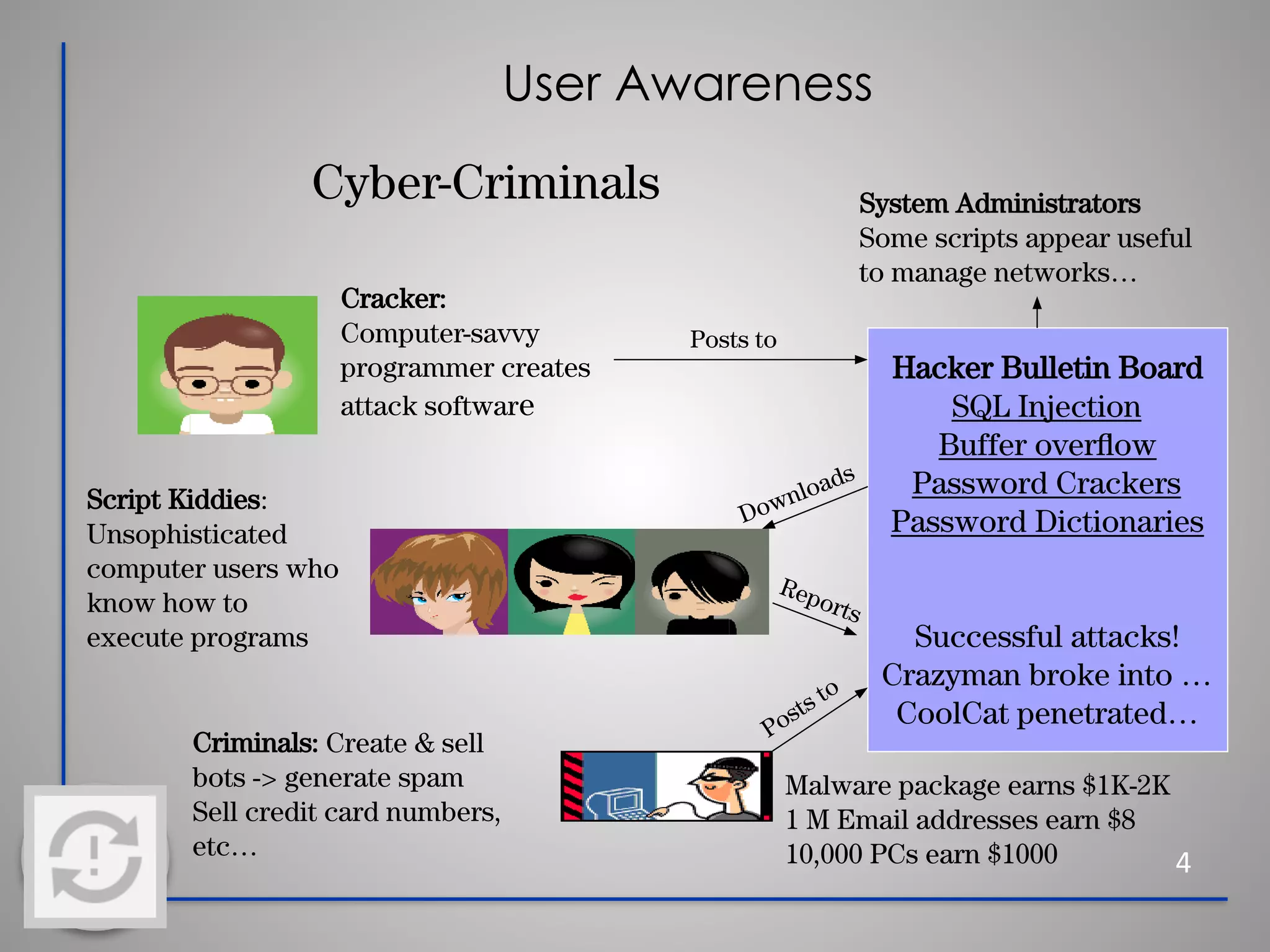
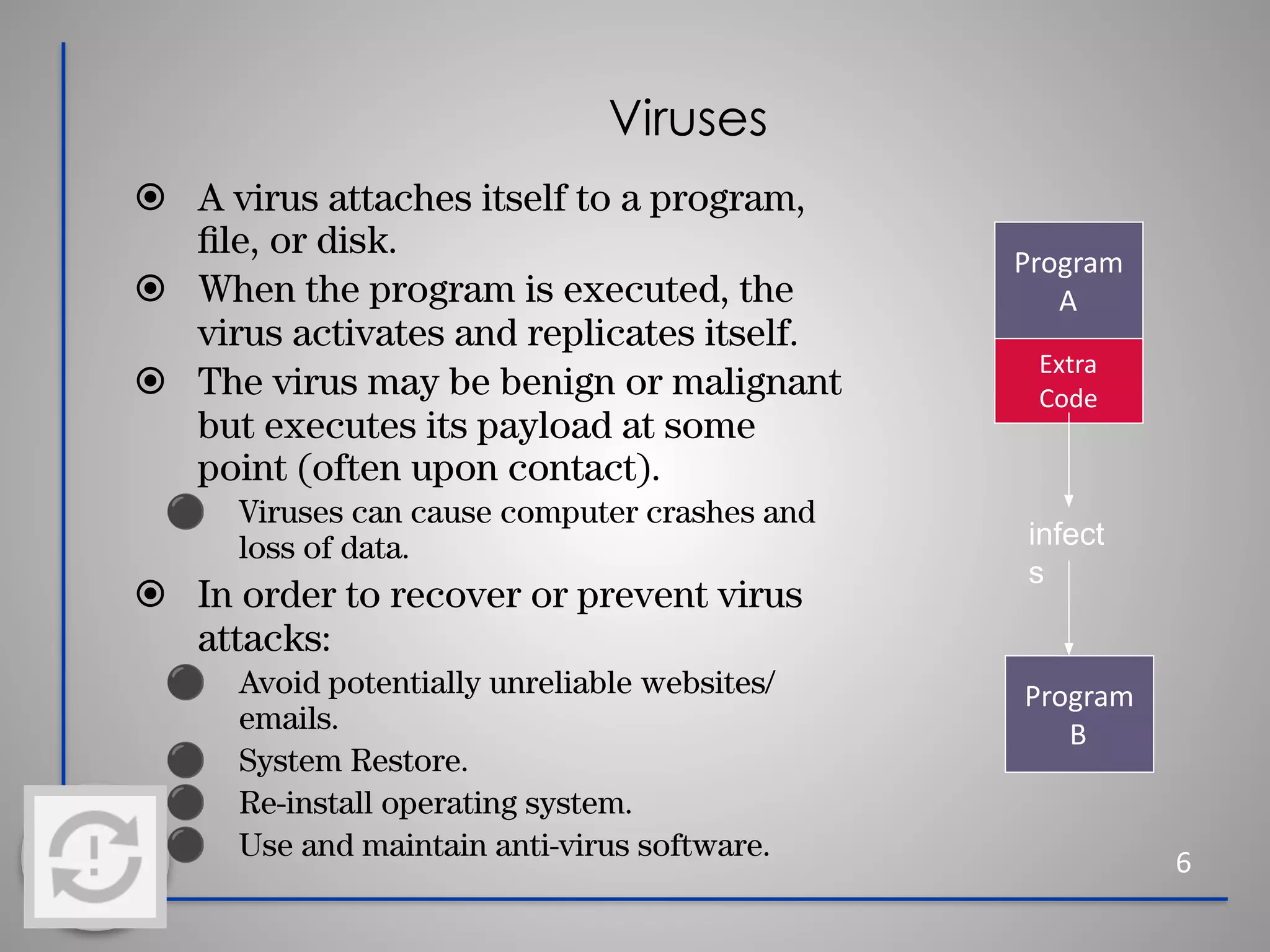
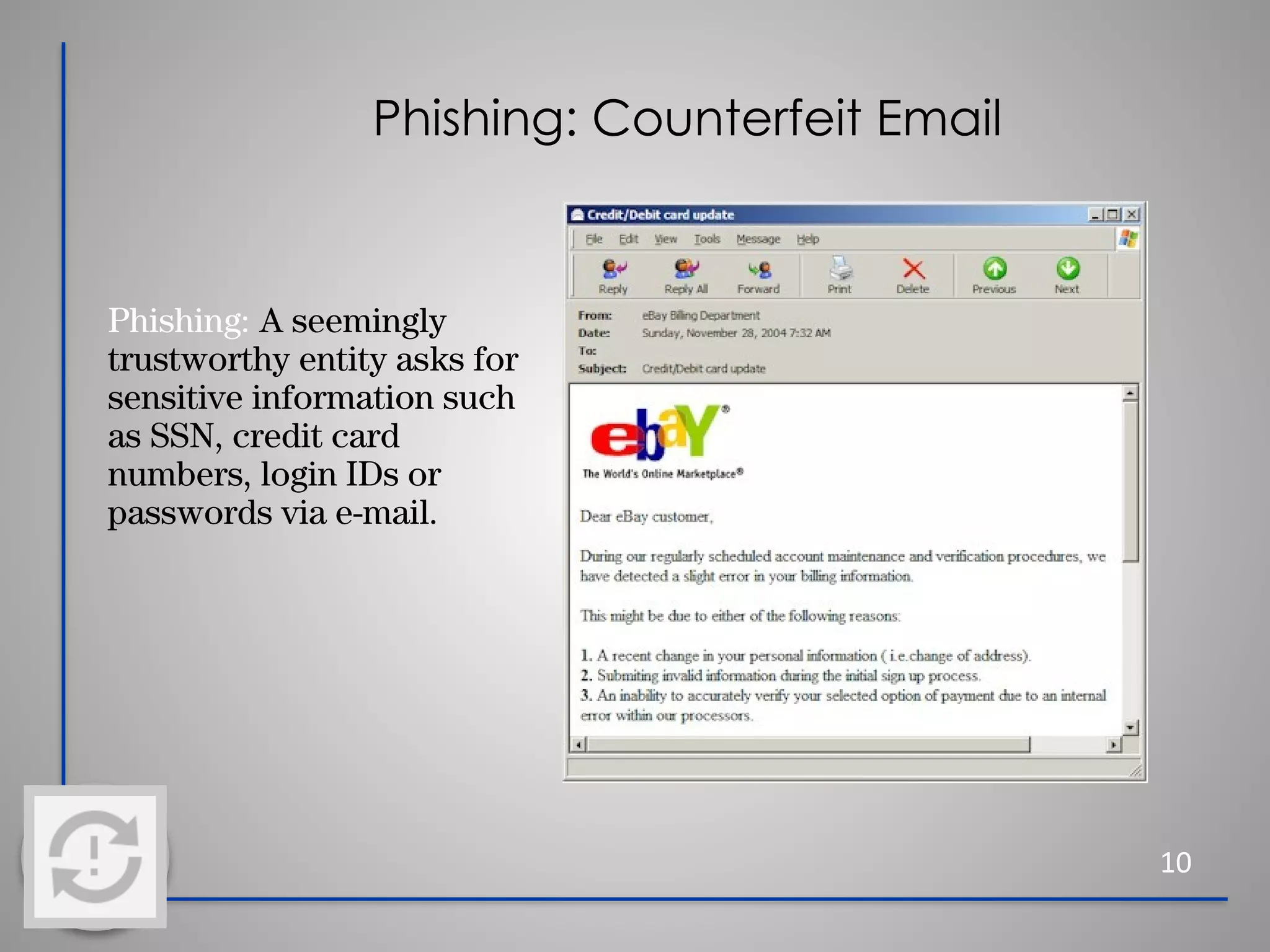
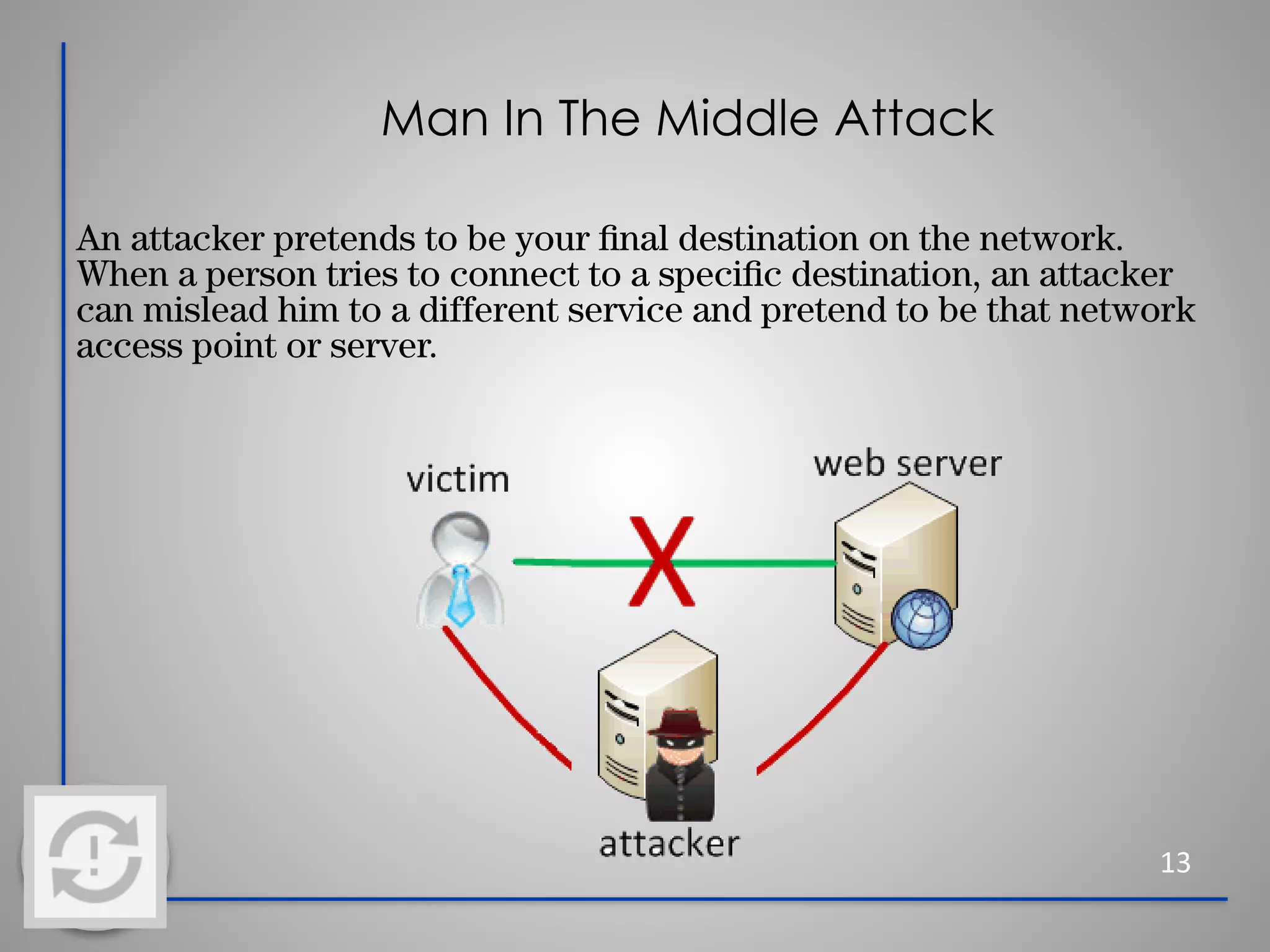
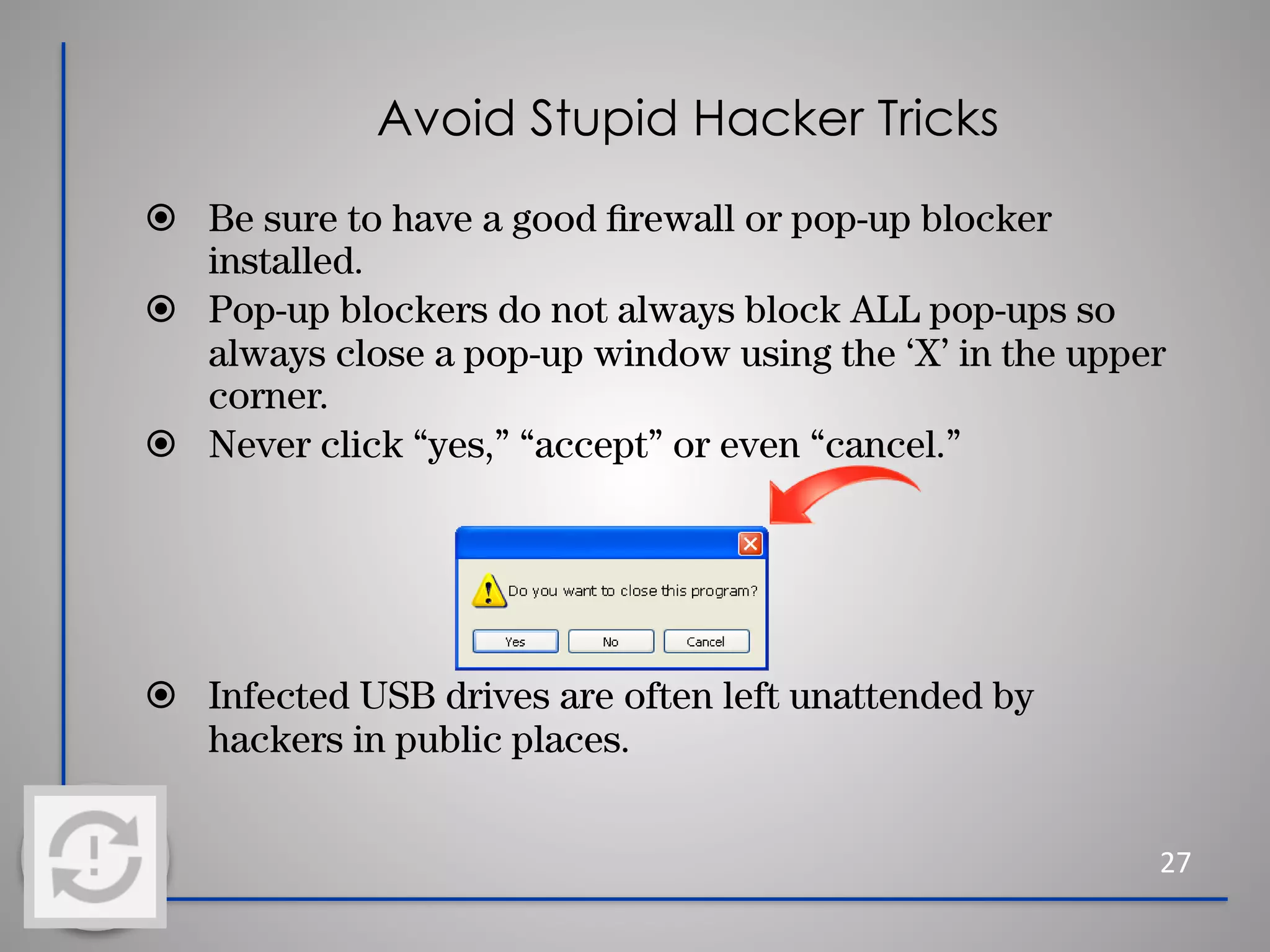
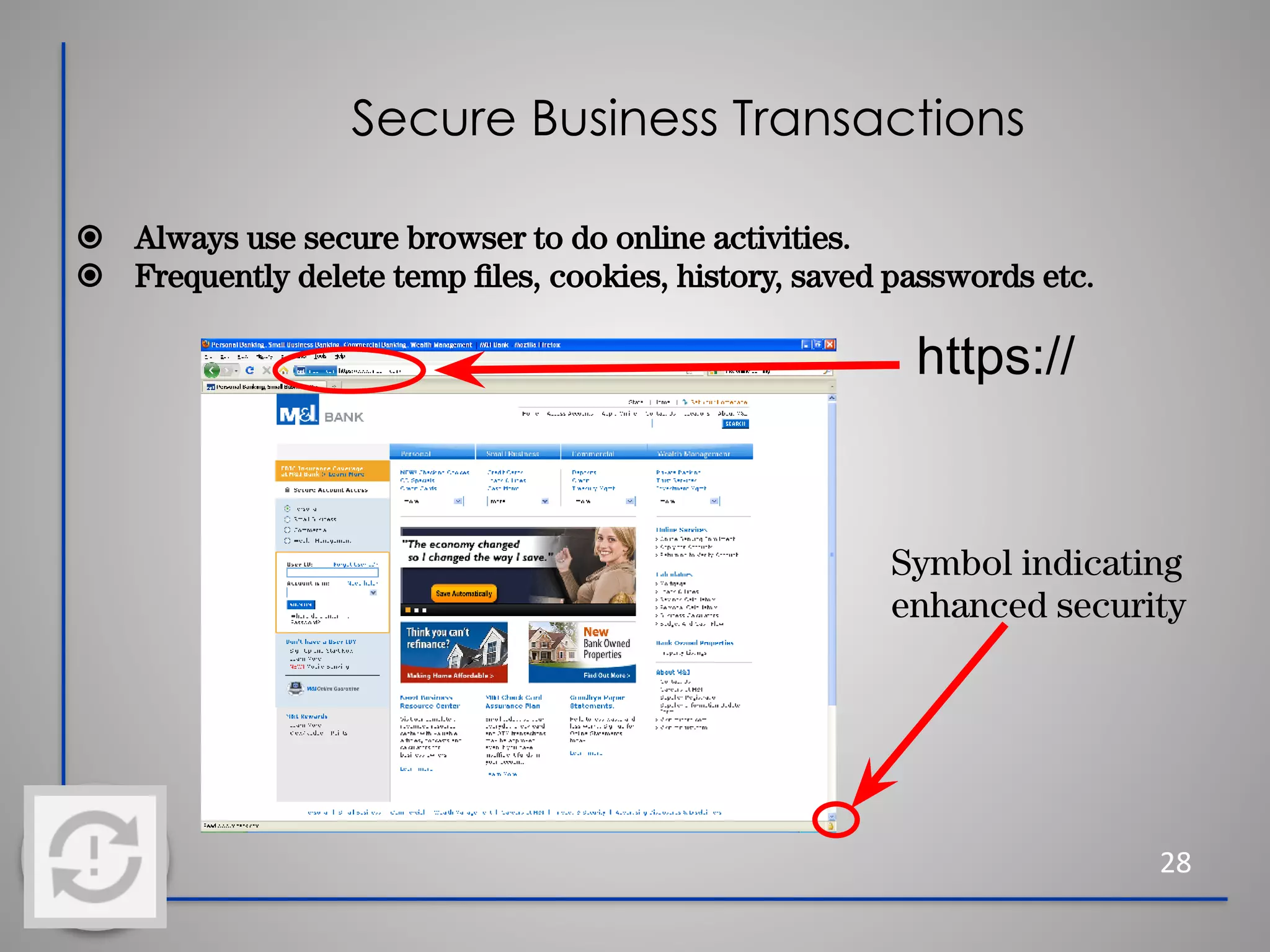
This document provides information about cybersecurity and threats. It discusses the importance of cybersecurity and some common threats like viruses, worms, Trojan horses, and social engineering. It provides details on specific threats like phishing, man-in-the-middle attacks, and rootkits. The document also offers tips for secure practices like using strong passwords, backing up data, applying software updates, and reporting any suspected cybersecurity incidents. The overall message is that cybersecurity is important to protect individuals and organizations from online threats and risks.