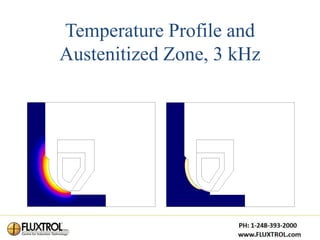
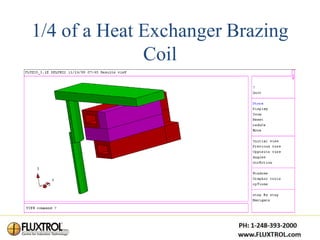
This document discusses induction heating in the automotive powertrain industry. It outlines the advantages of induction heating, its current applications, and need for continued advancement. Specifically, it calls for cooperative efforts to improve induction heating education and develop shared resources like material property databases and simulation tools to help design better induction coils and processes.