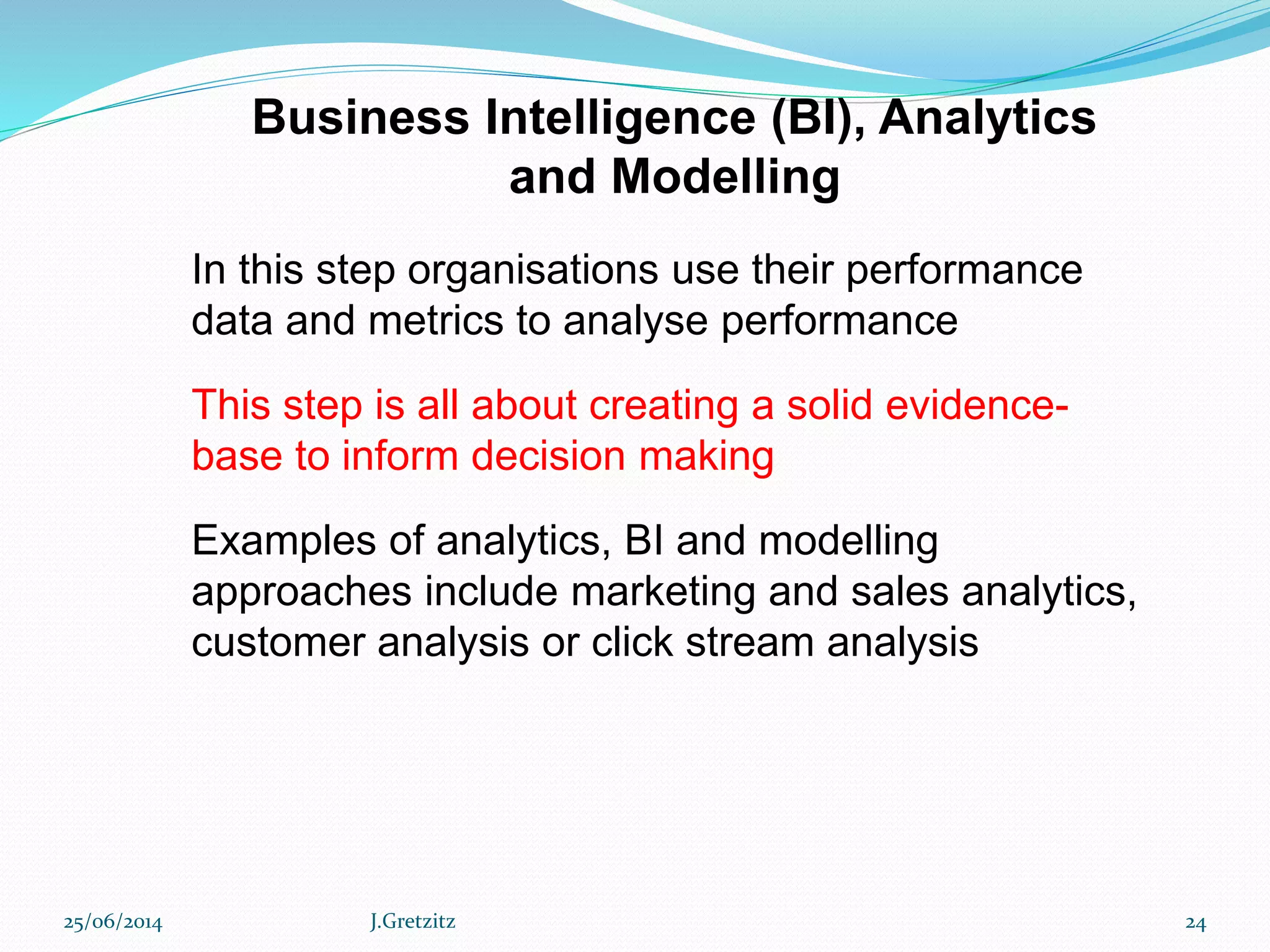
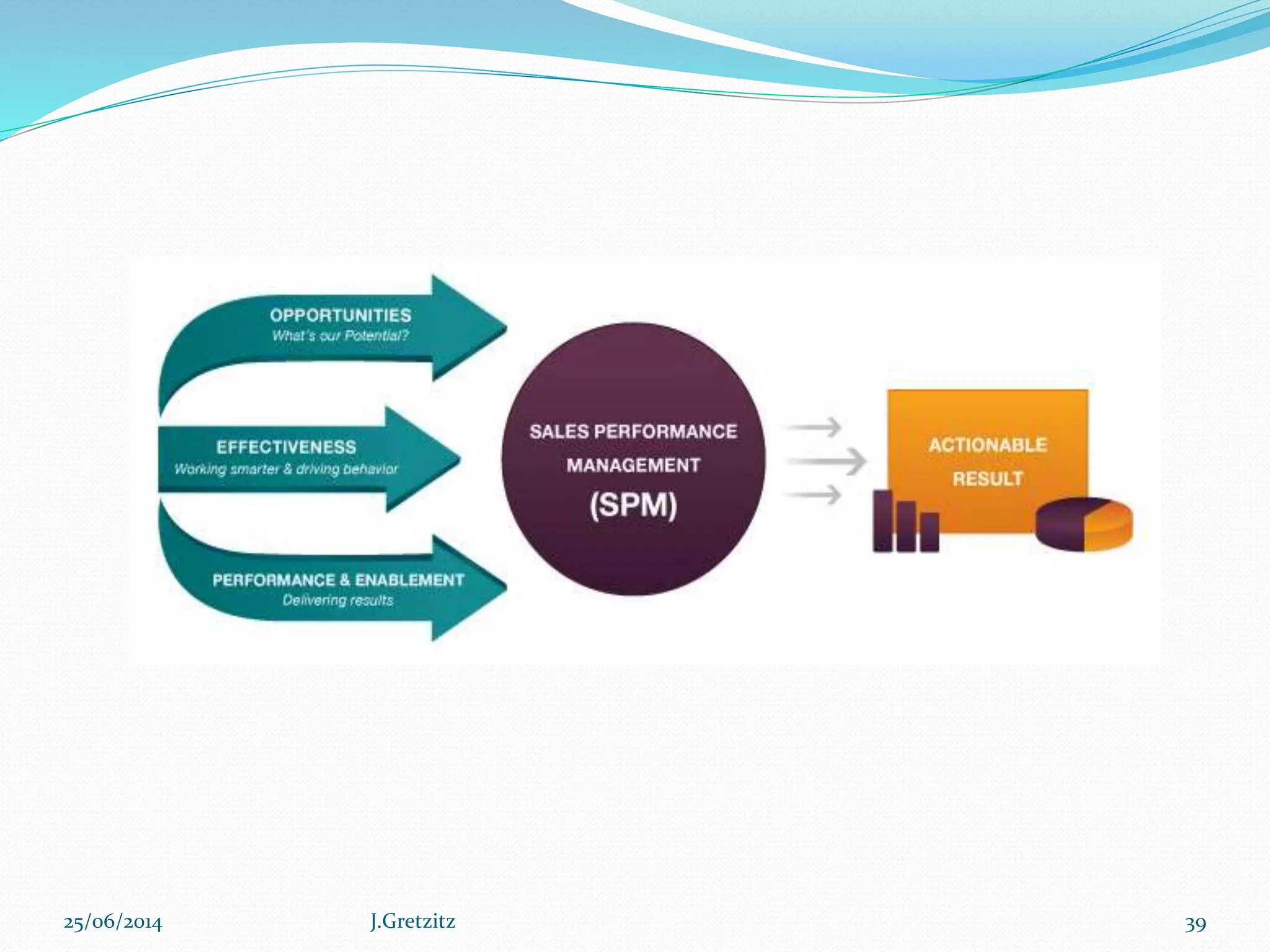
Performance management originated in the late 1970s and refers to a set of management processes that help organizations improve strategy execution, decision-making, and performance. It involves defining strategic objectives, measuring performance, analyzing results, and aligning people and culture. More advanced approaches integrate performance management with other key processes like financial planning, project management, and risk management to create a holistic view of organizational performance. Technology solutions can help organizations systematically manage performance across the enterprise.