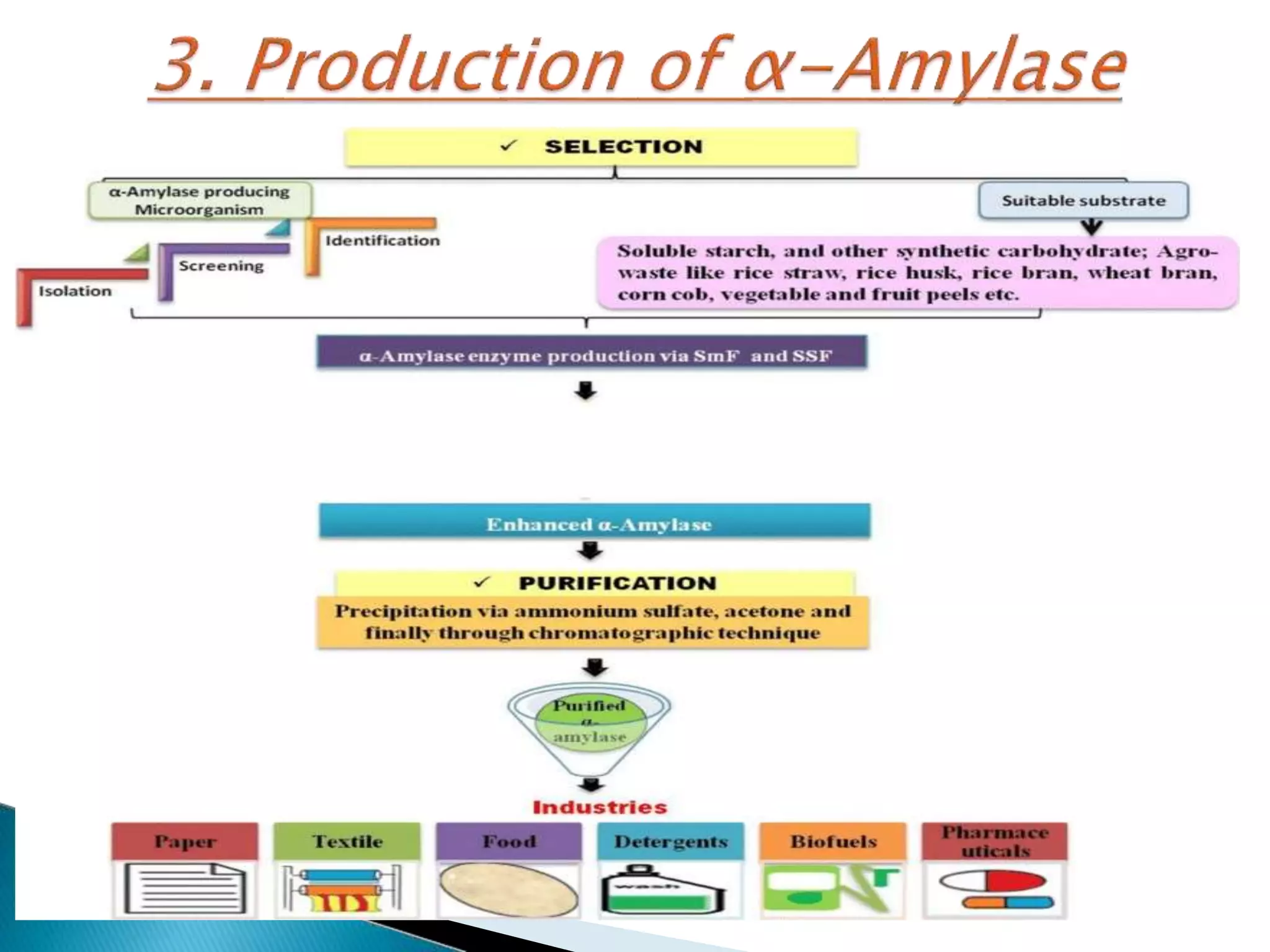
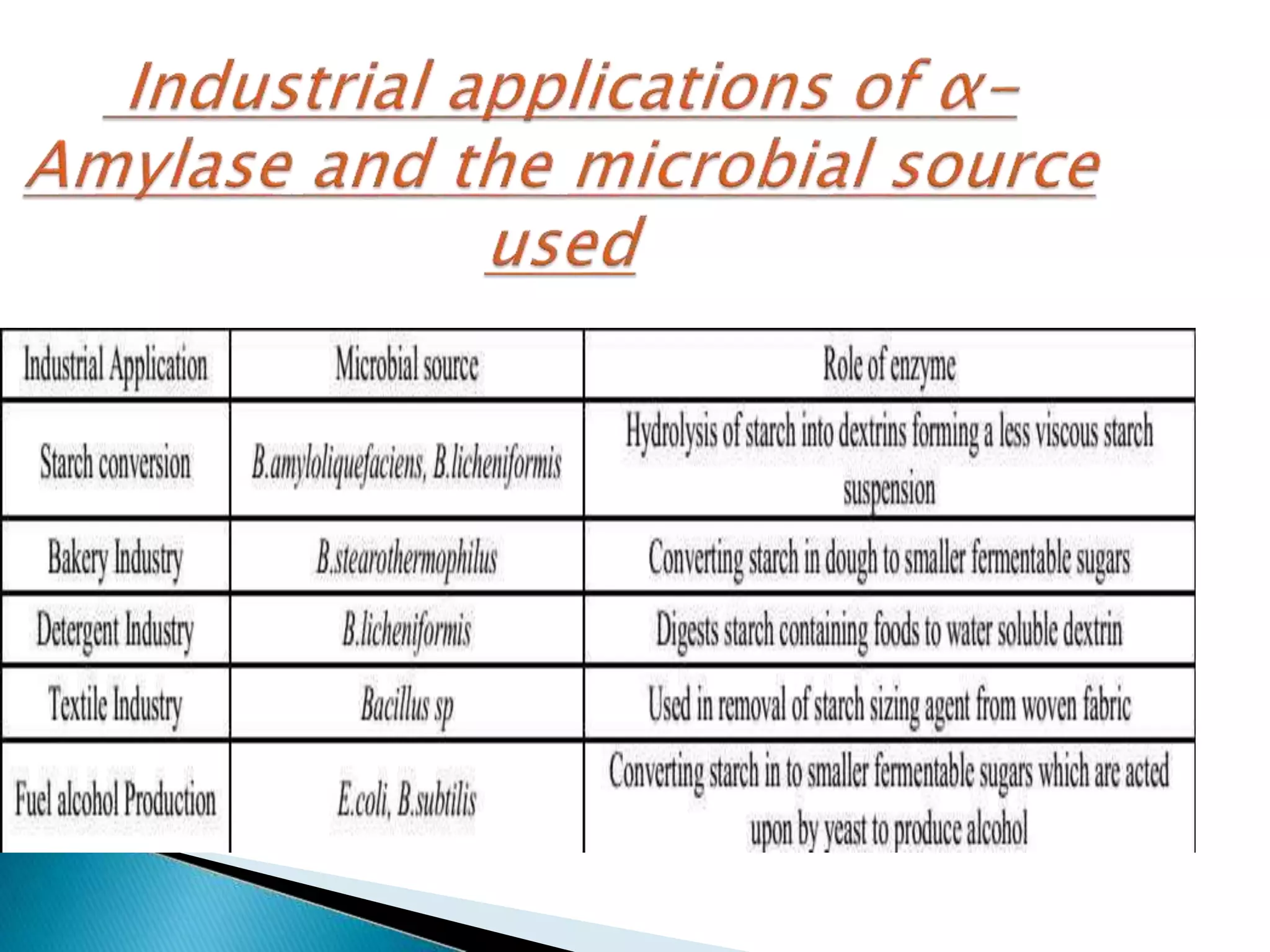
α-Amylase, β-amylase, and γ-amylase are important industrial enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of starch. α-Amylase randomly cleaves internal glycosidic linkages in starch molecules to produce dextrins and oligosaccharides. β-Amylase acts from the non-reducing end of polysaccharide chains to yield successive maltose units, while γ-amylase can cleave both α(1-6) and α(1-4) linkages to produce glucose. These amylases are commonly produced via submerged or solid state fermentation using microorganisms, with each method offering advantages for enzyme extraction and control