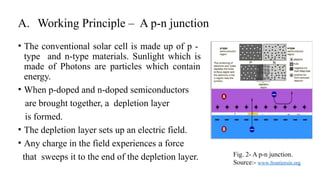
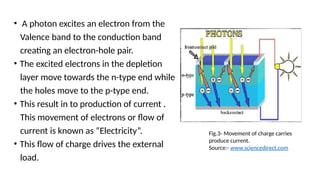
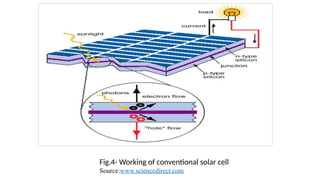
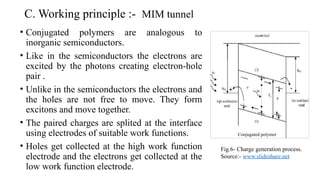
The seminar presentation discusses the development and advantages of plastic solar cell technology in comparison to conventional solar cells. It outlines the working principles, applications, and efficiency differences, noting that plastic solar cells can harness infrared rays and function under cloudy conditions, making them more versatile and cost-effective. The conclusion emphasizes the potential of plastic solar cells in reducing reliance on fossil fuels and achieving economic feasibility in energy production.