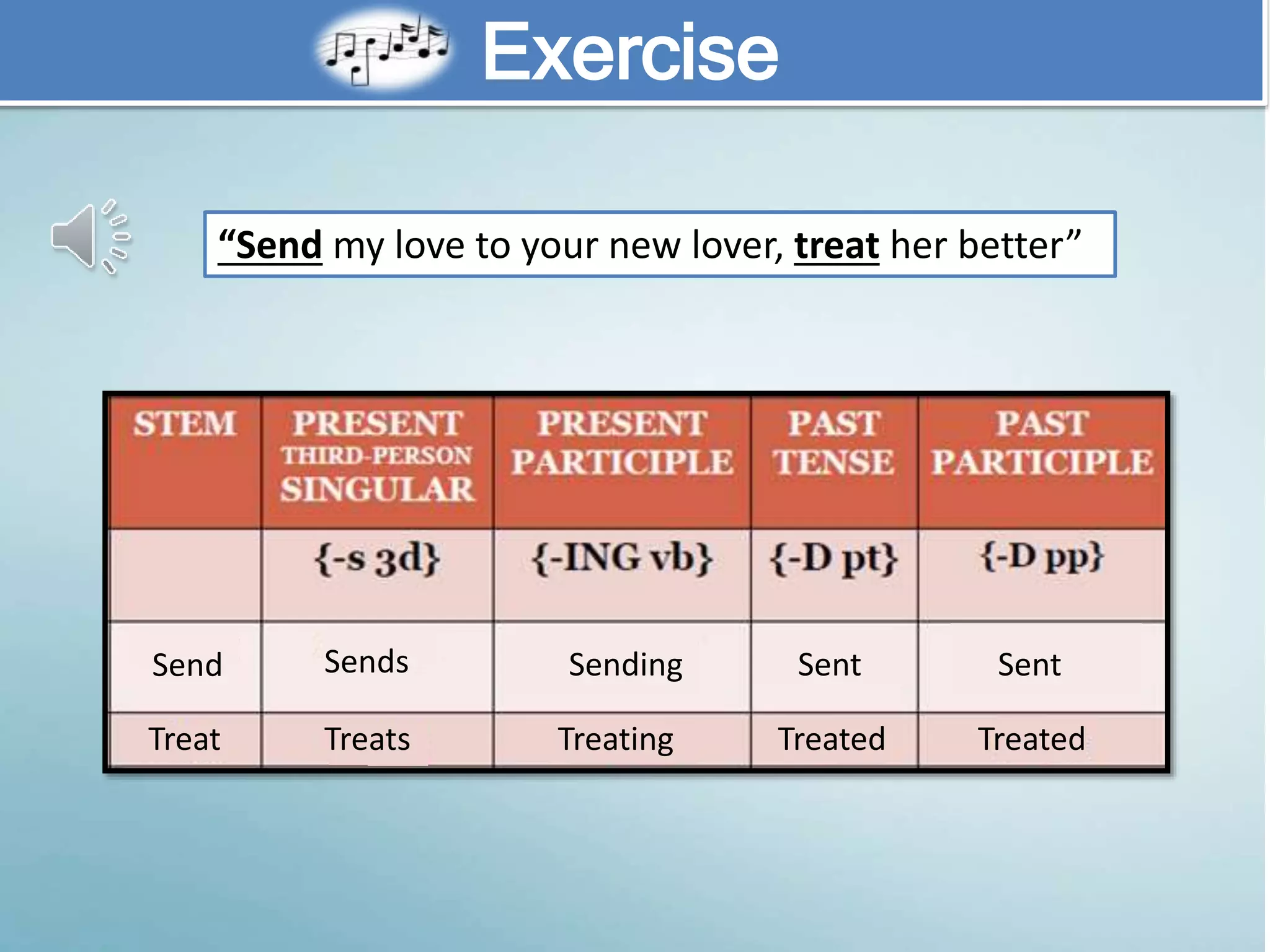
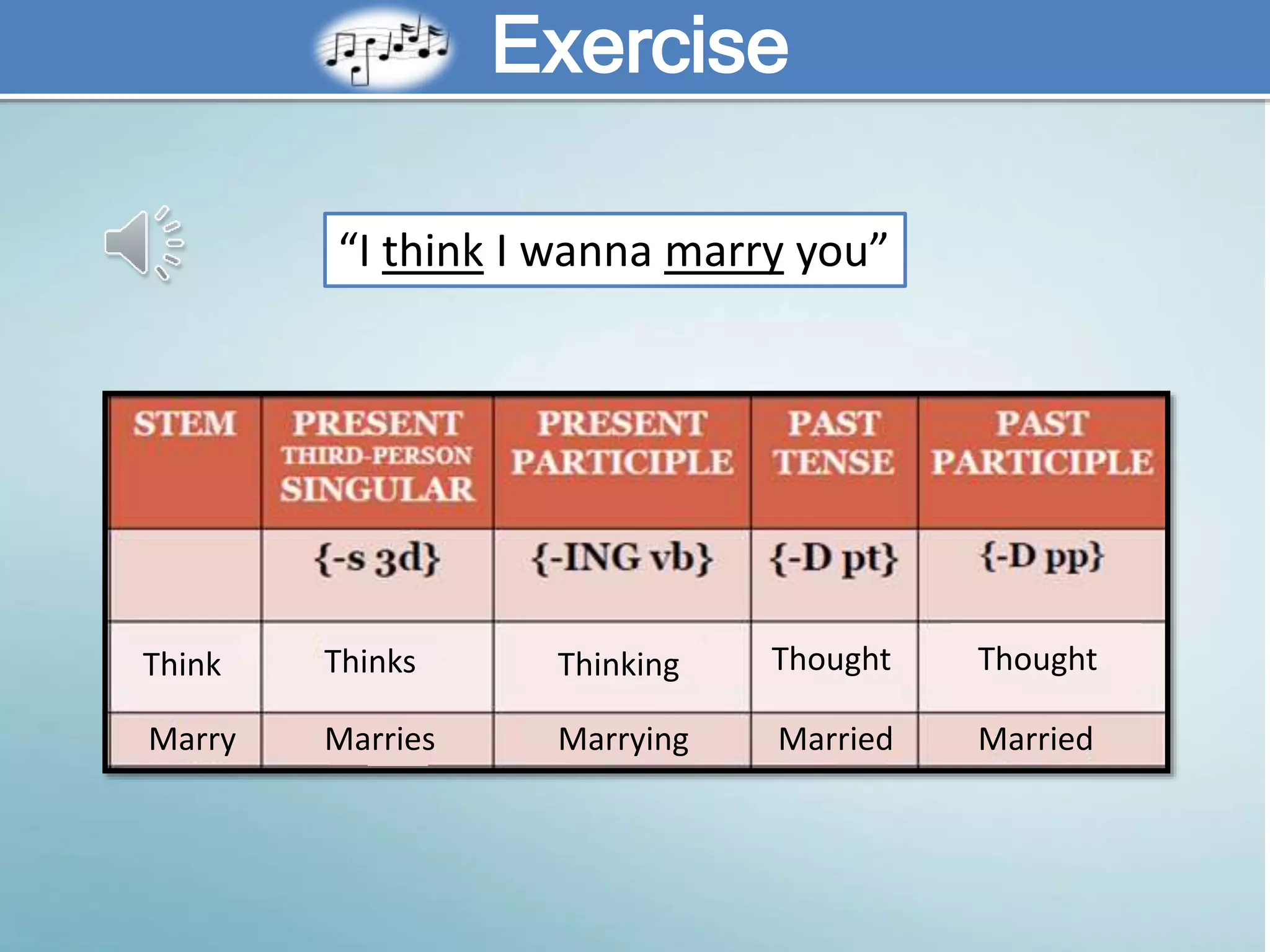
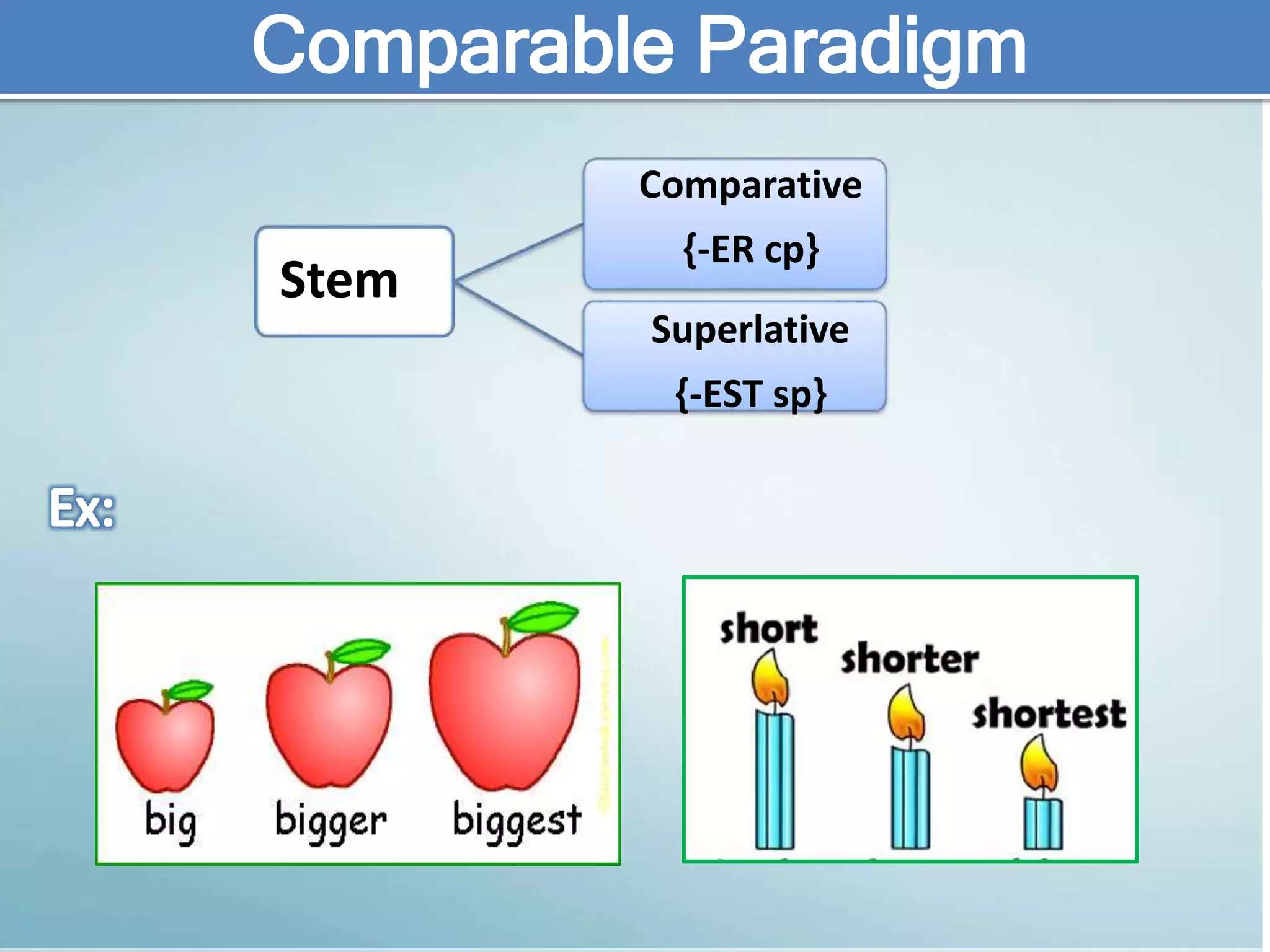
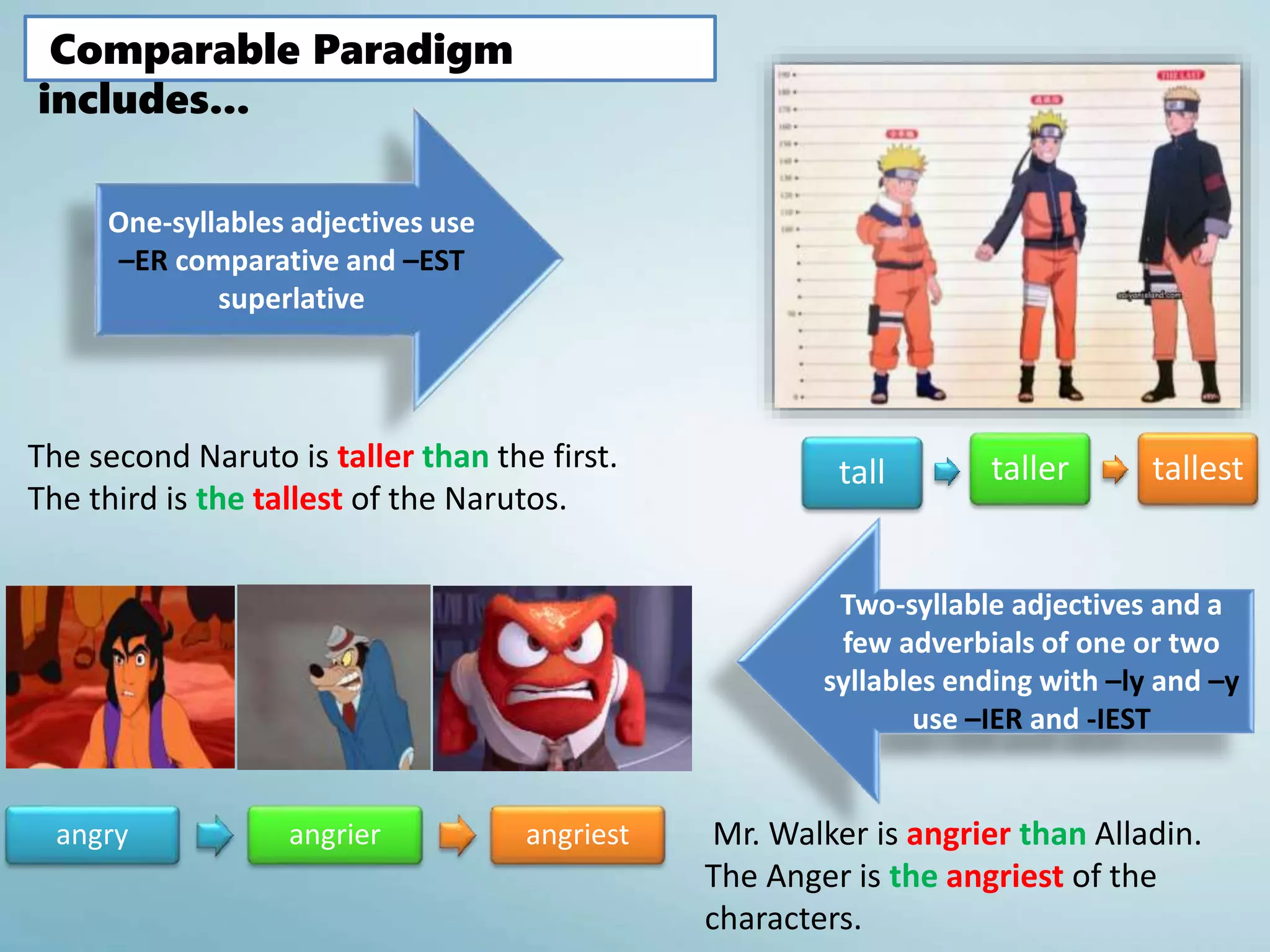
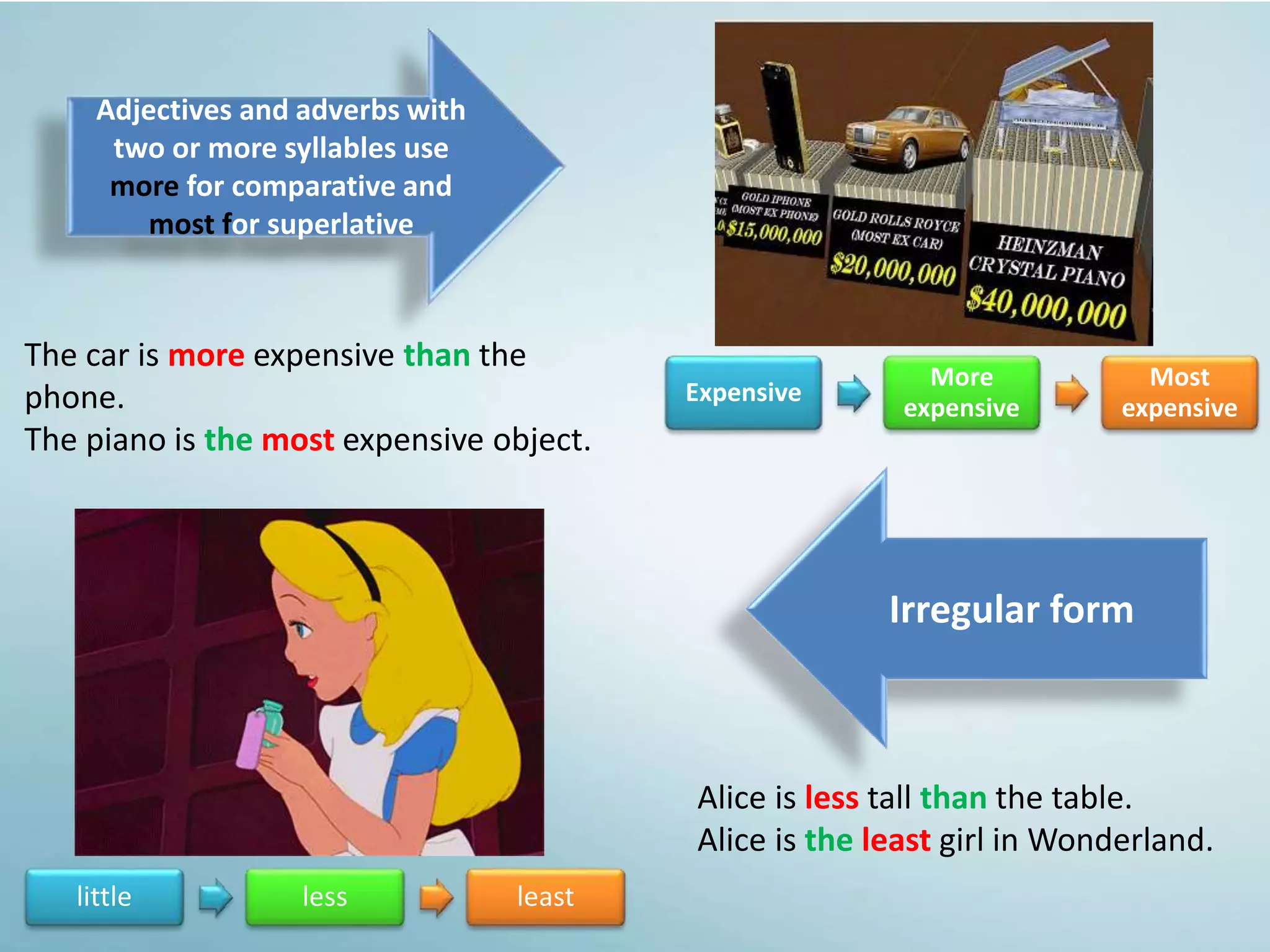
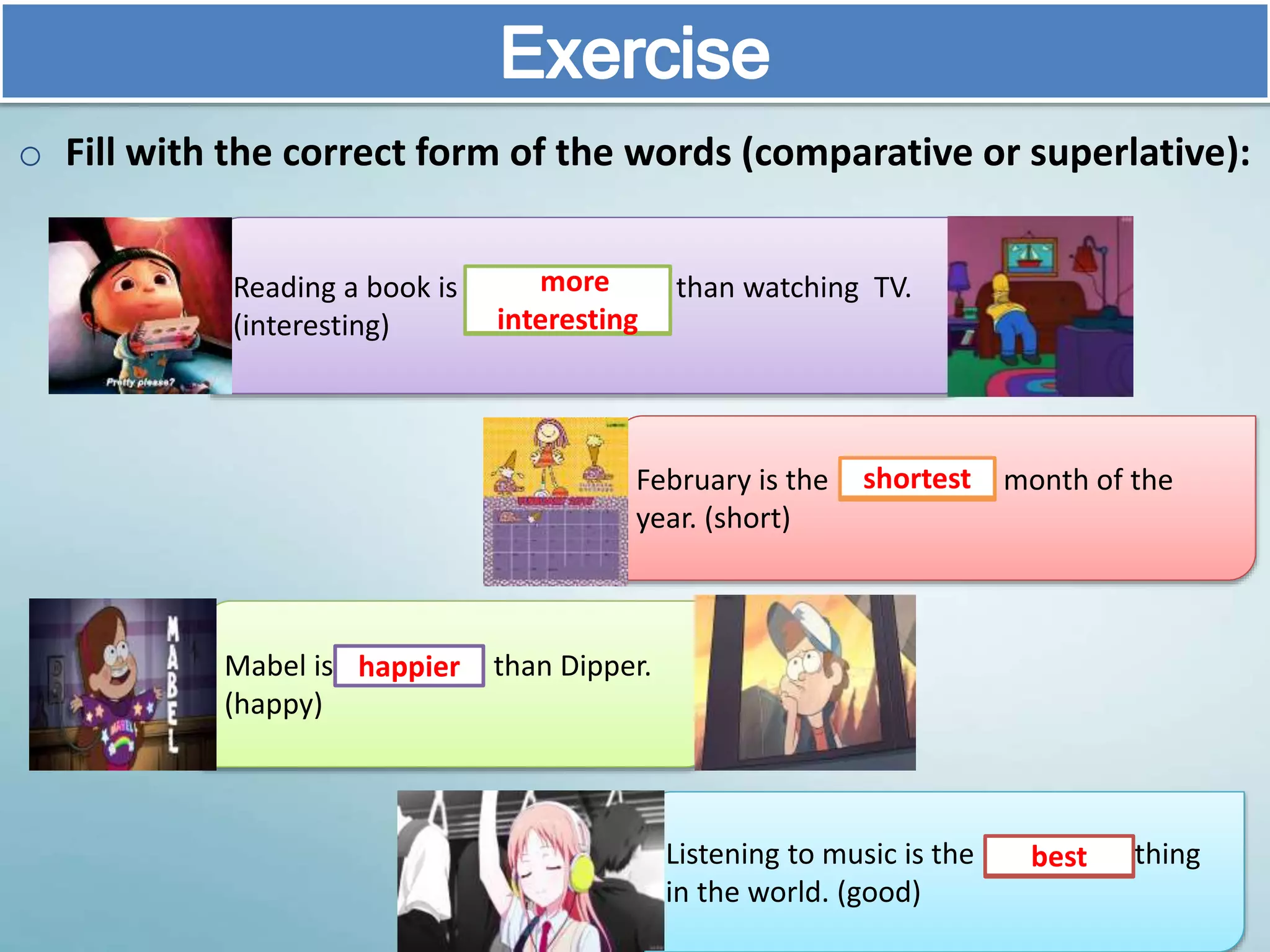
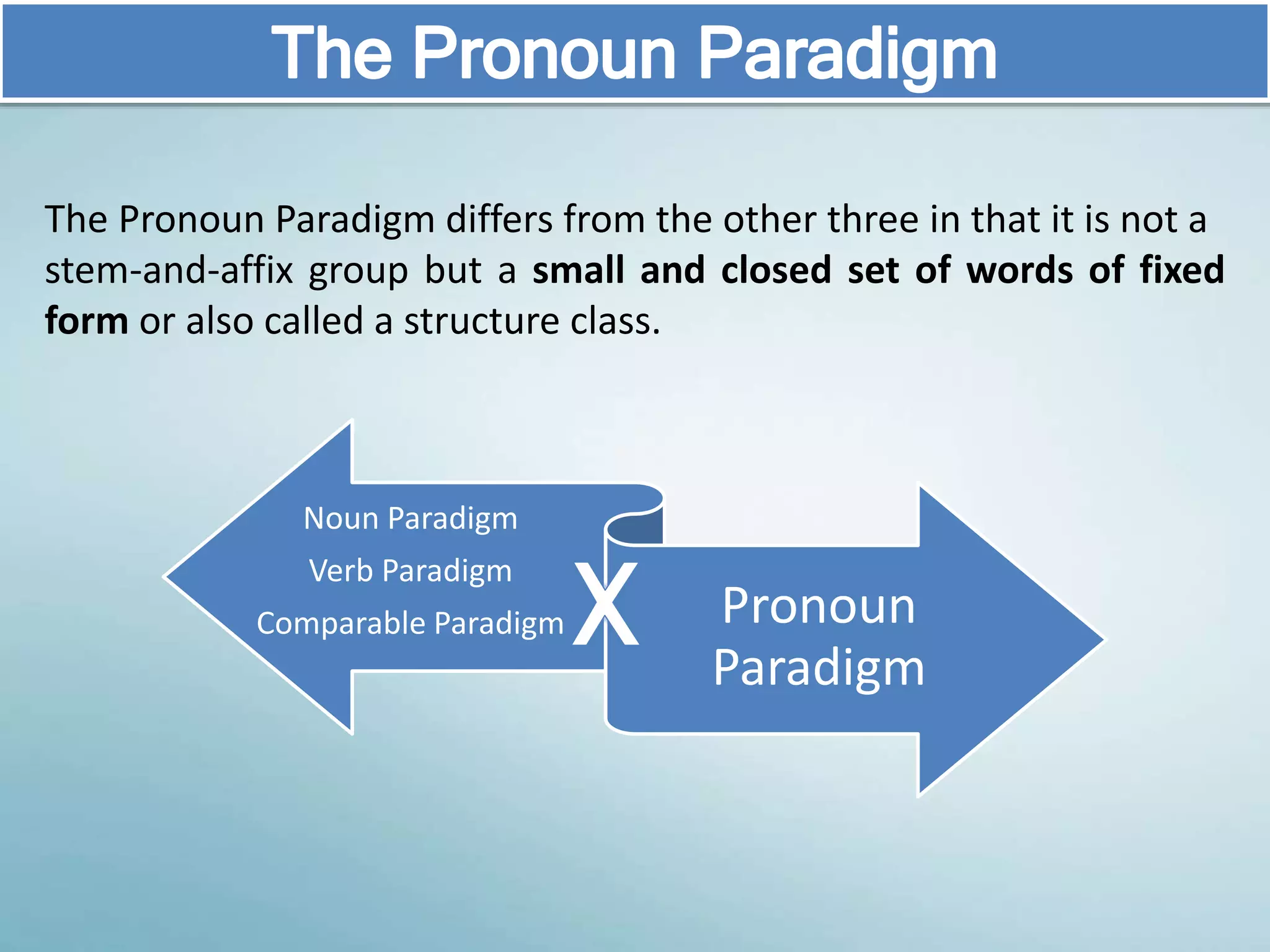
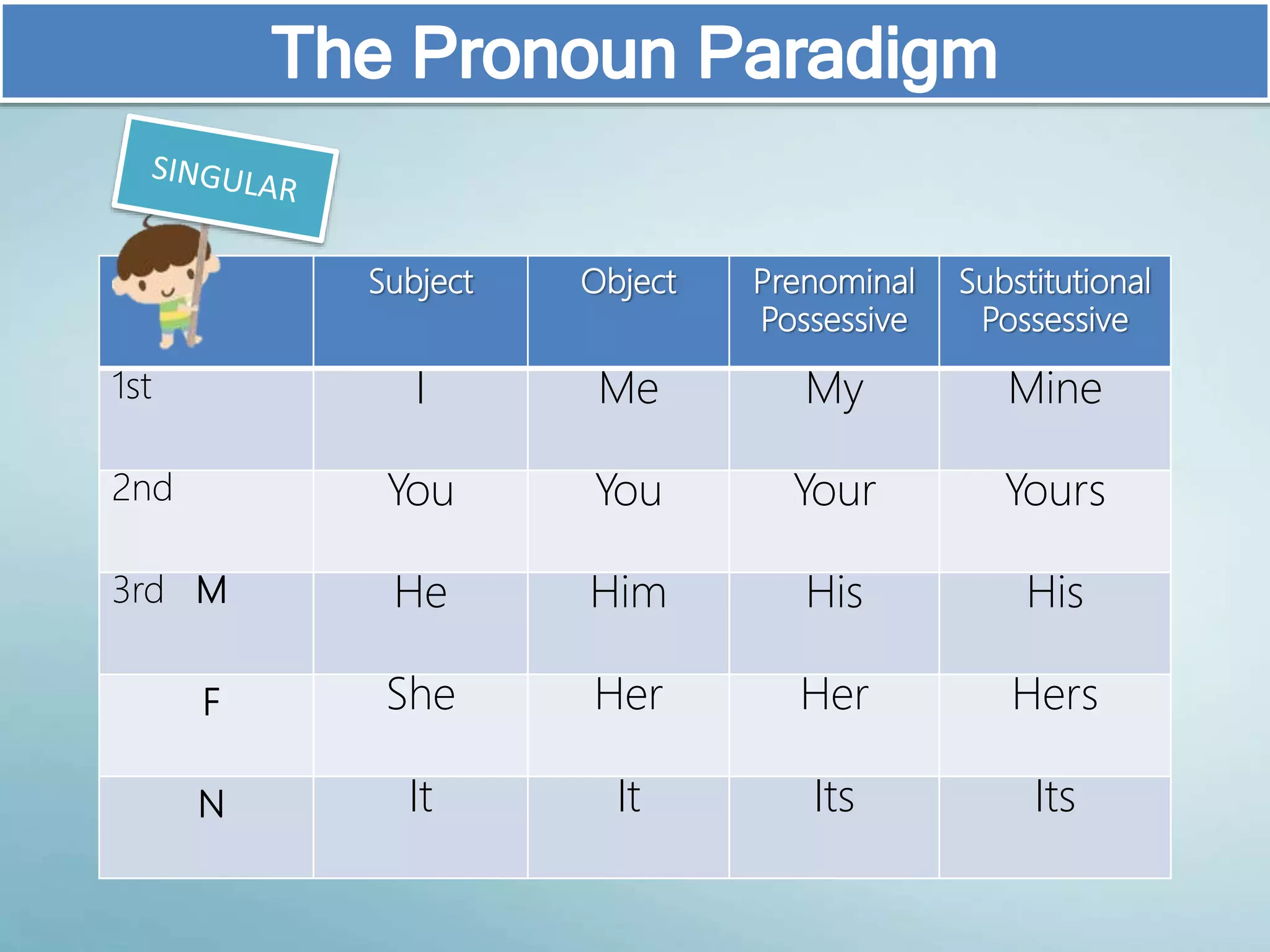
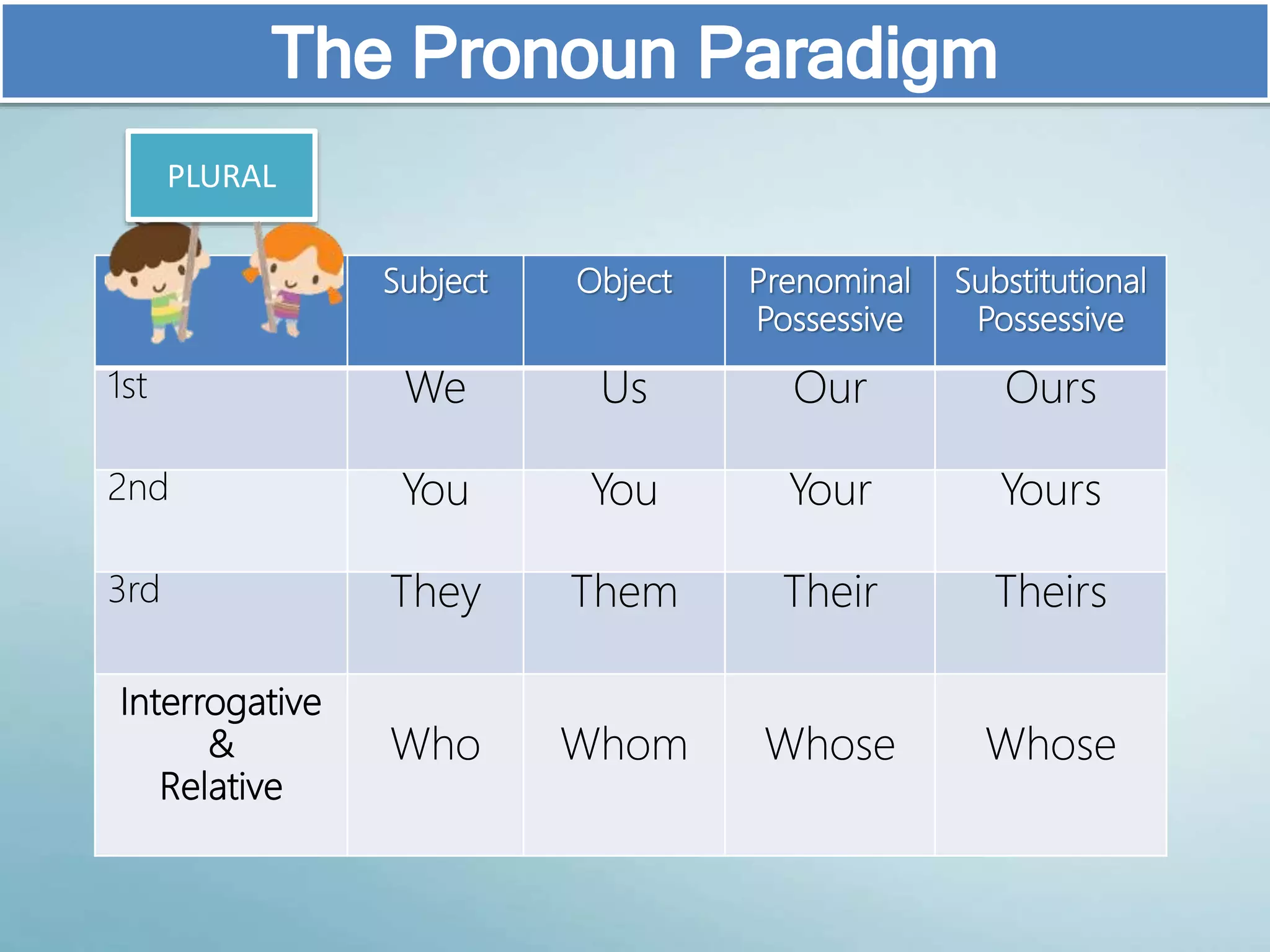
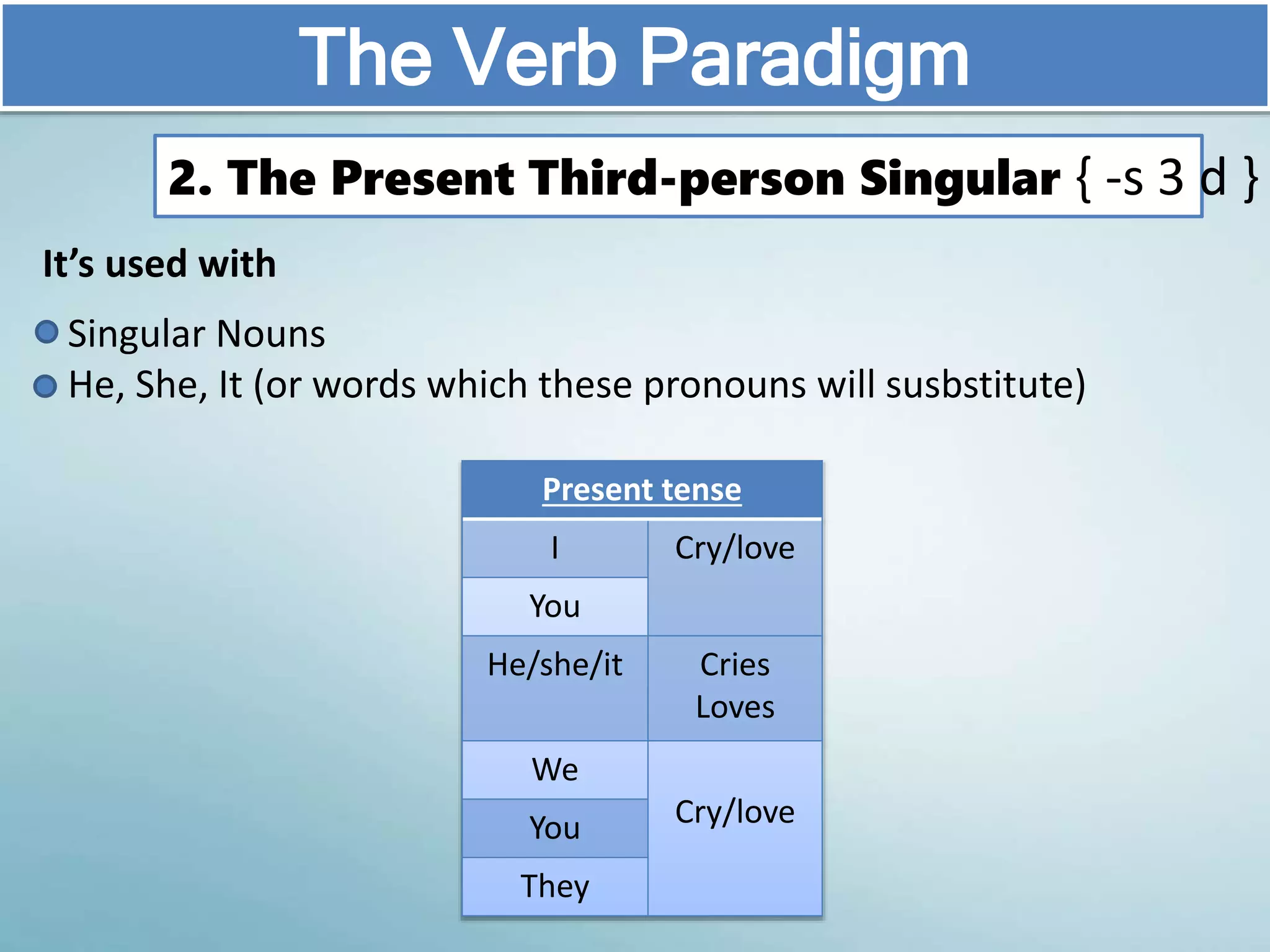
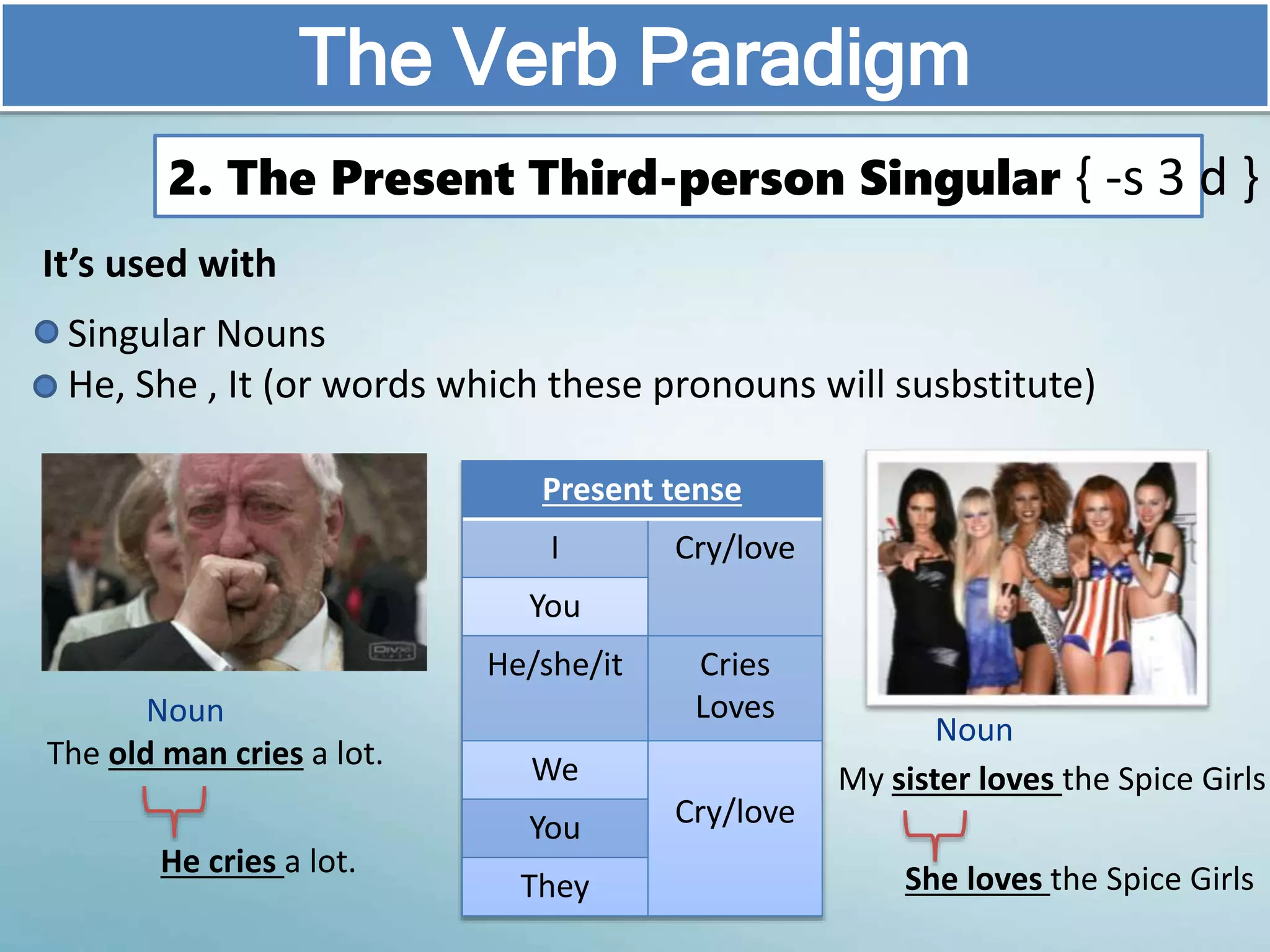
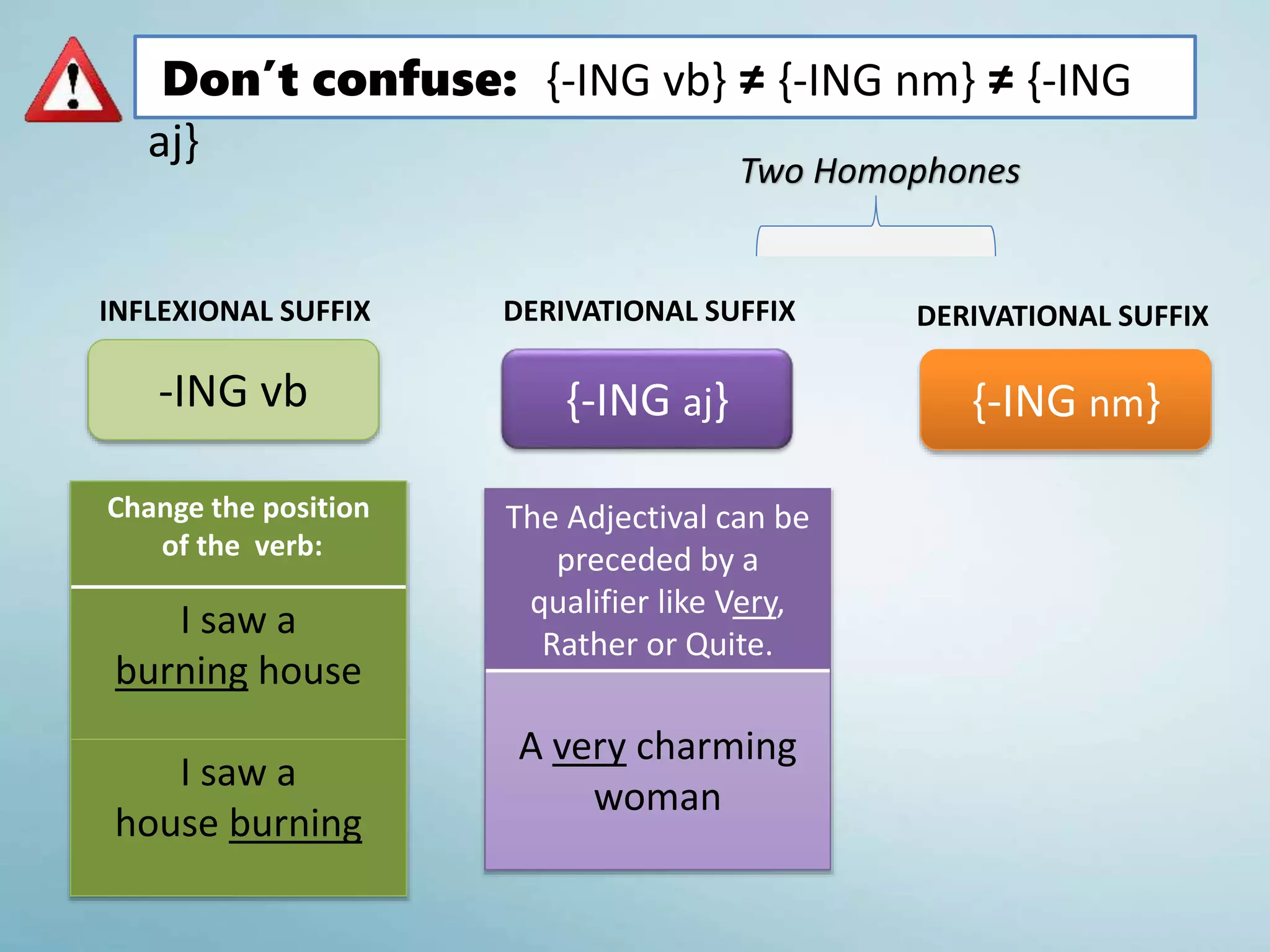
The document discusses various aspects of verb paradigms, including present tense usage, third-person singular forms, and the present participle's role in progressive aspects. It also covers adjectives, comparatives, superlatives, and the unique nature of pronouns within grammatical paradigms. Additionally, it highlights inflectional paradigms and offers examples of each grammatical concept.









![It has regular and irregular forms.
It is used with verb ‘to have’ (have, has, had, having) to form verbal
phrases indicating PERFECTIVE ASPECT.
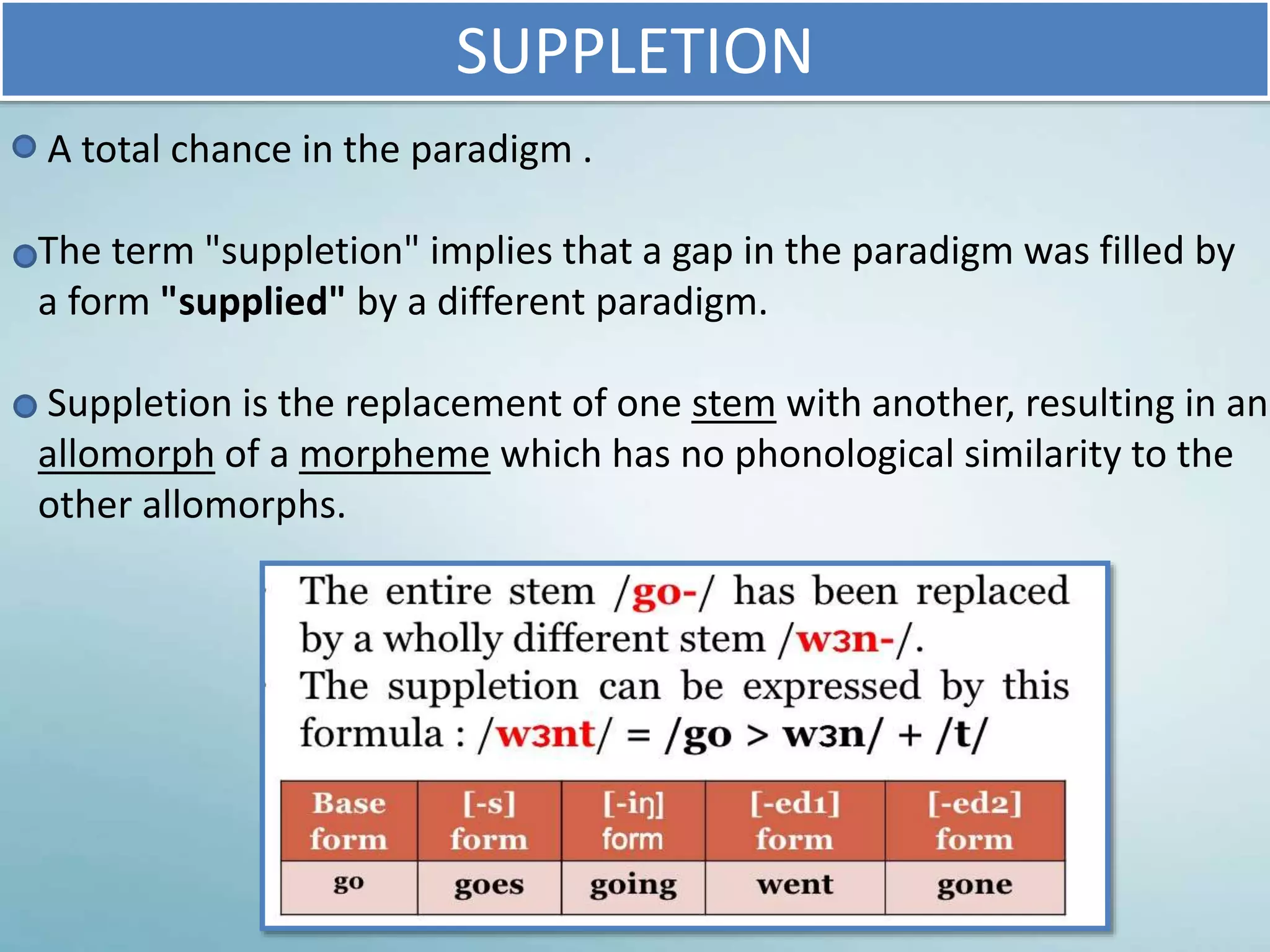
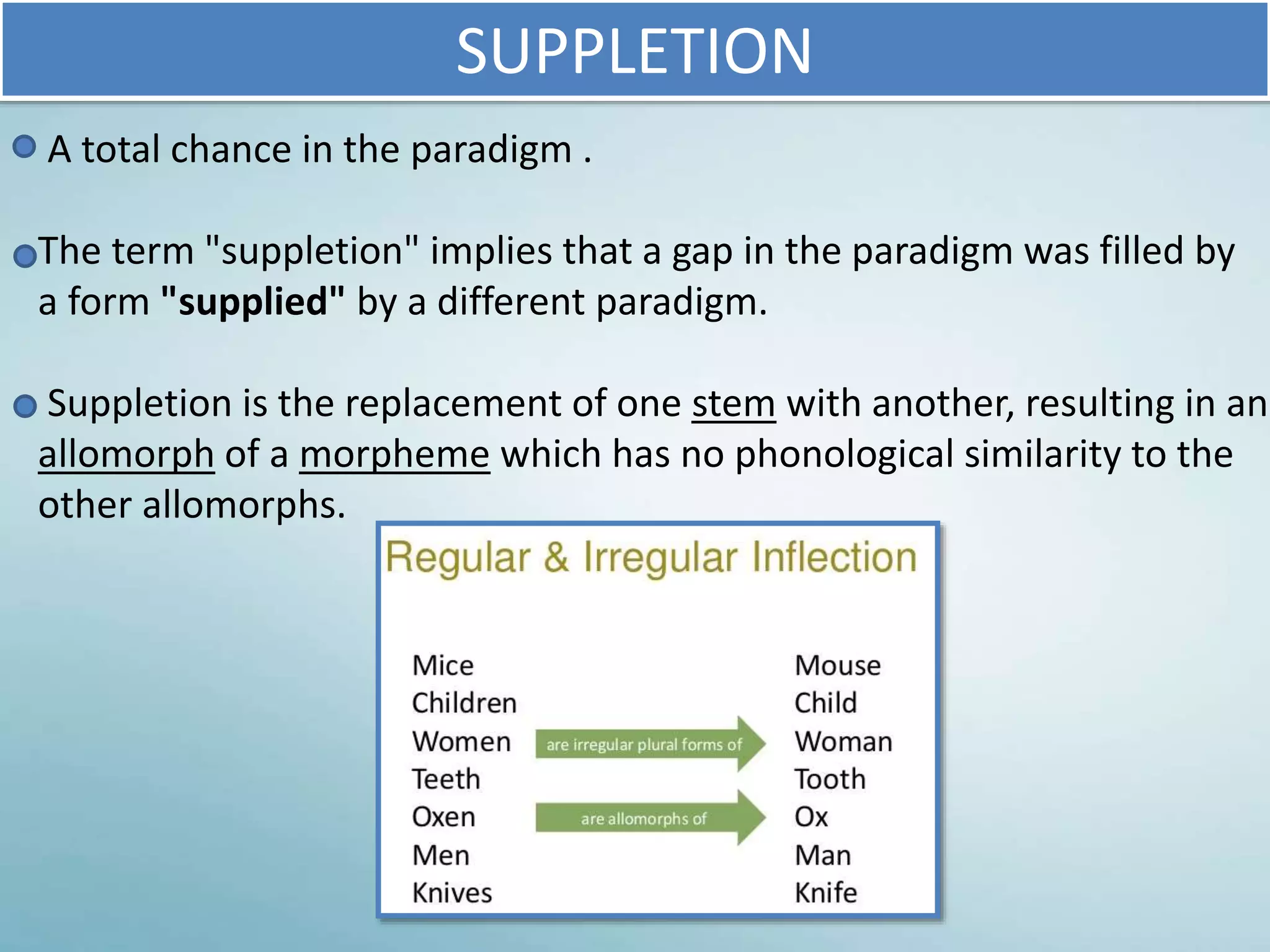
The Verb Paradigm
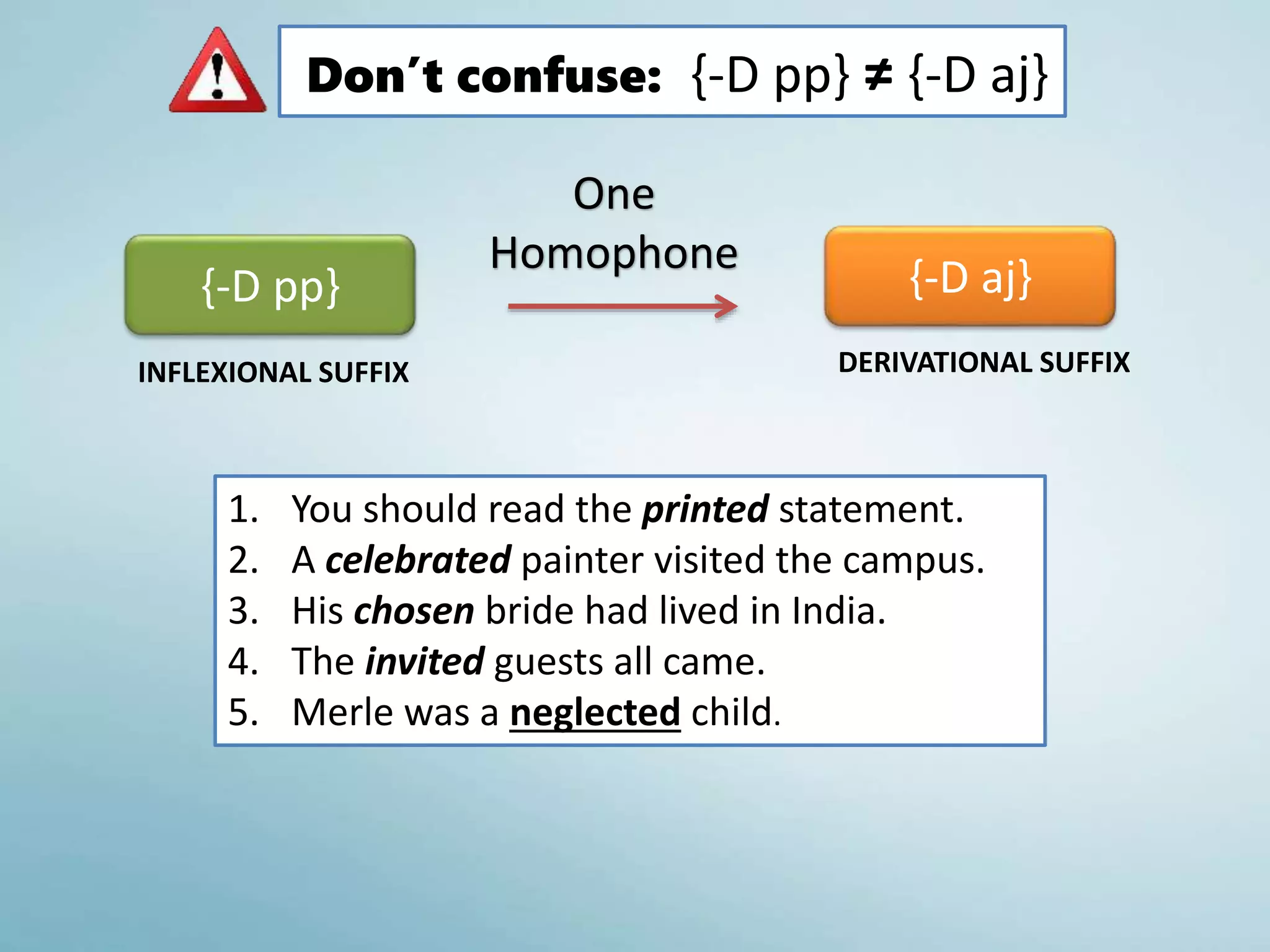
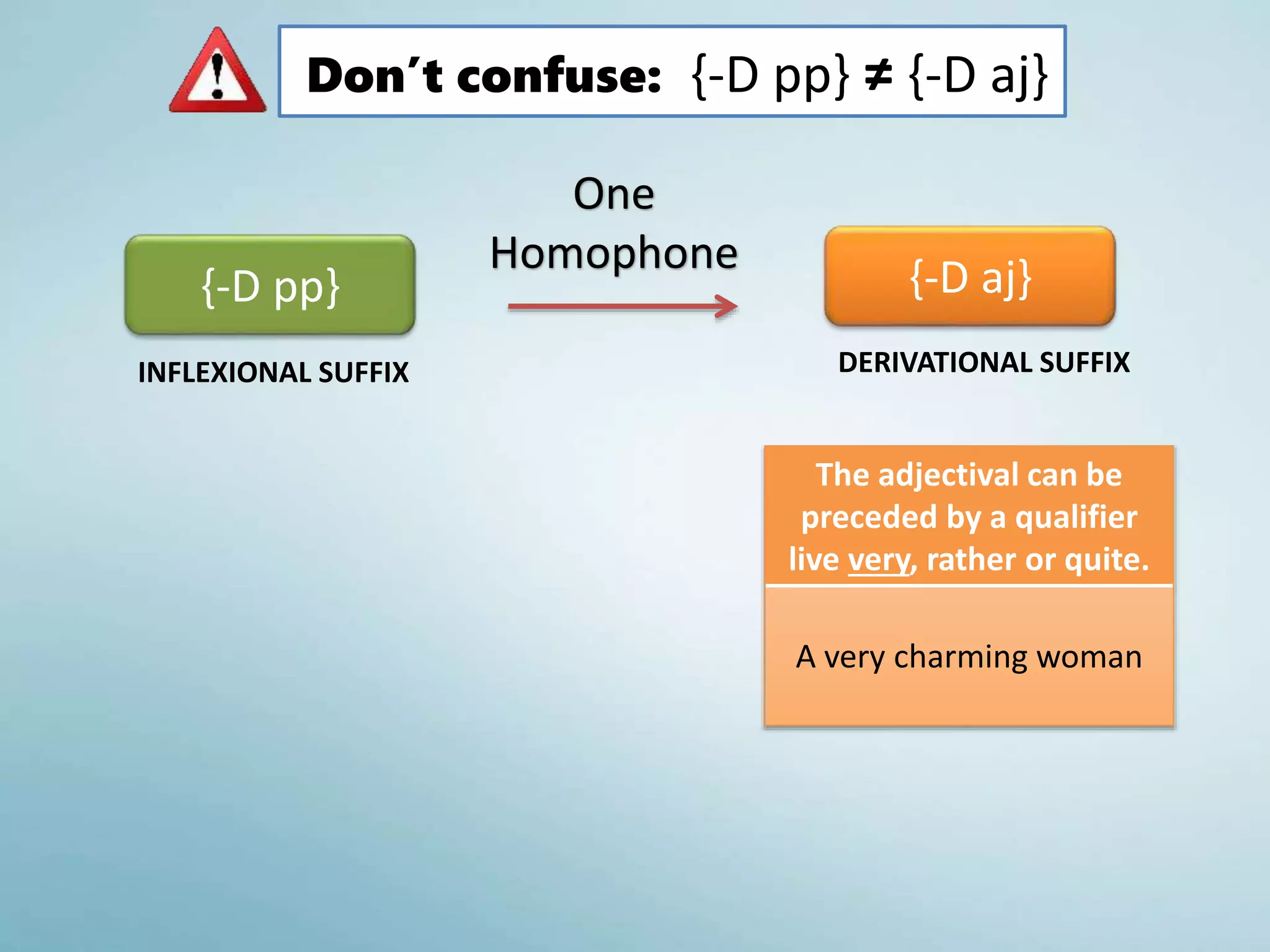
5. The Past Participle {-D pp}
[Thing receiving action] + [be] + [past participle of verb] + [by] + [thing doing action]
It can be used with verb ‘to be’ to form the passive form
indicating PASSIVE VOICE.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inflectionalparadigm-2parte-170820014309/75/Inflectional-paradigm-Parte-2-15-2048.jpg)