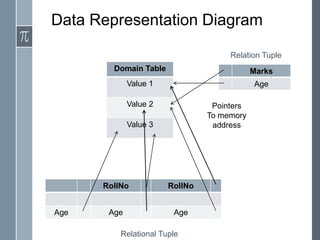
In-memory databases (IMDBs) store data primarily in RAM for faster access than disk-based databases. While an older concept, IMDBs have become more practical due to lower RAM costs, multi-core CPUs, and 64-bit systems allowing more memory. IMDBs have different architectures, data representations, indexing, and query processing optimized for memory versus disk. They also face challenges in providing durability without disk and scaling to very large data sizes.