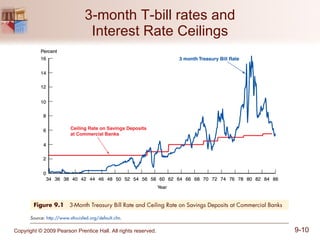
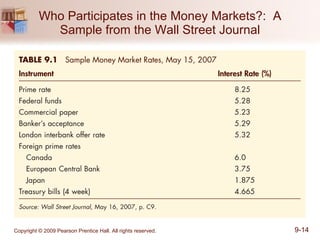
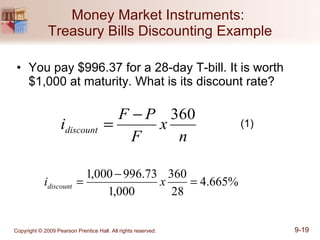
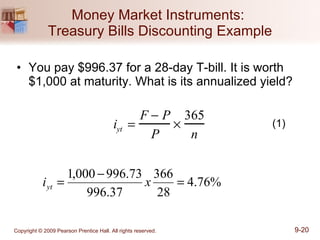
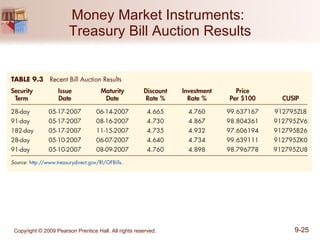
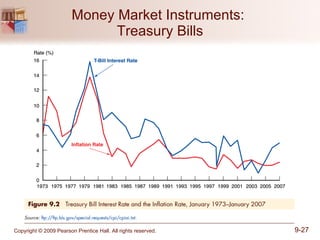
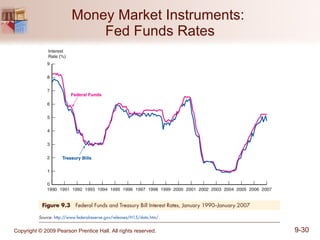
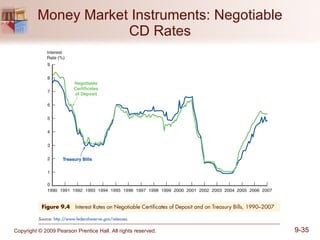
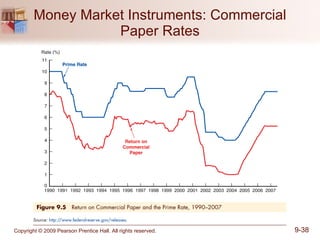
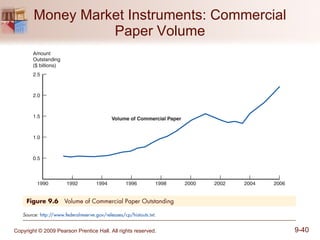
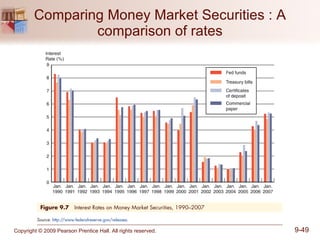
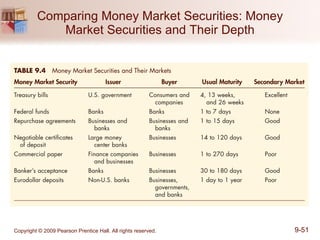
The document discusses money markets and the various securities traded within them. Money markets provide short-term funding for participants and a place for investors to store excess cash. Major securities discussed include Treasury bills, certificates of deposit, commercial paper, and repurchase agreements. These instruments vary in issuers, maturity length, and liquidity. Money markets help corporations and governments manage mismatches between cash inflows and outflows.