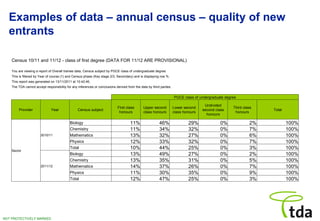
The Training and Development Agency for Schools (TDA) is responsible for teacher training in England. It allocates over 37,000 training places each year across various routes including undergraduate, postgraduate, employment-based. It also regulates teacher training providers and ensures quality through criteria for accreditation and inspection by Ofsted. The TDA collects data on trainees and providers to monitor quality and inform recruitment and funding.