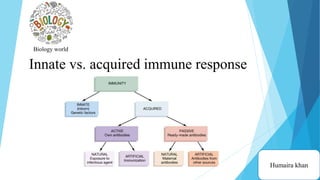
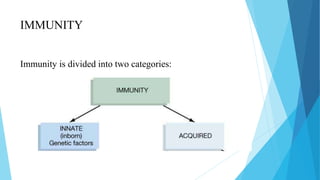
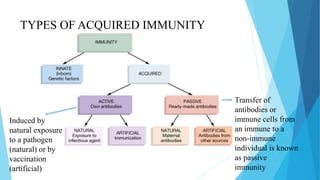
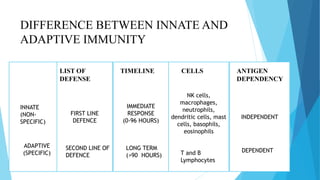
The document discusses the difference between innate and adaptive (acquired) immunity. Innate immunity is non-specific and present since birth, providing a first-line defense against pathogens. Adaptive immunity develops over time through exposure to pathogens and provides long-term, antigen-specific protection through the actions of B and T lymphocytes. While innate immunity acts immediately, adaptive immunity requires more time to respond specifically to pathogens and develop immunological memory.