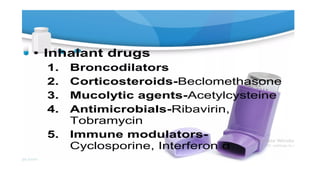
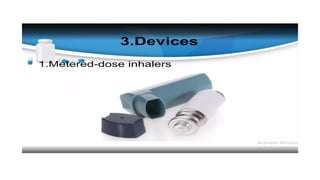
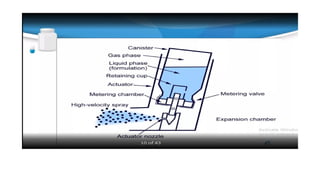
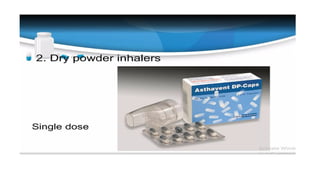
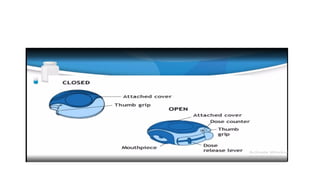
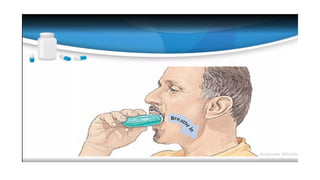
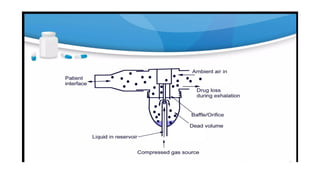
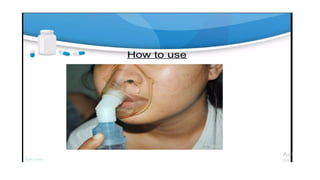
Inhalation is the administration of drugs via the respiratory route, with applications in conditions like asthma and bronchitis. While it offers benefits such as reduced systemic toxicity and rapid medication onset, inhalation therapy can be time-consuming and dependent on effective delivery devices like inhalers and nebulizers. Additionally, humidification may be necessary to assist in airway clearance for patients with compromised mucociliary function.